Intro
Unlock geospatial intelligence with 5 Navy Geospatial MOS tips, leveraging geographic information systems, spatial analysis, and mapping techniques for career success.
The Navy Geospatial Intelligence (GEOINT) community is a vital component of the US Navy's intelligence apparatus, providing critical support to naval operations around the world. As a Navy Geospatial Intelligence Specialist (MOS), you play a crucial role in analyzing and interpreting geospatial data to inform decision-making at all levels of command. Here are five tips to help you succeed in this exciting and challenging field.
Geospatial intelligence is a rapidly evolving field, with new technologies and techniques emerging all the time. To stay ahead of the curve, it's essential to be committed to ongoing learning and professional development. This might involve pursuing advanced training or certifications, attending industry conferences, or participating in online forums and discussion groups. By staying up-to-date with the latest developments in geospatial intelligence, you'll be better equipped to provide timely and accurate support to naval operations.
The work of a Navy Geospatial Intelligence Specialist is highly technical, requiring a strong foundation in geographic information systems (GIS), remote sensing, and spatial analysis. However, it's also important to remember that geospatial intelligence is a team sport, and that your work will often involve collaborating with other intelligence specialists, operational planners, and commanders. To be successful in this role, you'll need to be able to communicate complex technical information in a clear and concise way, and to work effectively with others to achieve common goals.
One of the most significant challenges facing Navy Geospatial Intelligence Specialists is the need to analyze and interpret large volumes of complex data, often under tight deadlines. To succeed in this environment, it's essential to be highly organized and focused, with a strong attention to detail and a ability to prioritize tasks effectively. This might involve using specialized software or tools to manage and analyze data, or developing workflows and procedures to streamline your work and minimize errors.
Understanding Geospatial Intelligence

Key Components of Geospatial Intelligence
To understand geospatial intelligence, it's helpful to break it down into its key components. These include: * Geographic information systems (GIS): GIS is a critical component of geospatial intelligence, providing a framework for analyzing and interpreting geographic data. * Remote sensing: Remote sensing involves the use of satellite or aerial imagery to collect data about the environment. * Spatial analysis: Spatial analysis involves the use of specialized software and techniques to analyze and interpret geographic data.Geospatial Intelligence in Naval Operations

Applications of Geospatial Intelligence
Geospatial intelligence has a wide range of applications in naval operations, including: * Navigation: Geospatial intelligence can be used to support navigation, providing accurate and up-to-date information about the location and movement of ships and other assets. * Targeting: Geospatial intelligence can be used to support targeting, providing accurate and detailed information about potential targets. * Surveillance: Geospatial intelligence can be used to support surveillance, providing real-time information about the location and movement of ships and other assets.Tools and Techniques of Geospatial Intelligence

Key Tools and Techniques
Some of the key tools and techniques used in geospatial intelligence include: * GIS software: GIS software provides a framework for analyzing and interpreting geographic data. * Remote sensing platforms: Remote sensing platforms, such as satellite and aerial imagery, provide a means of collecting data about the environment. * Spatial analysis techniques: Spatial analysis techniques, such as spatial autocorrelation and spatial regression, provide a means of analyzing and interpreting geographic data.Challenges and Opportunities in Geospatial Intelligence
Key Challenges and Opportunities
Some of the key challenges and opportunities in geospatial intelligence include: * Big data: The increasing volume and complexity of geographic data presents a significant challenge for Navy Geospatial Intelligence Specialists, who must be able to analyze and interpret large volumes of data quickly and accurately. * Cloud computing: Cloud computing provides a means of storing and processing large volumes of geographic data, and of leveraging advanced analytics and machine learning techniques to support naval operations. * Cybersecurity: The increasing use of geospatial intelligence in naval operations also presents a significant cybersecurity risk, as hackers and other adversaries seek to exploit vulnerabilities in geospatial systems and networks.Best Practices for Geospatial Intelligence
Key Best Practices
Some of the key best practices for geospatial intelligence include: * Collaboration: Collaboration is critical in geospatial intelligence, where teams of specialists must work together to analyze and interpret complex geographic data. * Communication: Effective communication is also critical in geospatial intelligence, where specialists must be able to convey complex technical information to non-technical stakeholders. * Continuous learning: Continuous learning is essential in geospatial intelligence, where new technologies and techniques are emerging all the time.Future of Geospatial Intelligence

Key Trends and Developments
Some of the key trends and developments that are likely to shape the future of geospatial intelligence include: * Artificial intelligence: Artificial intelligence and machine learning are likely to play an increasingly important role in geospatial intelligence, where they can be used to analyze and interpret large volumes of complex geographic data. * Cybersecurity: Cybersecurity is likely to become an increasingly important consideration in geospatial intelligence, where the risk of cyber attack is growing all the time. * Cloud computing: Cloud computing is likely to play an increasingly important role in geospatial intelligence, where it can be used to store and process large volumes of geographic data.Navy Geospatial Intelligence Image Gallery





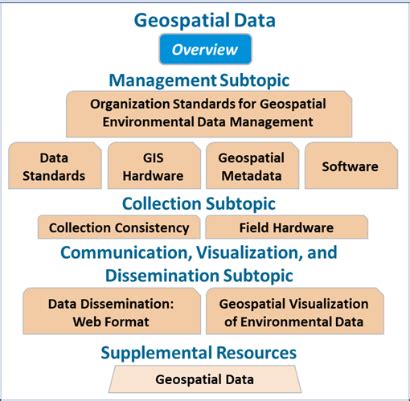

What is geospatial intelligence?
+Geospatial intelligence is the analysis and interpretation of geographic data, including satellite and aerial imagery, GIS data, and other forms of spatial information.
What are the key components of geospatial intelligence?
+The key components of geospatial intelligence include geographic information systems (GIS), remote sensing, and spatial analysis.
What are the applications of geospatial intelligence in naval operations?
+Geospatial intelligence has a wide range of applications in naval operations, including navigation, targeting, surveillance, and reconnaissance.
What are the challenges and opportunities in geospatial intelligence?
+The challenges in geospatial intelligence include the increasing volume and complexity of geographic data, as well as the growing importance of cybersecurity. The opportunities include the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning, as well as the expanding role of geospatial intelligence in naval operations.
What are the best practices for geospatial intelligence?
+The best practices for geospatial intelligence include collaboration, communication, and continuous learning. It's also important to leverage agile development methodologies and to prioritize cybersecurity.
As a Navy Geospatial Intelligence Specialist, you play a critical role in supporting naval operations around the world. By staying up-to-date with the latest developments in geospatial intelligence, leveraging best practices and lessons learned from other fields, and prioritizing collaboration, communication, and continuous learning, you can help to ensure the success of naval operations and the safety of our nation. We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights and information about the field of geospatial intelligence, and we encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below. Whether you're a seasoned geospatial intelligence professional or just starting out in your career, we invite you to join the conversation and to help shape the future of this exciting and rapidly evolving field.
