Intro
Explore the inner workings of a power plant, discovering energy generation, transmission, and distribution processes, including thermal, nuclear, and renewable systems.
The world of power plants is a fascinating and complex one, playing a crucial role in meeting the ever-increasing demand for electricity. Power plants are the backbone of modern society, providing the energy needed to power homes, businesses, and industries. From traditional fossil fuel-based plants to newer, more sustainable options like solar and wind farms, the technology and infrastructure behind power generation are continuously evolving. Understanding how a power plant operates, its components, and the challenges it faces is essential for appreciating the intricacies of the energy sector.
Power plants have been around for over a century, with the first power plant opening in 1882 in Appleton, Wisconsin, USA. Since then, the technology has advanced significantly, with various types of power plants emerging, each with its unique characteristics and advantages. The primary function of a power plant is to convert energy from one form to another, typically from chemical or thermal energy into electrical energy. This process involves several key steps and components, including fuel handling, combustion, steam generation, and electricity production.
The importance of power plants cannot be overstated. They are the primary source of electricity for millions of people worldwide, powering everything from household appliances to large industrial machinery. Moreover, power plants are a significant contributor to a country's economy, providing employment opportunities and driving economic growth. However, the operation of power plants also raises concerns about environmental impact, efficiency, and sustainability, prompting ongoing research and development into cleaner, more efficient energy production methods.
Introduction to Power Plant Components
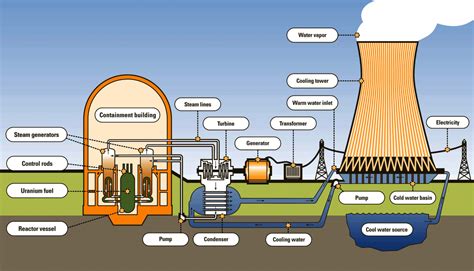
A typical power plant consists of several key components, each playing a vital role in the electricity generation process. These components include boilers, turbines, generators, transformers, and transmission lines. The boiler is responsible for producing steam by burning fuel, such as coal, natural gas, or biomass. The steam then drives a turbine, which is connected to a generator. The generator converts the mechanical energy of the turbine into electrical energy. Transformers are used to increase the voltage of the electricity to facilitate transmission over long distances, while transmission lines carry the electricity from the power plant to substations and eventually to consumers.
Boilers and Steam Generation
The boiler is a critical component of a power plant, as it is responsible for producing the steam that drives the turbine. Boilers can be fueled by a variety of sources, including coal, natural gas, and biomass. The choice of fuel depends on several factors, including availability, cost, and environmental considerations. Coal, for example, is a common fuel source for power plants due to its abundance and relatively low cost. However, it is also a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions, prompting a shift towards cleaner fuels like natural gas and renewable energy sources.Types of Power Plants
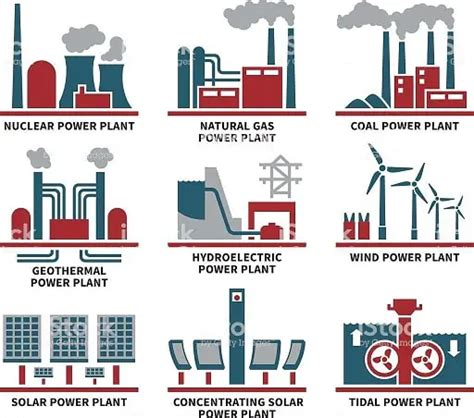
There are several types of power plants, each with its unique characteristics and advantages. Thermal power plants, which include coal, gas, and oil-fired plants, are the most common type. These plants use heat to produce steam, which drives a turbine to generate electricity. Hydroelectric power plants, on the other hand, use the energy of moving water to drive turbines. Nuclear power plants use nuclear reactions to produce steam, while renewable energy sources like solar and wind are becoming increasingly popular due to their sustainability and decreasing costs.
Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources are playing an increasingly important role in the energy sector, driven by concerns about climate change, air pollution, and energy sustainability. Solar and wind power are the most prominent renewable energy sources, with solar power involving the use of photovoltaic panels to convert sunlight into electricity, and wind power using turbines to generate electricity from wind energy. Other renewable energy sources include hydroelectric power, geothermal energy, and biomass. The integration of renewable energy sources into the grid poses several challenges, including intermittency and energy storage, but offers significant benefits in terms of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving energy security.Challenges Facing Power Plants
Power plants face several challenges, including environmental concerns, efficiency, and sustainability. The burning of fossil fuels for electricity generation is a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change. Additionally, power plants are often inefficient, with a significant amount of energy being lost as heat. The integration of renewable energy sources into the grid also poses challenges, including intermittency and energy storage. Furthermore, the increasing demand for electricity, coupled with aging infrastructure, requires significant investment in new power plants and grid modernization.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Improving energy efficiency and sustainability is crucial for the future of power plants. This can be achieved through the adoption of cleaner fuels, such as natural gas and renewable energy sources, and the implementation of more efficient technologies, such as combined cycle gas turbines and advanced solar panels. Energy storage technologies, like batteries, can also help mitigate the intermittency of renewable energy sources, ensuring a stable and reliable energy supply. Moreover, smart grid technologies can optimize energy distribution, reducing energy losses and improving the overall efficiency of the energy system.Future of Power Plants

The future of power plants is likely to be shaped by several factors, including technological advancements, environmental concerns, and changing energy demand patterns. The integration of renewable energy sources, energy storage, and smart grid technologies will play a crucial role in creating a more sustainable and efficient energy system. Additionally, the development of new technologies, such as advanced nuclear power and carbon capture and storage, could significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions from power plants. The future of power plants will also be influenced by policy and regulatory frameworks, which will need to balance the need for reliable and affordable energy with the imperative to reduce environmental impact.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
Policy and regulatory frameworks will play a critical role in shaping the future of power plants. Governments and regulatory bodies will need to create incentives for the adoption of cleaner energy technologies, while also ensuring that the energy system remains reliable and affordable. This can be achieved through mechanisms like carbon pricing, tax incentives for renewable energy investments, and grid connection policies that facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources. Moreover, policies aimed at improving energy efficiency, such as building codes and appliance standards, can help reduce energy demand and mitigate the need for new power plants.Gallery of Power Plant Images
Power Plant Image Gallery










Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary function of a power plant?
+The primary function of a power plant is to convert energy from one form to another, typically from chemical or thermal energy into electrical energy.
What are the different types of power plants?
+There are several types of power plants, including thermal, hydroelectric, nuclear, solar, wind, and geothermal power plants.
What is the role of renewable energy sources in the energy sector?
+Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are playing an increasingly important role in the energy sector, driven by concerns about climate change, air pollution, and energy sustainability.
How can energy efficiency be improved in power plants?
+Energy efficiency can be improved in power plants through the adoption of cleaner fuels, the implementation of more efficient technologies, and the optimization of energy distribution through smart grid technologies.
What is the future of power plants?
+The future of power plants will be shaped by technological advancements, environmental concerns, and changing energy demand patterns, with a focus on sustainability, efficiency, and the integration of renewable energy sources.
As we move forward, it's essential to consider the complexities and challenges associated with power plants, from environmental concerns to technological advancements. By understanding the intricacies of power generation and the role of power plants in our daily lives, we can work towards creating a more sustainable and efficient energy system. Whether you're an industry professional, a policymaker, or simply a concerned citizen, there's much to learn and discover about the world of power plants. We invite you to share your thoughts, ask questions, and explore the many facets of this critical component of our modern world. Together, we can build a brighter, more sustainable energy future.
