Intro
Discover Air Force Officer Rankings, from Second Lieutenant to General, and learn about military hierarchy, insignia, and career progression in the US Air Force, including commissioned officers and enlisted personnel.
The United States Air Force is one of the most prestigious and respected branches of the military, with a long history of excellence and a strong tradition of leadership. For those who aspire to join the Air Force, understanding the officer ranking system is essential. The Air Force officer rankings are a crucial aspect of the military's hierarchy, and they play a significant role in determining an officer's responsibilities, pay, and benefits. In this article, we will delve into the world of Air Force officer rankings, exploring the different levels, their responsibilities, and the requirements for advancement.
The Air Force officer ranking system is designed to provide a clear and structured path for officers to advance in their careers. The system is based on a combination of factors, including time in service, performance, and education. The rankings are divided into several categories, including commissioned officers, warrant officers, and enlisted personnel. Commissioned officers are the highest-ranking officers in the Air Force and are responsible for leading and managing units, making strategic decisions, and overseeing operations.
Air Force Officer Ranks
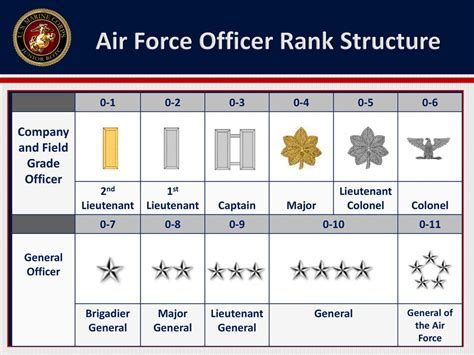
The Air Force officer ranks are as follows:
- Second Lieutenant (2nd Lt): The entry-level rank for commissioned officers, typically held by new officers who have just graduated from the Air Force Academy or completed officer training.
- First Lieutenant (1st Lt): A junior officer rank, typically held by officers who have completed their initial training and are serving in their first assignment.
- Captain (Capt): A company-grade officer rank, typically held by officers who have gained experience and are serving in leadership positions.
- Major (Maj): A field-grade officer rank, typically held by officers who have significant experience and are serving in senior leadership positions.
- Lieutenant Colonel (Lt Col): A senior field-grade officer rank, typically held by officers who have extensive experience and are serving in high-level leadership positions.
- Colonel (Col): A senior officer rank, typically held by officers who have achieved a high level of success and are serving in executive leadership positions.
- Brigadier General (Brig Gen): A one-star general officer rank, typically held by officers who have achieved a high level of success and are serving in senior leadership positions.
- Major General (Maj Gen): A two-star general officer rank, typically held by officers who have achieved a high level of success and are serving in executive leadership positions.
- Lieutenant General (Lt Gen): A three-star general officer rank, typically held by officers who have achieved a high level of success and are serving in senior leadership positions.
- General (Gen): A four-star general officer rank, the highest rank in the Air Force, typically held by officers who have achieved the highest level of success and are serving in the most senior leadership positions.
Responsibilities of Air Force Officers

Air Force officers have a wide range of responsibilities, depending on their rank and assignment. Some of the key responsibilities of Air Force officers include:
- Leading and managing units: Air Force officers are responsible for leading and managing units, which can range from small teams to large organizations.
- Making strategic decisions: Air Force officers are responsible for making strategic decisions that impact the success of their units and the Air Force as a whole.
- Overseeing operations: Air Force officers are responsible for overseeing operations, which can include everything from combat missions to humanitarian relief efforts.
- Developing and implementing policies: Air Force officers are responsible for developing and implementing policies that guide the actions of their units and the Air Force.
- Mentoring and training personnel: Air Force officers are responsible for mentoring and training personnel, which is essential for developing the skills and knowledge of junior officers and enlisted personnel.
Requirements for Advancement

The requirements for advancement in the Air Force officer ranks vary depending on the rank and the individual's performance and experience. Some of the key requirements for advancement include:
- Time in service: Officers must have a certain amount of time in service to be eligible for promotion to the next rank.
- Performance: Officers must demonstrate excellent performance in their current rank to be eligible for promotion.
- Education: Officers may need to complete additional education or training to be eligible for promotion to certain ranks.
- Leadership experience: Officers must have leadership experience to be eligible for promotion to senior ranks.
- Physical fitness: Officers must meet physical fitness standards to be eligible for promotion.
Air Force Officer Career Paths
Air Force officers can pursue a variety of career paths, depending on their interests and skills. Some of the most common career paths for Air Force officers include:
- Pilot: Air Force pilots fly a variety of aircraft, including fighter jets, transport planes, and helicopters.
- Navigator: Air Force navigators are responsible for navigating aircraft and ensuring the safety of the crew and passengers.
- Intelligence officer: Air Force intelligence officers are responsible for gathering and analyzing intelligence to support military operations.
- Logistics officer: Air Force logistics officers are responsible for managing the supply chain and ensuring that units have the equipment and supplies they need to operate effectively.
- Communications officer: Air Force communications officers are responsible for managing communications systems and ensuring that units can communicate effectively.
Air Force Officer Benefits
Air Force officers enjoy a wide range of benefits, including:
- Competitive pay: Air Force officers are paid a competitive salary, which is based on their rank and time in service.
- Comprehensive health insurance: Air Force officers and their families are eligible for comprehensive health insurance, which includes medical, dental, and vision coverage.
- Retirement benefits: Air Force officers are eligible for retirement benefits, which include a pension and access to the Veterans Administration healthcare system.
- Education benefits: Air Force officers are eligible for education benefits, which include tuition assistance and access to the GI Bill.
- Travel opportunities: Air Force officers have the opportunity to travel and serve in a variety of locations around the world.
Air Force Officer Training

Air Force officers undergo rigorous training to prepare them for their roles. The training includes:
- Officer training school: New officers attend officer training school, which provides them with the skills and knowledge they need to succeed as officers.
- Specialty training: Officers may receive specialty training in their specific career field, such as pilot training or intelligence training.
- Leadership training: Officers receive leadership training, which helps them develop the skills they need to lead and manage units effectively.
- Professional development: Officers are encouraged to pursue professional development opportunities, such as graduate education and certification programs.
Gallery of Air Force Officer Ranks
Air Force Officer Ranks Image Gallery










Frequently Asked Questions
What are the requirements for becoming an Air Force officer?
+To become an Air Force officer, you must meet certain requirements, including being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 35, and having a high school diploma or equivalent. You must also meet physical fitness standards and pass a background check.
What is the difference between a commissioned officer and a warrant officer?
+A commissioned officer is a high-ranking officer who has been commissioned by the President of the United States. A warrant officer is a technical expert who has been appointed by a warrant. Commissioned officers are typically responsible for leading and managing units, while warrant officers are responsible for providing technical expertise.
How do I advance in rank as an Air Force officer?
+To advance in rank as an Air Force officer, you must meet certain requirements, including time in service, performance, and education. You must also demonstrate leadership potential and complete additional training and education as required.
What are the benefits of being an Air Force officer?
+The benefits of being an Air Force officer include competitive pay, comprehensive health insurance, retirement benefits, education benefits, and travel opportunities. Air Force officers also have the opportunity to serve their country and make a difference in the world.
How do I become a pilot in the Air Force?
+To become a pilot in the Air Force, you must meet certain requirements, including being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 35, and having a high school diploma or equivalent. You must also pass a physical exam and complete a background check. You will then attend officer training school and complete pilot training.
In conclusion, the Air Force officer ranking system is a complex and structured hierarchy that provides a clear path for advancement and leadership development. Air Force officers play a critical role in the success of the military, and their responsibilities and benefits are significant. If you are considering a career as an Air Force officer, it is essential to understand the requirements, benefits, and opportunities that are available to you. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences about the Air Force officer ranking system in the comments below.
