Intro
Compare military branch pay scales, salaries, and benefits across Army, Navy, Air Force, and Marines, including enlisted and officer ranks, to make informed decisions about your military career.
The military is a significant institution in many countries, providing a wide range of career opportunities for individuals who want to serve their nation. One of the most critical factors that potential recruits consider when deciding which military branch to join is the pay. In this article, we will delve into a comprehensive military branch pay comparison, exploring the different pay scales, benefits, and allowances offered by each branch.
The United States military is composed of five branches: the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard. Each branch has its unique culture, mission, and pay structure. Understanding the pay comparison between these branches is essential for individuals who want to make an informed decision about their military career. The pay scales for each branch are based on factors such as rank, time in service, and job specialty.
The military pay system is designed to provide a fair and competitive compensation package for service members. The pay scales are adjusted annually to reflect changes in the cost of living and other factors. In addition to basic pay, service members also receive a range of benefits and allowances, including housing allowance, food allowance, and uniform allowance. These benefits can significantly impact the overall compensation package and should be considered when evaluating the pay comparison between branches.
Military Branch Pay Scales

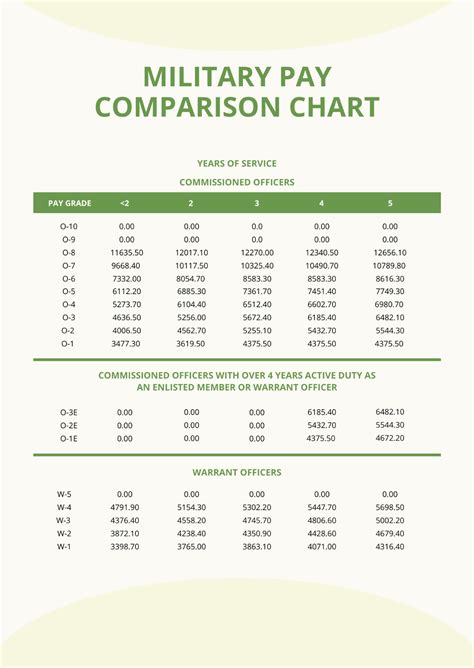
The military branch pay scales are based on the Department of Defense's pay tables, which are updated annually. The pay scales for each branch are similar, with some variations based on rank and time in service. The Army, Navy, Air Force, and Marine Corps follow the same pay scale, while the Coast Guard has a slightly different pay scale due to its status as a unique branch that operates under the Department of Homeland Security during peacetime.
The pay scales for each branch are divided into several categories, including enlisted personnel, warrant officers, and commissioned officers. Enlisted personnel are the backbone of the military, making up the majority of the force. Warrant officers are technical experts who have advanced education and training in a specific field. Commissioned officers are leaders who have completed a four-year college degree and officer training.
Enlisted Personnel Pay

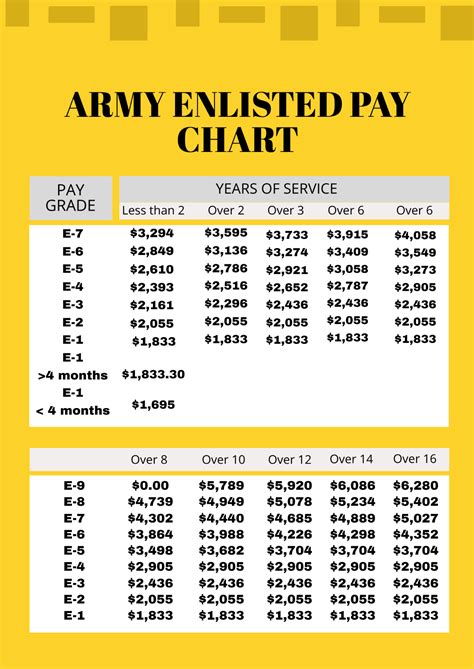
Enlisted personnel are the largest group of service members, and their pay scales vary based on rank and time in service. The pay scales for enlisted personnel are as follows:
- Private (E-1): $1,733 per month
- Private First Class (E-2): $1,942 per month
- Specialist/Corporal (E-4): $2,515 per month
- Sergeant (E-5): $2,944 per month
- Staff Sergeant (E-6): $3,311 per month
The pay scales for enlisted personnel increase with time in service and rank. Service members who have more time in service and higher ranks receive higher pay.
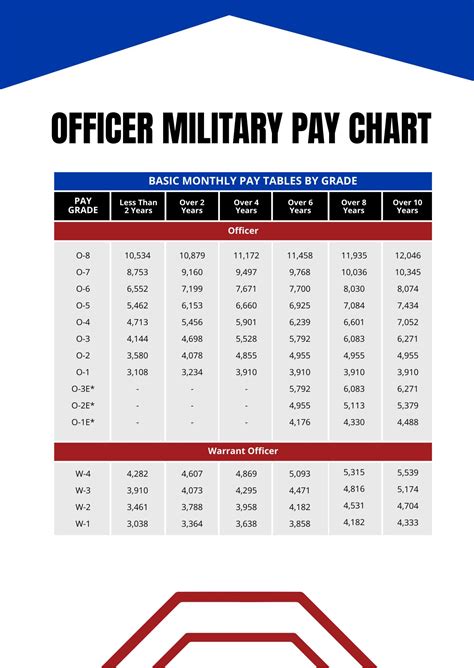
Warrant Officer Pay
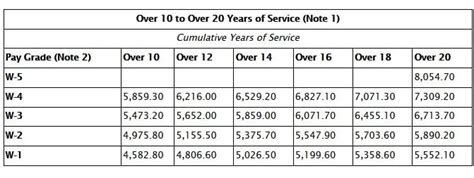
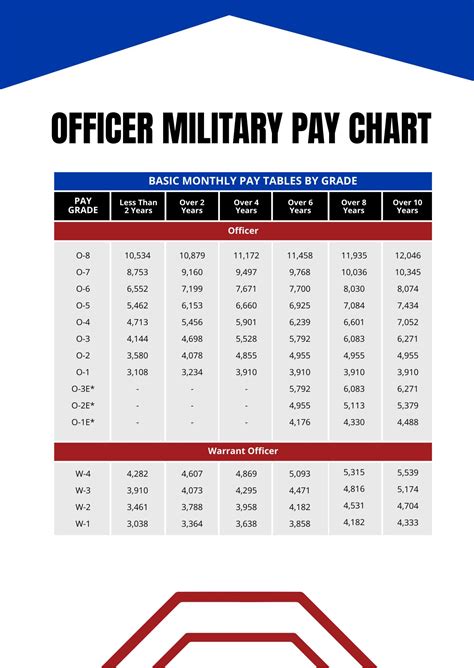
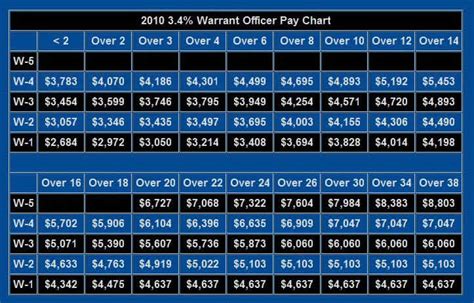
Warrant officers are technical experts who have advanced education and training in a specific field. The pay scales for warrant officers are as follows:
- Warrant Officer 1 (W-1): $3,309 per month
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (W-2): $3,853 per month
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (W-3): $4,514 per month
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (W-4): $5,274 per month
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (W-5): $6,139 per month
The pay scales for warrant officers increase with time in service and rank. Service members who have more time in service and higher ranks receive higher pay.
Commissioned Officer Pay

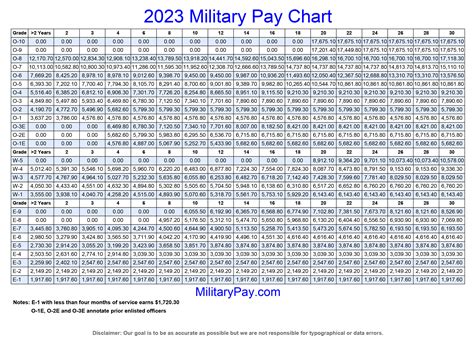
Commissioned officers are leaders who have completed a four-year college degree and officer training. The pay scales for commissioned officers are as follows:
- Second Lieutenant (O-1): $3,287 per month
- First Lieutenant (O-2): $3,787 per month
- Captain (O-3): $4,514 per month
- Major (O-4): $5,274 per month
- Lieutenant Colonel (O-5): $6,139 per month
The pay scales for commissioned officers increase with time in service and rank. Service members who have more time in service and higher ranks receive higher pay.
Benefits and Allowances

In addition to basic pay, service members also receive a range of benefits and allowances. These benefits can significantly impact the overall compensation package and should be considered when evaluating the pay comparison between branches. Some of the benefits and allowances include:
- Housing allowance: Service members who live off base receive a housing allowance to help cover the cost of rent or mortgage.
- Food allowance: Service members receive a food allowance to help cover the cost of food.
- Uniform allowance: Service members receive a uniform allowance to help cover the cost of uniforms and equipment.
- Education benefits: Service members may be eligible for education benefits, such as the GI Bill, to help cover the cost of college or vocational training.
- Health insurance: Service members and their families receive health insurance through TRICARE.
Pay Comparison Between Branches
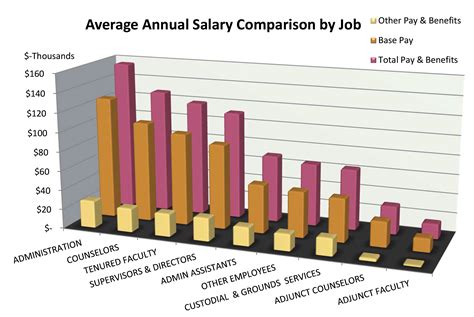
The pay comparison between branches is based on the pay scales and benefits offered by each branch. The Army, Navy, Air Force, and Marine Corps follow the same pay scale, while the Coast Guard has a slightly different pay scale. The pay scales for each branch are similar, with some variations based on rank and time in service.
The Coast Guard has a slightly higher pay scale than the other branches, due to its status as a unique branch that operates under the Department of Homeland Security during peacetime. The Coast Guard also offers a range of benefits and allowances, including a housing allowance, food allowance, and uniform allowance.
The Army, Navy, Air Force, and Marine Corps offer similar pay scales and benefits, with some variations based on rank and time in service. These branches also offer a range of education benefits, including the GI Bill, to help service members cover the cost of college or vocational training.
Gallery of Military Pay Comparison
Military Pay Comparison Image Gallery



Frequently Asked Questions
What is the highest paying military branch?
+The Coast Guard has a slightly higher pay scale than the other branches, due to its status as a unique branch that operates under the Department of Homeland Security during peacetime.
What are the benefits of joining the military?
+The military offers a range of benefits, including education benefits, health insurance, and housing allowance. Service members also receive a competitive pay package and have the opportunity to serve their country.
How do I choose which military branch to join?
+Choosing which military branch to join depends on your individual goals and preferences. Consider factors such as pay, benefits, and job opportunities when making your decision. It's also a good idea to research each branch and talk to recruiters to get a better understanding of what each branch has to offer.
What is the pay scale for enlisted personnel?
+The pay scale for enlisted personnel varies based on rank and time in service. The pay scales for enlisted personnel are as follows: Private (E-1): $1,733 per month, Private First Class (E-2): $1,942 per month, Specialist/Corporal (E-4): $2,515 per month, Sergeant (E-5): $2,944 per month, Staff Sergeant (E-6): $3,311 per month.
What is the pay scale for warrant officers?
+The pay scale for warrant officers varies based on rank and time in service. The pay scales for warrant officers are as follows: Warrant Officer 1 (W-1): $3,309 per month, Chief Warrant Officer 2 (W-2): $3,853 per month, Chief Warrant Officer 3 (W-3): $4,514 per month, Chief Warrant Officer 4 (W-4): $5,274 per month, Chief Warrant Officer 5 (W-5): $6,139 per month.
In conclusion, the military branch pay comparison is a complex topic that depends on various factors, including rank, time in service, and job specialty. Each branch has its unique culture, mission, and pay structure, and understanding these differences is essential for individuals who want to make an informed decision about their military career. By considering the pay scales, benefits, and allowances offered by each branch, service members can make a more informed decision about which branch to join and how to advance their career. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences on this topic and to ask questions in the comments section below.
