Intro
Discover Army National Guard Ranks, including enlisted and officer ranks, with explanations of rank structures, insignia, and responsibilities, to understand the hierarchy and career progression within the National Guard military organization.
The Army National Guard is a reserve component of the United States Army, and its ranks are similar to those of the regular Army. Understanding the ranks of the Army National Guard is essential for anyone interested in joining or working with the organization. The ranks of the Army National Guard are divided into several categories, including enlisted, warrant officer, and officer ranks. Each rank has its own set of responsibilities, requirements, and benefits.
The Army National Guard ranks are designed to provide a clear chain of command and to recognize the skills and experience of its members. The ranks are also used to determine pay, promotions, and benefits. In this article, we will explore the different ranks of the Army National Guard, their responsibilities, and the requirements for advancing to each rank.
Enlisted Ranks

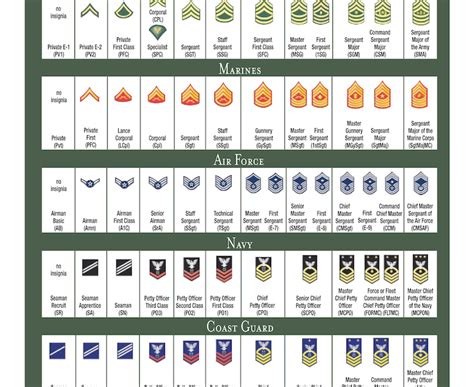
The enlisted ranks of the Army National Guard are the backbone of the organization. These ranks include Private (PVT), Private First Class (PFC), Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL), Sergeant (SGT), Staff Sergeant (SSG), Sergeant First Class (SFC), Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (MSG/1SG), and Sergeant Major (SGM). Each enlisted rank has its own set of responsibilities and requirements.
- Private (PVT) is the entry-level rank for new recruits.
- Private First Class (PFC) is the second-lowest rank, and soldiers typically achieve this rank after completing basic training.
- Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL) is a junior non-commissioned officer rank, and soldiers typically achieve this rank after completing advanced individual training.
- Sergeant (SGT) is a non-commissioned officer rank, and soldiers typically achieve this rank after completing a leadership course.
- Staff Sergeant (SSG) is a senior non-commissioned officer rank, and soldiers typically achieve this rank after completing a senior leadership course.
- Sergeant First Class (SFC) is a senior non-commissioned officer rank, and soldiers typically achieve this rank after completing a master leadership course.
- Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (MSG/1SG) is a senior enlisted rank, and soldiers typically achieve this rank after completing a senior enlisted leadership course.
- Sergeant Major (SGM) is the highest enlisted rank, and soldiers typically achieve this rank after completing a senior enlisted leadership course and serving in a senior leadership position.
Warrant Officer Ranks
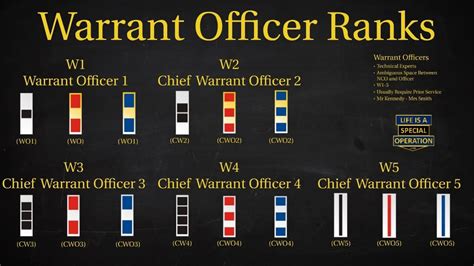
The warrant officer ranks of the Army National Guard are technical experts who have completed specialized training in a specific field. These ranks include Warrant Officer 1 (WO1), Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2), Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3), Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4), and Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5).
- Warrant Officer 1 (WO1) is the entry-level warrant officer rank, and soldiers typically achieve this rank after completing warrant officer candidate school.
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2) is a junior warrant officer rank, and soldiers typically achieve this rank after completing a warrant officer basic course.
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3) is a senior warrant officer rank, and soldiers typically achieve this rank after completing a warrant officer advanced course.
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4) is a senior warrant officer rank, and soldiers typically achieve this rank after completing a warrant officer senior course.
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5) is the highest warrant officer rank, and soldiers typically achieve this rank after completing a warrant officer master course.
Officer Ranks
The officer ranks of the Army National Guard are leaders who have completed a commissioning program, such as the Officer Candidate School or the United States Military Academy. These ranks include Second Lieutenant (2LT), First Lieutenant (1LT), Captain (CPT), Major (MAJ), Lieutenant Colonel (LTC), Colonel (COL), and Brigadier General (BG).
- Second Lieutenant (2LT) is the entry-level officer rank, and officers typically achieve this rank after completing a commissioning program.
- First Lieutenant (1LT) is a junior officer rank, and officers typically achieve this rank after completing a leadership course.
- Captain (CPT) is a company-level officer rank, and officers typically achieve this rank after completing a company command course.
- Major (MAJ) is a field-grade officer rank, and officers typically achieve this rank after completing a field-grade officer course.
- Lieutenant Colonel (LTC) is a senior field-grade officer rank, and officers typically achieve this rank after completing a senior officer course.
- Colonel (COL) is a senior officer rank, and officers typically achieve this rank after completing a senior officer course and serving in a senior leadership position.
- Brigadier General (BG) is the highest officer rank, and officers typically achieve this rank after completing a general officer course and serving in a senior leadership position.
Benefits of Joining the Army National Guard
The Army National Guard offers a range of benefits to its members, including education assistance, health insurance, and retirement benefits. Members of the Army National Guard can also take advantage of training and education opportunities, such as the GI Bill and the Army National Guard's own education assistance program.- Education assistance: The Army National Guard offers education assistance to its members, including the GI Bill and the Army National Guard's own education assistance program.
- Health insurance: The Army National Guard offers health insurance to its members, including medical, dental, and vision coverage.
- Retirement benefits: The Army National Guard offers retirement benefits to its members, including a pension and retirement pay.
- Training and education opportunities: The Army National Guard offers a range of training and education opportunities to its members, including leadership courses, technical training, and degree programs.
Requirements for Joining the Army National Guard
To join the Army National Guard, individuals must meet certain requirements, including age, citizenship, and education requirements. They must also pass a physical fitness test and a background check.- Age: To join the Army National Guard, individuals must be between the ages of 17 and 35.
- Citizenship: To join the Army National Guard, individuals must be citizens of the United States.
- Education: To join the Army National Guard, individuals must have a high school diploma or equivalent.
- Physical fitness: To join the Army National Guard, individuals must pass a physical fitness test, which includes a 2-mile run, push-ups, and sit-ups.
- Background check: To join the Army National Guard, individuals must pass a background check, which includes a review of their criminal history and credit report.
Army National Guard Image Gallery








What are the benefits of joining the Army National Guard?
+The Army National Guard offers a range of benefits to its members, including education assistance, health insurance, and retirement benefits.
What are the requirements for joining the Army National Guard?
+To join the Army National Guard, individuals must meet certain requirements, including age, citizenship, and education requirements. They must also pass a physical fitness test and a background check.
How do I advance in rank in the Army National Guard?
+To advance in rank in the Army National Guard, individuals must meet certain requirements, including time in service, education, and training. They must also pass a promotion board and receive a recommendation from their commander.
In conclusion, the Army National Guard ranks are an essential part of the organization, providing a clear chain of command and recognizing the skills and experience of its members. The ranks are divided into enlisted, warrant officer, and officer ranks, each with its own set of responsibilities and requirements. The Army National Guard offers a range of benefits to its members, including education assistance, health insurance, and retirement benefits. To join the Army National Guard, individuals must meet certain requirements, including age, citizenship, and education requirements. We encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about the Army National Guard ranks and benefits. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave them below.
