Intro
Discover 5 ways to calculate pay, including salary, hourly wage, and commission. Learn pay calculation methods, payroll processing, and compensation techniques.
Calculating pay is a crucial aspect of managing finances, whether you're an employer or an employee. Understanding the different methods of calculating pay can help you navigate the complex world of compensation and benefits. In this article, we'll explore five ways to calculate pay, including their benefits, drawbacks, and practical applications.
The importance of accurate pay calculation cannot be overstated. It not only affects an employee's take-home pay but also impacts their morale, productivity, and job satisfaction. Employers who fail to calculate pay correctly may face legal and financial consequences, including fines, penalties, and damage to their reputation. On the other hand, employees who understand how their pay is calculated can make informed decisions about their career, budget, and financial planning.
Pay calculation is also closely tied to the overall compensation and benefits package. Employers who offer competitive pay and benefits can attract and retain top talent, improve employee engagement, and drive business success. In contrast, employers who fail to provide fair and transparent pay calculation may struggle to recruit and retain employees, leading to increased turnover and decreased productivity. As the job market continues to evolve, it's essential for employers and employees to stay up-to-date on the latest pay calculation methods and best practices.
Introduction to Pay Calculation Methods

There are several ways to calculate pay, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The five methods we'll explore in this article include hourly wage, salary, commission, piece rate, and bonus-based pay. Understanding these methods can help employers create a fair and competitive compensation package, while employees can use this knowledge to negotiate better pay and benefits.
Hourly Wage Calculation
Hourly wage calculation is one of the most common methods of pay calculation. It involves paying employees a fixed rate per hour worked, with the total pay calculated by multiplying the hourly rate by the number of hours worked. This method is often used for part-time or temporary workers, as well as for jobs that require a high level of flexibility, such as freelancing or consulting.
The benefits of hourly wage calculation include:
- Easy to calculate and administer
- Provides a clear and transparent pay structure
- Allows for flexibility in scheduling and work arrangements However, hourly wage calculation also has some drawbacks, including:
- May not provide a stable or predictable income
- Can lead to overtime pay, which can be costly for employers
- May not account for variations in job duties or responsibilities
Example of Hourly Wage Calculation
For example, let's say an employee works 40 hours per week at an hourly rate of $20 per hour. Their total pay would be: 40 hours x $20 per hour = $800 per weekSalary Calculation
Salary calculation involves paying employees a fixed annual or monthly salary, regardless of the number of hours worked. This method is often used for full-time employees, as well as for jobs that require a high level of expertise or responsibility.
The benefits of salary calculation include:
- Provides a stable and predictable income
- Allows for easier budgeting and financial planning
- Can be more cost-effective for employers than hourly wage calculation However, salary calculation also has some drawbacks, including:
- May not account for variations in job duties or responsibilities
- Can lead to burnout or overwork, as employees may feel pressured to work long hours without additional pay
- May not provide a clear and transparent pay structure
Example of Salary Calculation
For example, let's say an employee earns an annual salary of $50,000, paid biweekly. Their total pay would be: $50,000 per year / 26 pay periods per year = $1,923 per pay periodCommission-Based Pay Calculation

Commission-based pay calculation involves paying employees a percentage of their sales or revenue generated. This method is often used for sales professionals, as well as for jobs that require a high level of performance or results.
The benefits of commission-based pay calculation include:
- Provides a clear and direct link between pay and performance
- Can be highly motivating for employees, as they have a direct stake in their sales or revenue
- Allows for flexibility in pay, as employees can earn more or less depending on their performance However, commission-based pay calculation also has some drawbacks, including:
- May not provide a stable or predictable income
- Can lead to high levels of stress or pressure, as employees may feel pressured to meet sales targets
- May not account for variations in job duties or responsibilities
Example of Commission-Based Pay Calculation
For example, let's say an employee earns a commission of 10% on all sales generated, with a monthly sales target of $10,000. Their total pay would be: $10,000 per month x 10% commission = $1,000 per monthPiece Rate Pay Calculation

Piece rate pay calculation involves paying employees a fixed rate per unit of work completed, such as per piece or per project. This method is often used for manufacturing or production jobs, as well as for jobs that require a high level of precision or quality.
The benefits of piece rate pay calculation include:
- Provides a clear and direct link between pay and productivity
- Can be highly motivating for employees, as they have a direct stake in their output
- Allows for flexibility in pay, as employees can earn more or less depending on their productivity However, piece rate pay calculation also has some drawbacks, including:
- May not provide a stable or predictable income
- Can lead to high levels of stress or pressure, as employees may feel pressured to meet production targets
- May not account for variations in job duties or responsibilities
Example of Piece Rate Pay Calculation
For example, let's say an employee earns a piece rate of $5 per unit produced, with a daily production target of 100 units. Their total pay would be: 100 units per day x $5 per unit = $500 per dayBonus-Based Pay Calculation

Bonus-based pay calculation involves paying employees a bonus or incentive pay based on their performance or achievements. This method is often used for jobs that require a high level of performance or results, as well as for jobs that require a high level of expertise or responsibility.
The benefits of bonus-based pay calculation include:
- Provides a clear and direct link between pay and performance
- Can be highly motivating for employees, as they have a direct stake in their performance
- Allows for flexibility in pay, as employees can earn more or less depending on their performance However, bonus-based pay calculation also has some drawbacks, including:
- May not provide a stable or predictable income
- Can lead to high levels of stress or pressure, as employees may feel pressured to meet performance targets
- May not account for variations in job duties or responsibilities
Example of Bonus-Based Pay Calculation
For example, let's say an employee earns a bonus of 20% of their annual salary, based on their performance evaluation. Their total pay would be: $50,000 per year x 20% bonus = $10,000 per yearPay Calculation Image Gallery





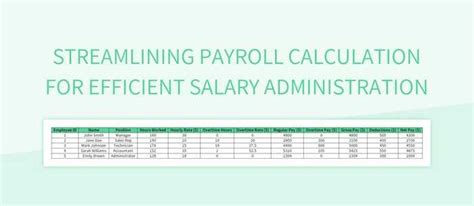
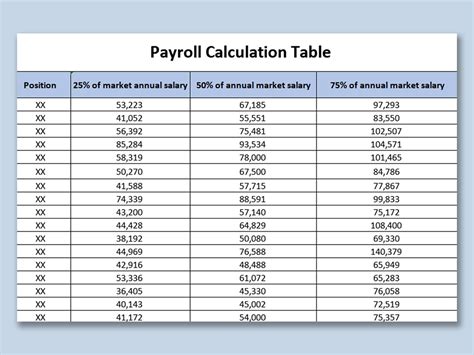
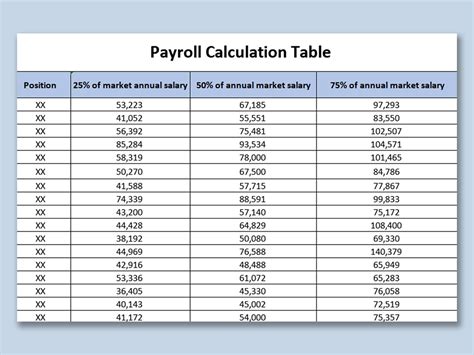
What is the difference between hourly wage and salary calculation?
+Hourly wage calculation involves paying employees a fixed rate per hour worked, while salary calculation involves paying employees a fixed annual or monthly salary, regardless of the number of hours worked.
How do I calculate my take-home pay?
+To calculate your take-home pay, you need to subtract taxes, deductions, and other withholdings from your gross pay. You can use a pay calculator or consult with a financial advisor to determine your take-home pay.
What is the purpose of pay calculation?
+The purpose of pay calculation is to determine the amount of money an employee should receive for their work, based on their hourly wage, salary, or other compensation methods. Accurate pay calculation is essential for ensuring fair and transparent pay practices, as well as for maintaining employee morale and motivation.
How often should I review my pay calculation method?
+You should review your pay calculation method regularly, ideally every 6-12 months, to ensure it remains fair, competitive, and aligned with your business goals and objectives. You may also need to review your pay calculation method in response to changes in employment laws, tax regulations, or other external factors.
Can I use multiple pay calculation methods for different employees?
+Yes, you can use multiple pay calculation methods for different employees, depending on their job duties, responsibilities, and compensation agreements. For example, you may use hourly wage calculation for part-time employees, salary calculation for full-time employees, and commission-based pay calculation for sales professionals.
In conclusion, calculating pay is a complex and multifaceted process that requires careful consideration of various factors, including job duties, responsibilities, compensation agreements, and employment laws. By understanding the different pay calculation methods and their benefits and drawbacks, employers and employees can work together to create a fair, transparent, and competitive compensation package that drives business success and employee satisfaction. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with pay calculation in the comments below, and to explore our other resources and articles on employment and compensation.
