Intro
Explore the devastating effects of nuclear blasts within 5 distinct zones, including fireball, radiation, and blast wave areas, understanding nuclear fallout and disaster response.
The threat of nuclear war has been a looming specter over humanity for decades, with the potential for devastating consequences that could affect millions of people worldwide. One of the most significant concerns is the impact of a nuclear blast on the surrounding area, with the effects ranging from immediate destruction to long-term health problems. In this article, we will explore the different nuclear blast zones, their characteristics, and the potential consequences for those caught in the blast.
The effects of a nuclear blast can be divided into five distinct zones, each with its own unique characteristics and consequences. Understanding these zones is crucial for developing effective emergency response plans and mitigating the damage caused by a nuclear explosion. The five nuclear blast zones are: the fireball zone, the blast wave zone, the thermal radiation zone, the radiation zone, and the fallout zone.
Introduction to Nuclear Blast Zones
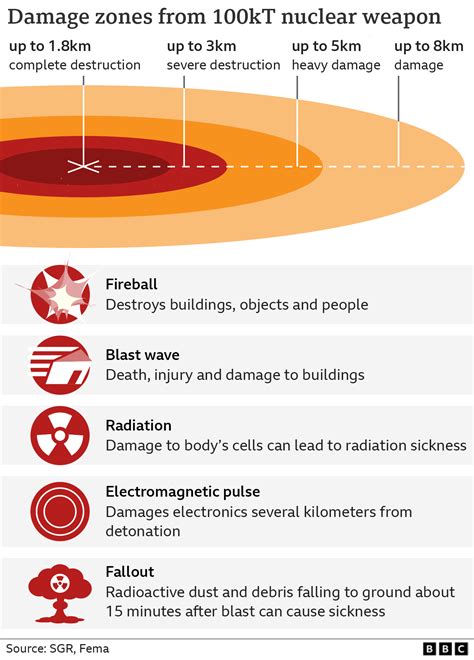
Fireball Zone

Blast Wave Zone

Characteristics of the Blast Wave Zone
The blast wave zone is the most destructive area after the fireball zone, with the potential for widespread destruction and loss of life. The characteristics of the blast wave zone include: * Peak overpressure: The pressure exerted by the blast wave, which can reach levels of up to 100 psi (pounds per square inch) * Dynamic pressure: The pressure exerted by the blast wave as it moves through the air, which can reach levels of up to 100 psi * Wind speed: The speed of the winds generated by the blast wave, which can reach speeds of up to hundreds of miles per hourThermal Radiation Zone
Effects of Thermal Radiation
The effects of thermal radiation can be severe, with the potential for burns, fires, and injuries. The effects of thermal radiation include: * First-degree burns: Burns that affect the outer layer of skin * Second-degree burns: Burns that affect both the outer and inner layers of skin * Third-degree burns: Burns that extend through all layers of skin and can cause permanent damageRadiation Zone

Types of Radiation
The types of radiation emitted by a nuclear explosion include: * Gamma radiation: High-energy radiation that can penetrate solid objects * Beta radiation: High-energy radiation that can penetrate skin and soft tissues * Alpha radiation: Low-energy radiation that can be stopped by a sheet of paperFallout Zone

Effects of Fallout
The effects of fallout can be severe, with the potential for long-term health effects and environmental damage. The effects of fallout include: * Cancer: Increased risk of cancer from exposure to radioactive particles * Genetic damage: Increased risk of genetic damage from exposure to radioactive particles * Environmental damage: Contamination of soil, water, and air, which can have long-term effects on ecosystemsNuclear Blast Zones Image Gallery








What is the most destructive area of a nuclear blast?
+The most destructive area of a nuclear blast is the fireball zone, where the temperatures are so high that everything is vaporized.
What are the effects of thermal radiation on humans?
+The effects of thermal radiation on humans include burns, fires, and injuries. The severity of the effects depends on the distance from the blast and the duration of exposure.
What is the difference between gamma radiation and beta radiation?
+Gamma radiation is high-energy radiation that can penetrate solid objects, while beta radiation is high-energy radiation that can penetrate skin and soft tissues.
What are the long-term effects of fallout on the environment?
+The long-term effects of fallout on the environment include contamination of soil, water, and air, which can have long-term effects on ecosystems and human health.
How can people protect themselves from radiation exposure?
+People can protect themselves from radiation exposure by wearing protective clothing, including masks and gloves, and staying indoors during a nuclear emergency.
In conclusion, the effects of a nuclear blast can be devastating, with the potential for widespread destruction and loss of life. Understanding the different nuclear blast zones and their characteristics is crucial for developing effective emergency response plans and mitigating the damage caused by a nuclear explosion. By being informed and prepared, we can reduce the risks associated with nuclear blasts and create a safer and more secure world for everyone. We invite you to share your thoughts and concerns about nuclear blast zones in the comments section below, and to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about this important topic.
