Intro
Discover 5 ways invasion happens, including biological, environmental, and ecological invasions, exploring invasive species, habitat disruption, and ecosystem imbalance.
Invasion, whether it be in the context of biology, technology, or societal structures, is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that can have profound impacts on the invaded system. Understanding how invasion happens is crucial for developing strategies to prevent, mitigate, or even harness its effects. Invasion can occur in various forms, including biological invasions where non-native species enter an ecosystem, technological invasions where new technologies disrupt existing markets or social structures, and cultural invasions where ideas, practices, or beliefs from one culture significantly influence another.
The process of invasion, regardless of its form, often follows certain patterns and principles. For instance, in biological invasions, the introduction of a non-native species can happen through human activity, such as trade, travel, or the intentional release of species for hunting or other purposes. Similarly, technological invasions can occur through the development and dissemination of new technologies that offer superior functionality or cost-effectiveness compared to existing solutions, leading to the displacement of older technologies. Cultural invasions can result from globalization, migration, or the spread of media and information technologies that facilitate the exchange of ideas across different cultures.
The impact of invasion can be far-reaching, affecting not only the immediate environment or market but also having broader ecological, economic, and social implications. In ecosystems, invasive species can outcompete native species for resources, alter habitats, and disrupt the balance of the ecosystem, potentially leading to biodiversity loss. Technological invasions can lead to job displacement, changes in consumer behavior, and shifts in economic power structures. Cultural invasions can result in the erosion of traditional practices, the homogenization of cultures, and conflicts between different cultural groups.
Given the significance and potential consequences of invasion, it is essential to explore the different ways through which invasion can occur. By understanding these mechanisms, we can better prepare for and respond to invasions, whether they be biological, technological, or cultural. This knowledge can inform strategies for preventing harmful invasions, mitigating their impacts, and even leveraging beneficial invasions to drive positive change.
Introduction to Invasion Mechanisms
Invasion mechanisms can be categorized based on the vector of introduction, the characteristics of the invading entity, and the response of the invaded system. For biological invasions, common vectors include human transportation, both intentional and unintentional, and natural dispersal methods. Technological invasions are often driven by innovation and the adoption of new technologies by consumers or industries. Cultural invasions can be facilitated by migration patterns, media dissemination, and educational exchanges.
Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing effective management and mitigation strategies. For instance, knowing the primary vectors of biological invasion can help in implementing stricter quarantine and inspection protocols for international trade and travel. Similarly, anticipating the pathways of technological invasion can aid in preparing workers for the transition to new industries and in investing in education and retraining programs.
Biological Invasion

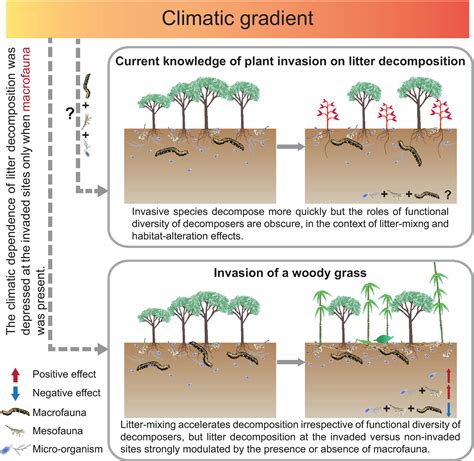
Biological invasion refers to the introduction and establishment of non-native species in an ecosystem. This can occur through various means, including human activity such as the pet trade, where exotic pets are released into the wild, or through the ballast water of ships, which can carry aquatic organisms from one region to another. Biological invasions can have devastating effects on native ecosystems, including the displacement of native species, alteration of ecosystem processes, and reduction of biodiversity.
Examples of biological invasions include the introduction of the zebra mussel to the Great Lakes, which has clogged water intake pipes and altered the native species composition, and the spread of the emerald ash borer, which has killed millions of ash trees across North America. Understanding the pathways and impacts of biological invasions is essential for developing effective conservation and management strategies to protect native ecosystems.
Pathways of Biological Invasion
The pathways through which biological invasions occur can be broadly categorized into intentional and unintentional introductions. Intentional introductions include the release of non-native species for hunting, fishing, or other recreational purposes, as well as the intentional introduction of species for biological control. Unintentional introductions, on the other hand, can occur through human activity such as trade, travel, and the transport of goods.
Technological Invasion

Technological invasion refers to the process by which new technologies enter and significantly impact a market, industry, or society. This can occur through the development of new products, services, or processes that offer advantages over existing technologies, leading to their displacement. Technological invasions can have profound effects on economies, leading to the creation of new industries, the disruption of existing ones, and changes in employment patterns.
Examples of technological invasions include the rise of the personal computer, which displaced mainframe computing, and the emergence of smartphones, which have revolutionized personal communication and information access. Understanding the dynamics of technological invasion is crucial for businesses, policymakers, and individuals to adapt to and benefit from technological change.
Factors Influencing Technological Invasion
Several factors can influence the success and impact of technological invasions, including the degree of innovation, the cost and accessibility of the new technology, and the existing regulatory and market structures. The adaptability of consumers and industries to new technologies also plays a significant role in determining the pace and extent of technological invasion.
Cultural Invasion

Cultural invasion refers to the process by which cultural practices, ideas, or values from one culture are imposed upon or voluntarily adopted by another culture. This can occur through various means, including globalization, migration, and the dissemination of media and information technologies. Cultural invasions can lead to the homogenization of cultures, the erosion of traditional practices, and conflicts between different cultural groups.
Examples of cultural invasions include the spread of Western culture through globalization, which has led to the adoption of Western clothing, music, and food preferences in many non-Western societies, and the influence of social media platforms in shaping cultural norms and values. Understanding cultural invasions is essential for promoting cultural diversity and addressing the challenges posed by cultural exchange and homogenization.
Impacts of Cultural Invasion
The impacts of cultural invasion can be far-reaching, affecting not only the cultural identity of invaded societies but also their social, economic, and political structures. While cultural exchange can bring about positive changes, such as the sharing of knowledge and ideas, it also poses risks, including the loss of cultural heritage and the imposition of dominant cultural norms.
Gallery of Invasion Examples
Invasion Image Gallery








Frequently Asked Questions
What is biological invasion?
+Biological invasion refers to the introduction and establishment of non-native species in an ecosystem, which can have devastating effects on native ecosystems.
How does technological invasion occur?
+Technological invasion occurs through the development and dissemination of new technologies that offer superior functionality or cost-effectiveness compared to existing solutions, leading to the displacement of older technologies.
What are the impacts of cultural invasion?
+Cultural invasion can lead to the homogenization of cultures, the erosion of traditional practices, and conflicts between different cultural groups, affecting not only cultural identity but also social, economic, and political structures.
In conclusion, invasion, whether biological, technological, or cultural, is a complex phenomenon with significant impacts on ecosystems, economies, and societies. Understanding the mechanisms and pathways of invasion is crucial for developing strategies to prevent, mitigate, or leverage its effects. As we move forward in an increasingly interconnected world, the ability to navigate and manage invasions will become ever more critical. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with invasion, whether it be in the context of environmental conservation, technological innovation, or cultural exchange, and to explore the many resources available for learning more about this multifaceted topic. By engaging in this discussion and deepening our understanding of invasion, we can work towards creating a more resilient, diverse, and thriving world for all.
