Intro
Discover 5 ways to join the Navy, including enlistment, officer programs, and special operations. Learn about Navy recruitment, basic training, and career paths to serve as a sailor, officer, or specialist in the US Naval forces.
Joining the navy can be a prestigious and rewarding career path, offering a unique blend of adventure, personal growth, and service to one's country. The process of joining, however, can be complex and varies significantly from one country to another. Generally, navies around the world offer several pathways for individuals to enlist or commission, catering to different skills, educational backgrounds, and career aspirations. Here's an overview of five common ways to join the navy, applicable to many countries, though specific requirements may differ.
The decision to join the navy is not one to be taken lightly. It requires careful consideration of the challenges, benefits, and opportunities that such a career entails. For those who are drawn to the sea, who value discipline, and who are eager to serve their nation, the navy can offer a fulfilling and exciting career. Whether one is interested in sailing the world, operating advanced technology, or being part of a tight-knit community, the navy has much to offer.
Before embarking on the journey to join the navy, it's essential to understand the various entry points and the qualifications required for each. The navy seeks individuals with a wide range of skills and educational backgrounds, from those with high school diplomas to those with advanced degrees. This diversity allows the navy to maintain its operational effectiveness and to provide its personnel with opportunities for professional development and specialization.
Understanding Navy Career Paths

The navy offers two primary career paths: enlisted and officer. Enlisted personnel typically enter the navy after completing high school and undergo basic training followed by specialized training in their chosen field. Officers, on the other hand, usually hold a bachelor's degree and may enter the navy through various commissioning programs. Understanding these paths and their requirements is crucial for anyone considering a navy career.
Enlisted Careers in the Navy

Enlisted careers in the navy are diverse, ranging from aviation and engineering to healthcare and communications. To join as an enlisted member, one typically needs to meet basic eligibility requirements, which include being a U.S. citizen (for the U.S. Navy), being between the ages of 17 and 35 (with some exceptions), having a high school diploma, and passing the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test. The enlistment process involves taking the ASVAB, undergoing a physical exam, and completing boot camp.
Steps to Enlist in the Navy
To enlist in the navy, follow these steps: 1. **Meet the Basic Requirements**: Ensure you meet the age, citizenship, and educational requirements. 2. **Take the ASVAB Test**: This test helps determine your aptitude for various naval careers. 3. **Choose Your Career**: Select from the available enlisted ratings based on your ASVAB scores and personal interests. 4. **Prepare for Boot Camp**: Physically and mentally prepare yourself for the challenges of basic training. 5. **Complete Boot Camp**: Attend and successfully complete the navy's boot camp, where you'll learn the fundamentals of naval service.Officer Careers in the Navy
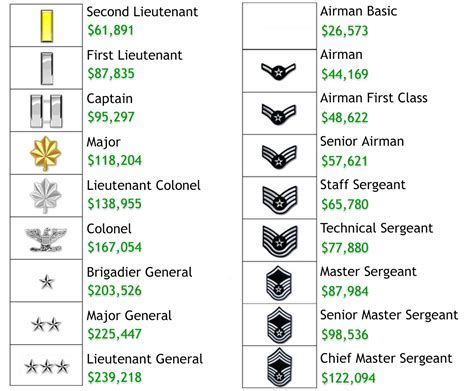
For those interested in becoming an officer, the navy offers several commissioning programs. These include the United States Naval Academy, Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC), Officer Candidate School (OCS), and direct commission programs for certain specialties like medicine or law. Officer candidates must hold a bachelor's degree from an accredited institution, meet physical fitness standards, and receive a commission through one of the navy's commissioning programs.
Paths to Becoming a Navy Officer
The paths to becoming a navy officer include: - **United States Naval Academy**: A four-year college experience that leads to a commission as an ensign upon graduation. - **ROTC**: A college program that allows students to earn a degree while receiving military training, leading to a commission. - **Officer Candidate School (OCS)**: A training program for individuals who already hold a bachelor's degree, leading to a commission as an officer. - **Direct Commission**: Available for professionals in certain fields, such as medicine, law, or chaplaincy, allowing them to enter the navy as officers.Navy Reserve and Part-Time Opportunities

For those who cannot commit to full-time military service or prefer a part-time role, the Navy Reserve offers an alternative. The Navy Reserve allows individuals to serve part-time, usually one weekend a month and two weeks a year, while pursuing civilian careers. This option is available for both enlisted personnel and officers and can provide valuable training, experience, and benefits, including education assistance and retirement benefits.
Benefits of Joining the Navy Reserve
Joining the Navy Reserve comes with several benefits, including: - **Education Assistance**: Opportunities for tuition reimbursement and other educational benefits. - **Career Skills**: Development of valuable skills that can enhance civilian career prospects. - **Travel Opportunities**: Chances to travel and experience different parts of the world. - **Retirement Benefits**: Eligibility for military retirement benefits after 20 years of service.Special Programs and Opportunities

The navy also offers special programs for individuals with unique skills or interests, such as the Navy's SEAL program for those interested in special operations, the Nuclear Field for individuals interested in nuclear power, and various apprenticeship programs for those looking to gain specific trade skills. These programs can provide challenging and rewarding career paths for those who qualify.
Examples of Special Programs
Some examples of special programs in the navy include: - **Navy SEALs**: An elite special operations force that conducts a variety of missions. - **Nuclear Field**: A program for individuals interested in nuclear power, involving the operation and maintenance of naval nuclear reactors. - **Apprenticeship Programs**: Opportunities to learn a trade or skill through on-the-job training and formal instruction.Navy Career Gallery









What are the basic requirements to join the navy?
+The basic requirements include being a citizen of the country, meeting the age requirement, having a high school diploma, and passing the ASVAB test.
How do I become a navy officer?
+You can become a navy officer through the Naval Academy, ROTC, Officer Candidate School, or direct commission programs for certain specialties.
What are the benefits of joining the Navy Reserve?
+The benefits include education assistance, career skills development, travel opportunities, and retirement benefits after 20 years of service.
In conclusion, joining the navy offers a wide range of opportunities for personal and professional growth, service to one's country, and the chance to be part of a unique and prestigious institution. Whether through enlisted or officer paths, full-time or part-time service, the navy has something to offer individuals from all walks of life. As you consider your future and the role you wish to play in the world, remember the navy as a potential path that can lead to adventure, camaraderie, and a sense of fulfillment that few other careers can match. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, or questions about joining the navy in the comments below, and to consider the many rewarding careers and opportunities that the navy has to offer.
