Intro
Explore 7 in-demand jobs for electrical engineers, including electronics engineering, power systems, and robotics, with opportunities in telecom, aerospace, and automotive industries.
The field of electrical engineering is vast and diverse, offering numerous career paths for individuals with a passion for electronics, electromagnetism, and electrical systems. Electrical engineers play a crucial role in designing, developing, and maintaining electrical systems, from small electronic devices to large-scale power grids. With their expertise, they can work in various industries, including energy, telecommunications, manufacturing, and construction. In this article, we will explore seven jobs that electrical engineers can do, highlighting the responsibilities, required skills, and growth prospects for each role.
Electrical engineers are in high demand due to the increasing need for efficient and sustainable energy solutions. Their work involves designing and developing electrical systems, testing and validating their performance, and ensuring compliance with safety standards and regulations. With the rise of emerging technologies like renewable energy, electric vehicles, and smart grids, the job prospects for electrical engineers are promising. Whether you're a recent graduate or an experienced professional, there are numerous career paths to explore in this exciting field.
The versatility of electrical engineers is evident in their ability to work in various industries, from aerospace and defense to healthcare and consumer electronics. They can design and develop medical devices, such as pacemakers and MRI machines, or work on the electrical systems of aircraft and spacecraft. With their strong foundation in mathematics and physics, electrical engineers can also pursue careers in research and development, creating innovative solutions to real-world problems. As technology continues to evolve, the demand for skilled electrical engineers will only continue to grow, making it an exciting and rewarding career choice.
Introduction to Electrical Engineering Careers

Electrical engineering is a dynamic field that encompasses a broad range of specialties, including power systems, control systems, electronics, and telecommunications. Electrical engineers can work on the design and development of electrical systems, from the generation and transmission of electricity to the distribution and utilization of electrical energy. They can also specialize in specific areas, such as microelectronics, nanotechnology, or biomedical engineering. With their expertise, electrical engineers can create innovative solutions to complex problems, improving the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of electrical systems.
Job 1: Power Systems Engineer

Power systems engineers design, develop, and maintain electrical power systems, including generation, transmission, and distribution systems. They ensure the efficient and reliable operation of power grids, substations, and transmission lines, as well as the safety and compliance of these systems with regulatory standards. Power systems engineers can work for utility companies, consulting firms, or government agencies, and their responsibilities may include:
- Designing and developing power system models and simulations
- Analyzing and optimizing power system performance
- Ensuring compliance with safety standards and regulations
- Collaborating with other engineers and stakeholders to implement power system projects
Job 2: Electronics Engineer

Electronics engineers design, develop, and test electronic systems, including digital and analog circuits, microcontrollers, and embedded systems. They work on a wide range of products, from consumer electronics and medical devices to aerospace and automotive systems. Electronics engineers can work for manufacturing companies, research institutions, or government agencies, and their responsibilities may include:
- Designing and developing electronic circuits and systems
- Testing and validating electronic system performance
- Ensuring compliance with safety standards and regulations
- Collaborating with other engineers and stakeholders to implement electronic system projects
Job 3: Control Systems Engineer

Control systems engineers design, develop, and implement control systems, including feedback control systems, robotics, and automation systems. They work on a wide range of applications, from process control and manufacturing to aerospace and automotive systems. Control systems engineers can work for manufacturing companies, research institutions, or government agencies, and their responsibilities may include:
- Designing and developing control system models and simulations
- Analyzing and optimizing control system performance
- Ensuring compliance with safety standards and regulations
- Collaborating with other engineers and stakeholders to implement control system projects
Job 4: Telecommunications Engineer

Telecommunications engineers design, develop, and implement telecommunications systems, including wireless and wired networks, satellite communications, and optical fiber systems. They work on a wide range of applications, from mobile phone networks and internet services to satellite communications and navigation systems. Telecommunications engineers can work for telecommunications companies, research institutions, or government agencies, and their responsibilities may include:
- Designing and developing telecommunications system models and simulations
- Analyzing and optimizing telecommunications system performance
- Ensuring compliance with safety standards and regulations
- Collaborating with other engineers and stakeholders to implement telecommunications system projects
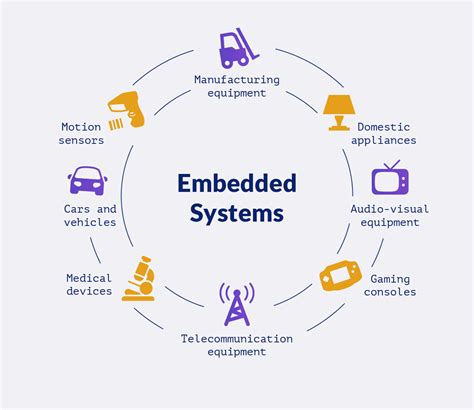
Job 5: Embedded Systems Engineer

Embedded systems engineers design, develop, and implement embedded systems, including microcontrollers, digital signal processors, and field-programmable gate arrays. They work on a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics and medical devices to aerospace and automotive systems. Embedded systems engineers can work for manufacturing companies, research institutions, or government agencies, and their responsibilities may include:
- Designing and developing embedded system models and simulations
- Analyzing and optimizing embedded system performance
- Ensuring compliance with safety standards and regulations
- Collaborating with other engineers and stakeholders to implement embedded system projects
Job 6: Robotics Engineer

Robotics engineers design, develop, and implement robotics systems, including robotic arms, autonomous vehicles, and humanoid robots. They work on a wide range of applications, from manufacturing and logistics to healthcare and service industries. Robotics engineers can work for manufacturing companies, research institutions, or government agencies, and their responsibilities may include:
- Designing and developing robotics system models and simulations
- Analyzing and optimizing robotics system performance
- Ensuring compliance with safety standards and regulations
- Collaborating with other engineers and stakeholders to implement robotics system projects
Job 7: Aerospace Engineer

Aerospace engineers design, develop, and implement aerospace systems, including aircraft, spacecraft, and missiles. They work on a wide range of applications, from commercial aviation and space exploration to military and defense systems. Aerospace engineers can work for aerospace companies, research institutions, or government agencies, and their responsibilities may include:
- Designing and developing aerospace system models and simulations
- Analyzing and optimizing aerospace system performance
- Ensuring compliance with safety standards and regulations
- Collaborating with other engineers and stakeholders to implement aerospace system projects
Gallery of Electrical Engineering Images
Electrical Engineering Image Gallery




What is the role of an electrical engineer in the development of renewable energy systems?
+Electrical engineers play a crucial role in the development of renewable energy systems, including solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. They design and develop the electrical systems that convert renewable energy into electricity, ensuring efficient and reliable operation.
What skills are required to become a successful electrical engineer?
+To become a successful electrical engineer, one needs to possess strong analytical and problem-solving skills, as well as excellent communication and teamwork skills. A strong foundation in mathematics and physics is also essential, along with proficiency in programming languages and software tools.
What are the job prospects for electrical engineers in the future?
+The job prospects for electrical engineers are promising, with increasing demand for skilled professionals in the fields of renewable energy, telecommunications, and automation. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment of electrical engineers is projected to grow 9% from 2020 to 2030, faster than the average for all occupations.
How can electrical engineers contribute to the development of sustainable and energy-efficient systems?
+Electrical engineers can contribute to the development of sustainable and energy-efficient systems by designing and developing systems that minimize energy consumption and reduce waste. They can also work on the development of renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind power, and implement energy-efficient technologies, such as smart grids and energy storage systems.
What are the most in-demand industries for electrical engineers?
+The most in-demand industries for electrical engineers include the energy and utilities sector, the telecommunications industry, the aerospace and defense sector, and the automotive industry. These industries require skilled electrical engineers to design and develop complex electrical systems, ensuring efficient and reliable operation.
In conclusion, electrical engineers play a vital role in the development and implementation of electrical systems, from power generation and transmission to telecommunications and automation. With their expertise, they can work in various industries, including energy, aerospace, and manufacturing, and contribute to the development of sustainable and energy-efficient systems. As technology continues to evolve, the demand for skilled electrical engineers will only continue to grow, making it an exciting and rewarding career choice. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences in the comments section below and to explore the various career paths available to electrical engineers. Whether you're a student or a professional, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into the world of electrical engineering and inspired you to pursue a career in this dynamic and rapidly evolving field.
