Intro
Compare National Guard vs Army: differences in deployment, training, and benefits, exploring reserve duties, active duty, and military careers, to make an informed decision.
The National Guard and the Army are two distinct entities within the United States military, each with its own unique role, responsibilities, and requirements. While both organizations are part of the country's defense system, they differ in their missions, structures, and operational modes. Understanding these differences is essential for individuals considering a career in the military, as well as for the general public seeking to appreciate the complexities of national defense.
The National Guard is a reserve component of the US Armed Forces, comprising both the Army National Guard and the Air National Guard. Its primary mission is to provide support to state and local authorities during domestic emergencies, such as natural disasters, civil unrest, and search and rescue operations. The National Guard also plays a critical role in national defense, deploying troops overseas in support of military operations. With its dual-state and federal mission, the National Guard is uniquely positioned to respond to a wide range of challenges, from homeland security to international conflict.
In contrast, the Army is a full-time, active-duty branch of the US military, responsible for land-based military operations. The Army's primary mission is to protect the country and its interests by fighting and winning wars, as well as conducting humanitarian and peacekeeping missions. The Army is a larger and more complex organization than the National Guard, with a broader range of responsibilities and a more extensive global presence. Army personnel are trained to operate in a variety of environments, from deserts to jungles, and are equipped with a wide range of weapons, vehicles, and technologies.
History and Mission

The Army, on the other hand, has a long and storied history dating back to the American Revolution. The Army's mission is to protect the country and its interests by fighting and winning wars, as well as conducting humanitarian and peacekeeping missions. The Army is a full-time, active-duty branch of the military, with a global presence and a wide range of responsibilities. From combat operations to disaster relief, the Army plays a critical role in defending the nation and promoting stability around the world.
Organization and Structure
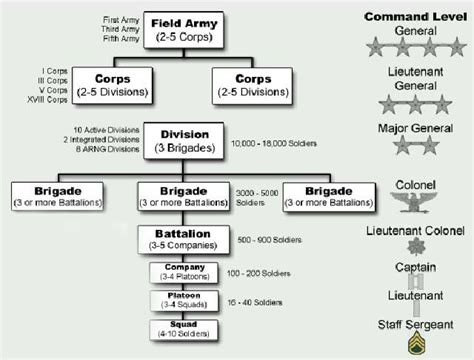
The Army, by contrast, is a larger and more complex organization, with a global presence and a wide range of responsibilities. The Army is divided into several major commands, including the US Army Forces Command, the US Army Training and Doctrine Command, and the US Army Materiel Command. The Army also has a number of specialized units, such as the Special Forces, the Rangers, and the Army Corps of Engineers. These units are trained to operate in a variety of environments and are equipped with a wide range of technologies and capabilities.
Key Differences
The main differences between the National Guard and the Army lie in their missions, structures, and operational modes. The National Guard is a reserve component with a dual-state and federal mission, while the Army is a full-time, active-duty branch of the military with a broader range of responsibilities. The National Guard is typically organized at the state level, while the Army has a global presence and a more complex organizational structure. Additionally, National Guard personnel often serve part-time, while Army personnel are full-time active-duty soldiers.Training and Equipment

The Army, on the other hand, has a more extensive and complex training program, reflecting its broader range of responsibilities and global presence. Army personnel receive training in areas such as combat operations, leadership, and specialized skills, as well as education and career development opportunities. The Army also has access to a wide range of advanced technologies and equipment, including tanks, aircraft, and cyber warfare systems.
Education and Career Opportunities
Both the National Guard and the Army offer education and career opportunities to their personnel. The National Guard provides tuition assistance, education counseling, and career guidance to its members, as well as opportunities for advancement and professional development. The Army also offers a range of education and career opportunities, including the GI Bill, education assistance programs, and career counseling. Additionally, the Army has a number of specialized schools and training programs, such as the US Army War College and the Army Command and General Staff College.Deployment and Operations

The Army, on the other hand, is a full-time, active-duty branch of the military, with a global presence and a wide range of responsibilities. Army personnel may be deployed in support of combat operations, peacekeeping missions, and humanitarian assistance, as well as in support of homeland security and disaster relief efforts. The Army has a number of specialized units, such as the Special Forces and the Rangers, which are trained to operate in a variety of environments and are equipped with advanced technologies and capabilities.
Support and Resources
Both the National Guard and the Army provide support and resources to their personnel, including medical care, mental health services, and family support programs. The National Guard also has a number of specialized programs, such as the National Guard Family Program and the National Guard Youth Program, which provide support and resources to Guard families and youth. The Army has a range of support programs, including the Army Family Readiness Group and the Army Substance Abuse Program, which provide assistance and resources to Army families and personnel.Benefits and Compensation

The Army, on the other hand, offers a more comprehensive benefits package, reflecting its full-time, active-duty status. Army personnel receive pay and benefits, as well as access to education and career opportunities, medical care, and retirement plans. The Army also offers a range of specialized benefits, such as the GI Bill and the Army's education assistance program, which provide financial assistance and support to Army personnel and their families.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, the National Guard and the Army are two distinct entities within the US military, each with its own unique role, responsibilities, and requirements. Understanding these differences is essential for individuals considering a career in the military, as well as for the general public seeking to appreciate the complexities of national defense. Whether you are interested in serving part-time in the National Guard or full-time in the Army, there are many resources and opportunities available to support your career and personal goals.National Guard Vs Army Image Gallery









What is the main difference between the National Guard and the Army?
+The main difference between the National Guard and the Army is their mission and operational mode. The National Guard is a reserve component with a dual-state and federal mission, while the Army is a full-time, active-duty branch of the military with a broader range of responsibilities.
Can I serve in both the National Guard and the Army?
+Yes, it is possible to serve in both the National Guard and the Army. However, this would require meeting the eligibility requirements for both organizations and completing the necessary training and service commitments.
What are the benefits of serving in the National Guard versus the Army?
+The benefits of serving in the National Guard versus the Army depend on individual circumstances and priorities. The National Guard offers part-time service, education and career opportunities, and access to medical care and retirement plans. The Army offers full-time service, comprehensive benefits, and access to education and career opportunities, as well as specialized training and equipment.
How do I choose between serving in the National Guard and the Army?
+Choosing between serving in the National Guard and the Army depends on individual circumstances, priorities, and goals. Consider factors such as service commitment, education and career opportunities, medical care, and retirement plans, as well as personal preferences and values.
What are the eligibility requirements for serving in the National Guard and the Army?
+The eligibility requirements for serving in the National Guard and the Army vary, but generally include meeting age, citizenship, education, and physical fitness requirements. Additionally, applicants must pass background checks, medical screenings, and aptitude tests.
We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the differences between the National Guard and the Army. Whether you are considering a career in the military or simply seeking to understand the complexities of national defense, we encourage you to continue exploring and learning about these two important organizations. Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below, and don't forget to share this article with others who may be interested in this topic.
