Intro
Discover the Army Reserve Officer age limit and eligibility requirements, including age waivers, commissioning options, and service obligations for prospective officers.
The Army Reserve is a vital component of the United States Army, providing support and augmenting the active duty force with trained and experienced soldiers. For those interested in serving as an officer in the Army Reserve, understanding the age limits and requirements is crucial. The age limit for Army Reserve officers varies depending on the individual's circumstances, such as their current rank, career field, and whether they are newly commissioning or transitioning from active duty.
Generally, the maximum age for a commissioned officer in the Army Reserve is 62 years old. However, this can vary based on the specific needs of the Army and the qualifications of the individual. It's also worth noting that while age is an important factor, it's not the only consideration for joining or continuing to serve in the Army Reserve as an officer. Other factors such as physical fitness, medical status, and professional experience play significant roles in determining eligibility.
For those looking to join the Army Reserve as a new officer, the typical age range is between 17 and 35 years old, though certain careers may have different age limits. For example, some medical specialties may allow for older individuals to join due to the high demand for these skills and the extensive education and training required to qualify. Additionally, prior service members may be eligible to join the Army Reserve at an older age, depending on their previous service and the needs of the Army.
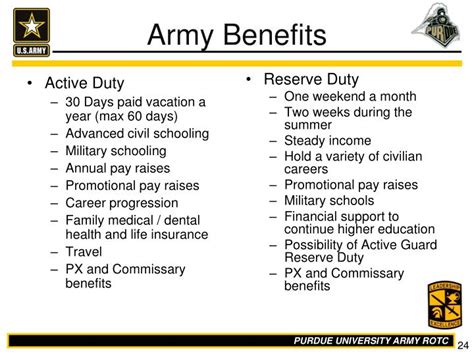
The Army Reserve offers numerous benefits to its officers, including opportunities for professional development, education assistance, and the chance to serve in a variety of roles both at home and abroad. Officers in the Army Reserve are also eligible for drill pay and annual training pay, which can be a significant supplement to their civilian income. Furthermore, serving in the Army Reserve can provide a sense of purpose and camaraderie that is hard to find in civilian life, as well as the opportunity to develop valuable leadership and technical skills.
Benefits of Serving in the Army Reserve

Serving in the Army Reserve comes with a multitude of benefits that can enhance one's personal and professional life. These benefits include, but are not limited to, education assistance, such as the Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR) and the Army Reserve's own education assistance programs. Officers can also take advantage of low-cost life insurance, home loan guarantees, and access to base facilities, which can include gyms, libraries, and commissaries.
Moreover, the experience and skills gained through service in the Army Reserve can be highly valued in the civilian job market. Employers often look favorably upon veterans and reservists due to their discipline, leadership abilities, and capacity to work well under pressure. This can lead to better job opportunities and higher pay in civilian careers.
Education Assistance Programs
The Army Reserve offers several education assistance programs designed to help officers achieve their educational goals. These programs can help pay for tuition, fees, and other educational expenses, making it more feasible for individuals to pursue higher education while serving in the Reserve.- Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR): This program provides up to 36 months of education benefits to eligible members of the Selected Reserve, including the Army Reserve. Benefits can be used for degree programs, certificate programs, apprenticeships, on-the-job training, and correspondence courses.
- Army Reserve Education Assistance Program (REAP): Although REAP is no longer open to new enrollees, those already participating can continue to receive benefits. REAP provides educational assistance to members of the Reserve components called or ordered to active duty in response to a war or national emergency.
- Army Reserve's own education assistance programs: These can vary and may include tuition assistance, scholarships, and other forms of educational support.
Eligibility Requirements

To be eligible to serve as an officer in the Army Reserve, individuals must meet certain criteria. These requirements can vary depending on whether the individual is seeking to join as a new officer or is transitioning from active duty or another component of the military.
- Age: As mentioned, the typical age range for new officers is between 17 and 35 years old, though this can vary by career field.
- Citizenship: Applicants must be U.S. citizens.
- Education: A bachelor's degree from an accredited institution is typically required for officer candidates.
- Physical Fitness: Applicants must meet the Army's physical fitness standards.
- Medical Standards: Applicants must meet the Army's medical standards for enlistment or commissioning.
- Security Clearance: Depending on the Military Occupational Specialty (MOS), a security clearance may be required.
- ASVAB Scores: Applicants must achieve minimum scores on the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test, though requirements can vary by MOS.
Application Process
The application process for becoming an officer in the Army Reserve involves several steps, including preliminary applications, interviews, medical and background checks, and finally, commissioning. It's a process that requires careful preparation and patience, as it can take several months to complete.- Meet with an Army Recruiter: The first step is to meet with an Army recruiter who specializes in officer accession. They can provide detailed information on the process and help determine the best path for the individual's circumstances.
- Take the ASVAB Test: If not already taken, applicants will need to take the ASVAB test to determine their eligibility for different MOSs.
- Apply for Officer Candidate School (OCS): For those without prior military service, OCS is the primary path to becoming an officer. The application process involves submitting transcripts, letters of recommendation, and passing a physical fitness test.
- Background Check and Medical Evaluation: Applicants will undergo a background check and a medical evaluation to ensure they meet the Army's standards.
- Officer Basic Leadership Course (BOLC): After commissioning, new officers will attend BOLC, which provides training specific to their branch.
Officer Career Paths

The Army Reserve offers a wide range of career paths for officers, each with its unique challenges and opportunities. These careers can be broadly categorized into several branches, including combat arms, combat support, and combat service support.
- Combat Arms: Includes branches like Infantry, Armor, and Field Artillery. Officers in these branches are involved in direct combat and are responsible for leading troops into battle.
- Combat Support: Encompasses branches such as Engineer, Signal Corps, and Military Intelligence. These officers provide critical support to combat operations, including constructing and maintaining infrastructure, communications, and intelligence gathering.
- Combat Service Support: Includes branches like Quartermaster, Transportation, and Ordnance. Officers in these branches are responsible for logistical support, ensuring that troops have the supplies and equipment they need to perform their missions.
Professional Development
The Army Reserve places a strong emphasis on professional development, offering numerous opportunities for officers to advance their careers and enhance their skills. This includes various training courses, leadership development programs, and education assistance.- Officer Evaluation Reports (OERs): Regular evaluations provide feedback on an officer's performance and potential for future assignments and promotions.
- Promotion Boards: Officers who meet the eligibility criteria can compete for promotion to higher ranks through centralized promotion boards.
- Advanced Civil Schooling (ACS): The Army Reserve offers opportunities for officers to pursue advanced degrees at civilian institutions, enhancing their professional development and increasing their value to the Army.
Service Opportunities

Officers in the Army Reserve have the opportunity to serve in a variety of roles and environments. This can range from part-time service, where officers drill one weekend a month and attend annual training, to full-time service, where officers are deployed or work in active duty positions.
- Drill Status: Most Army Reserve officers serve in a drill status, attending unit drills one weekend a month and participating in a two-week annual training period.
- Active Duty Operational Support (ADOS): Officers can volunteer or be assigned to ADOS tours, where they serve on active duty for a specified period, often in support of operational missions.
- Mobilization: In times of national emergency, Army Reserve officers may be mobilized to active duty, bringing their skills and experience to support the total force.
Mobilization and Deployment
The possibility of mobilization and deployment is a critical aspect of serving in the Army Reserve. Officers must be prepared to deploy in support of military operations, humanitarian missions, or disaster relief efforts.- Pre-deployment Training: Before deployment, officers and their units undergo intensive training to prepare them for their mission and the challenges they will face.
- Deployment Support: The Army Reserve provides various forms of support to officers and their families during deployments, including financial assistance, counseling services, and family support groups.
Family Support

The Army Reserve recognizes the importance of family support for its officers and offers various resources to help families cope with the challenges of military life. This includes support groups, counseling services, and assistance with education and employment for spouses.
- Family Readiness Groups (FRGs): These groups provide a network of support for families, offering information, resources, and a sense of community.
- Military Family Life Counselors (MFLCs): The Army Reserve provides access to counselors who can help families deal with the stresses of military life, including deployment and reintegration.
- Spouse Education and Career Opportunities (SECO): SECO offers resources and support to help spouses achieve their education and career goals, including scholarship opportunities and career counseling.
Community Involvement
Officers in the Army Reserve are often encouraged to engage in community service and outreach, helping to build bridges between the military and civilian communities. This can involve participating in local events, volunteering with community organizations, and supporting veteran's groups.- Veterans Service Organizations (VSOs): Many officers in the Army Reserve are involved with VSOs, which provide support to veterans and advocate for their interests.
- Community Events: Participating in parades, festivals, and other community events helps to foster goodwill and understanding between the military and the public.
- Mentorship Programs: Some officers may participate in mentorship programs, providing guidance and support to young people interested in military service or pursuing careers in related fields.
Conclusion and Future Directions

As the Army Reserve continues to evolve and adapt to the changing needs of the nation, it remains an attractive option for those seeking to serve their country, develop their professional skills, and be part of a vibrant community. For officers considering a career in the Army Reserve, understanding the age limits, eligibility requirements, and the variety of service opportunities available is essential.
The future of the Army Reserve is likely to be shaped by technological advancements, changing global security environments, and the ongoing need for flexible, adaptable forces. Officers in the Army Reserve will play a critical role in meeting these challenges, leveraging their skills, experience, and education to contribute to the success of the total force.
Final Thoughts
For those interested in serving as an officer in the Army Reserve, the rewards can be significant, from personal growth and professional development to the sense of pride and fulfillment that comes from serving one's country. Whether through part-time service, full-time tours, or deployment, the Army Reserve offers a unique and challenging way to make a difference.Army Reserve Image Gallery









What is the maximum age for an Army Reserve officer?
+The maximum age for an Army Reserve officer is typically 62 years old, though this can vary based on individual circumstances and the needs of the Army.
What are the eligibility requirements for joining the Army Reserve as an officer?
+Eligibility requirements include being a U.S. citizen, having a bachelor's degree, meeting physical and medical standards, and achieving minimum scores on the ASVAB test. Age limits also apply, typically between 17 and 35 years old for new officers.
What benefits does serving in the Army Reserve offer?
+Serving in the Army Reserve offers numerous benefits, including education assistance, low-cost life insurance, home loan guarantees, access to base facilities, and the opportunity to develop valuable leadership and technical skills. Officers also receive drill pay and annual training pay.
How do I apply to become an officer in the Army Reserve?
+The application process involves meeting with an Army recruiter, taking the ASVAB test, applying for Officer Candidate School (OCS), undergoing a background check and medical evaluation, and finally, attending the Officer Basic Leadership Course (BOLC) after commissioning.
Can I serve in the Army Reserve if I have prior military service?
+Yes, prior service members can join the Army Reserve. The process and eligibility may vary depending on the individual's previous service and the needs of the Army.
In conclusion, serving as an officer in the Army Reserve offers a unique blend of personal and professional development, service to one's country, and camaraderie. Whether you're looking to start a new career, continue your service, or simply find a way to make a difference, the Army Reserve has something to offer. We invite you to explore the opportunities available, ask questions, and consider how you can be part of this vital component of the U.S. military. Share your thoughts, experiences, or questions about serving in the Army Reserve, and let's continue the conversation on how to serve, grow, and thrive in this rewarding career path.
