Intro
Discover what case workers do, their roles, and responsibilities in social services, healthcare, and non-profit organizations, utilizing case management skills and support services to aid clients and communities in need.
Case workers, also known as social workers or case managers, play a vital role in ensuring the well-being and safety of individuals, families, and communities. They work in a variety of settings, including government agencies, non-profit organizations, hospitals, and private practices, to provide support and services to those in need. The importance of case workers cannot be overstated, as they often serve as the primary point of contact for individuals navigating complex social services and healthcare systems. In this article, we will delve into the world of case workers, exploring their responsibilities, benefits, and the impact they have on the lives of those they serve.
Case workers are highly trained professionals who possess a deep understanding of human behavior, social systems, and community resources. They work closely with clients to identify their strengths, needs, and goals, developing personalized plans to address these areas. This may involve connecting clients with resources such as food assistance, housing, employment training, and mental health services. By providing emotional support, guidance, and advocacy, case workers empower individuals to take control of their lives, make informed decisions, and achieve their full potential.
The role of case workers is multifaceted and demanding, requiring a unique blend of skills, knowledge, and compassion. They must be able to communicate effectively with clients, families, and other professionals, often in high-pressure situations. Case workers must also be able to navigate complex bureaucratic systems, advocating for clients' rights and interests while ensuring they receive the services and support they need. Despite the challenges, many case workers find their work highly rewarding, as they have the opportunity to make a positive impact on people's lives and contribute to the betterment of their communities.
Benefits of Case Workers

The benefits of case workers are numerous and far-reaching. By providing individualized support and connecting clients with vital resources, case workers help to improve health outcomes, increase economic stability, and enhance overall well-being. They also play a critical role in preventing crises, such as homelessness, child abuse, and neglect, by identifying and addressing risk factors early on. Furthermore, case workers often serve as a link between clients and community resources, helping to build stronger, more resilient communities.
Some of the key benefits of case workers include:
- Improved health outcomes: Case workers help clients access medical care, mental health services, and other essential resources, leading to better health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
- Increased economic stability: By connecting clients with employment training, education, and financial assistance, case workers help individuals achieve economic stability and self-sufficiency.
- Enhanced well-being: Case workers provide emotional support, guidance, and advocacy, empowering clients to take control of their lives and achieve their goals.
- Prevention of crises: Case workers identify and address risk factors, helping to prevent crises such as homelessness, child abuse, and neglect.
Types of Case Workers

There are several types of case workers, each with their own unique role and responsibilities. Some of the most common types of case workers include:
- Child welfare case workers: These professionals work with children and families to ensure their safety and well-being, often in situations where there is a risk of abuse or neglect.
- Mental health case workers: These case workers provide support and services to individuals with mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety, or substance abuse disorders.
- Medical case workers: These professionals work in healthcare settings, helping patients navigate the healthcare system and access necessary resources and services.
- Geriatric case workers: These case workers specialize in working with older adults, providing support and services to help them maintain their independence and quality of life.
Steps to Become a Case Worker
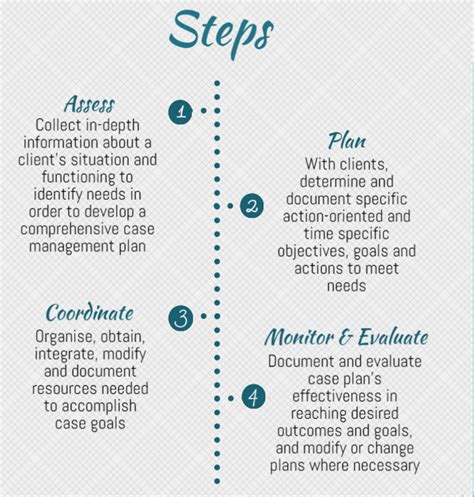
Becoming a case worker typically requires a combination of education, training, and experience. Here are the steps to become a case worker:
- Earn a bachelor's degree: Most case workers hold a bachelor's degree in social work, psychology, or a related field.
- Gain experience: Many case workers start their careers as interns or volunteers, gaining experience and building their skills in the field.
- Obtain certification: Some states require case workers to be certified or licensed, which typically involves passing an exam and completing continuing education requirements.
- Pursue a graduate degree: Advanced degrees, such as a master's in social work, can provide additional training and qualifications, leading to greater career opportunities and advancement.
- Develop essential skills: Case workers need strong communication, problem-solving, and interpersonal skills, as well as the ability to work with diverse populations and navigate complex systems.
Challenges Faced by Case Workers

Despite the rewards of being a case worker, the job can be demanding and emotionally challenging. Some of the common challenges faced by case workers include:
- High caseloads: Many case workers are responsible for managing large caseloads, which can lead to burnout and decreased job satisfaction.
- Limited resources: Case workers often face limited resources and funding, making it difficult to provide the level of support and services their clients need.
- Trauma and stress: Case workers may be exposed to traumatic and stressful situations, which can impact their mental health and well-being.
- Bureaucratic barriers: Navigating complex systems and bureaucracies can be frustrating and time-consuming, taking away from the time case workers can spend with clients.
Technological Advancements in Case Work

Technology has transformed the field of case work, providing new tools and resources to support clients and streamline services. Some of the technological advancements in case work include:
- Electronic health records: Digital records allow case workers to access and share client information more easily, improving communication and coordination of care.
- Telehealth services: Virtual platforms enable case workers to provide remote services, expanding access to care and reducing barriers to treatment.
- Mobile apps: Mobile apps can help case workers track client progress, access resources, and communicate with clients and other professionals.
- Data analytics: Advanced data analytics can help case workers identify trends, track outcomes, and make data-driven decisions to improve services and support.
Future of Case Work

The future of case work is exciting and evolving, with new technologies, innovative approaches, and shifting demographics presenting both opportunities and challenges. Some of the trends shaping the future of case work include:
- Increased focus on prevention: Case workers are shifting their focus from crisis intervention to prevention, working to identify and address risk factors early on.
- Greater emphasis on trauma-informed care: Trauma-informed care recognizes the impact of trauma on individuals and communities, providing a framework for case workers to deliver sensitive and supportive services.
- Growing demand for cultural competence: As populations become increasingly diverse, case workers must be able to work effectively with clients from different cultural backgrounds, providing culturally sensitive and responsive services.
- Integration of technology and human services: Technology will continue to play a larger role in case work, enabling case workers to provide more efficient, effective, and personalized services.
Gallery of Case Work Images
Case Work Image Gallery










What is the role of a case worker?
+A case worker is a professional who provides support and services to individuals, families, and communities, helping them navigate complex systems and access necessary resources.
What are the benefits of being a case worker?
+The benefits of being a case worker include making a positive impact on people's lives, contributing to the betterment of communities, and having a sense of personal fulfillment and satisfaction.
What are the challenges faced by case workers?
+Case workers face challenges such as high caseloads, limited resources, trauma and stress, and bureaucratic barriers, which can impact their job satisfaction and overall well-being.
How can I become a case worker?
+To become a case worker, you typically need to earn a bachelor's degree in social work or a related field, gain experience through internships or volunteering, and obtain certification or licensure in your state.
What is the future of case work?
+The future of case work is exciting and evolving, with trends such as increased focus on prevention, greater emphasis on trauma-informed care, and growing demand for cultural competence shaping the field.
As we conclude our exploration of the world of case workers, we invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and insights on the importance of case work and its impact on individuals and communities. Whether you are a case worker, a client, or simply someone who cares about the well-being of others, your voice matters. Join the conversation by commenting below, sharing this article with others, or taking action to support the vital work of case workers. Together, we can make a difference and create a brighter future for all.
