Intro
Discover submarine speed facts, exploring naval vessel velocities, underwater propulsion, and maritime technology, revealing fast submarine speeds and advanced oceanic engineering.
The world of submarines is a fascinating one, filled with cutting-edge technology and innovative designs. One of the most interesting aspects of submarines is their speed, which can vary greatly depending on the type of vessel and its intended use. In this article, we will delve into the world of submarine speed, exploring the different types of submarines, their speeds, and what makes them tick.
Submarines have been a crucial part of naval warfare for over a century, with their ability to operate undetected beneath the surface of the ocean making them a valuable asset for military forces around the world. But submarines are not just used for military purposes; they are also used for scientific research, exploration, and even tourism. With such a wide range of uses, it's no wonder that submarines come in a variety of shapes and sizes, each with its own unique characteristics and capabilities.
One of the most impressive things about submarines is their ability to reach high speeds, both on the surface and underwater. While most people think of submarines as slow-moving vessels, some can reach speeds of over 40 knots (74 km/h), making them almost as fast as surface ships. But what makes submarines so fast, and how do they achieve such high speeds? To answer these questions, we need to take a closer look at the different types of submarines and their propulsion systems.
Types of Submarines

There are several types of submarines, each with its own unique characteristics and capabilities. The most common types of submarines are ballistic missile submarines, attack submarines, and conventional submarines. Ballistic missile submarines are designed to carry nuclear missiles and are typically the largest and most heavily armed of all submarines. Attack submarines, on the other hand, are designed for combat and are equipped with a variety of weapons, including torpedoes and missiles. Conventional submarines are the most common type of submarine and are used for a variety of purposes, including scientific research and exploration.
Ballistic Missile Submarines
Ballistic missile submarines are the largest and most heavily armed of all submarines. They are designed to carry nuclear missiles and are typically equipped with a range of advanced sensors and communication systems. These submarines are capable of reaching speeds of up to 20 knots (37 km/h) and have a range of over 10,000 nautical miles (18,520 km).Attack Submarines
Attack submarines are designed for combat and are equipped with a variety of weapons, including torpedoes and missiles. They are typically smaller and more agile than ballistic missile submarines and are capable of reaching speeds of up to 30 knots (56 km/h). Attack submarines are used for a variety of purposes, including anti-submarine warfare and reconnaissance.Conventional Submarines
Conventional submarines are the most common type of submarine and are used for a variety of purposes, including scientific research and exploration. They are typically smaller and less heavily armed than ballistic missile submarines and attack submarines, but are still capable of reaching speeds of up to 20 knots (37 km/h).Submarine Propulsion Systems
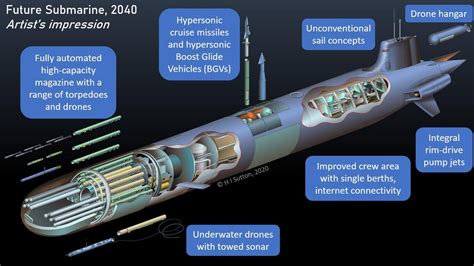
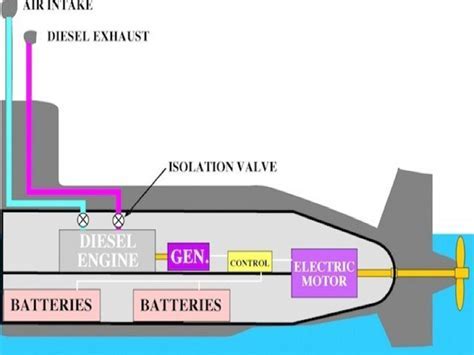
Submarines use a variety of propulsion systems, including diesel-electric, nuclear, and air-independent propulsion. Diesel-electric propulsion systems are the most common type of propulsion system used in submarines and involve the use of diesel engines to generate electricity, which is then used to power an electric motor. Nuclear propulsion systems, on the other hand, use a nuclear reactor to generate steam, which is then used to power a turbine. Air-independent propulsion systems use a variety of technologies, including fuel cells and closed-cycle diesel engines, to generate power without the need for air.
Diesel-Electric Propulsion
Diesel-electric propulsion systems are the most common type of propulsion system used in submarines. They involve the use of diesel engines to generate electricity, which is then used to power an electric motor. This type of propulsion system is relatively simple and inexpensive, but is limited by the need for air to operate the diesel engines.Nuclear Propulsion
Nuclear propulsion systems use a nuclear reactor to generate steam, which is then used to power a turbine. This type of propulsion system is more complex and expensive than diesel-electric propulsion, but offers a number of advantages, including a longer range and higher speed.Air-Independent Propulsion
Air-independent propulsion systems use a variety of technologies, including fuel cells and closed-cycle diesel engines, to generate power without the need for air. This type of propulsion system is relatively new and is still being developed, but offers a number of advantages, including a longer range and higher speed.Submarine Speed Records
Submarines have been setting speed records for decades, with the first recorded speed record being set in 1960 by the USS Triton, which reached a speed of 30 knots (56 km/h). Since then, a number of submarines have set new speed records, including the USS Albacore, which reached a speed of 33 knots (61 km/h) in 1965, and the USS Los Angeles, which reached a speed of 35 knots (65 km/h) in 1980.
Current Speed Records
The current speed record for a submarine is held by the USS Virginia, which reached a speed of 40 knots (74 km/h) in 2004. This record was set during a test run in the Atlantic Ocean and demonstrates the impressive speed and maneuverability of modern submarines.Future Developments
As technology continues to advance, it is likely that submarines will become even faster and more efficient. The development of new propulsion systems, such as advanced diesel-electric and air-independent propulsion, is expected to play a major role in this process. Additionally, the use of advanced materials and designs, such as stealth technology and streamlined hulls, is expected to further improve the speed and maneuverability of submarines.Gallery of Submarine Images
Submarine Image Gallery







Frequently Asked Questions
What is the fastest submarine in the world?
+The fastest submarine in the world is the USS Virginia, which has a top speed of over 40 knots (74 km/h).
What is the most common type of submarine propulsion system?
+The most common type of submarine propulsion system is the diesel-electric propulsion system, which uses diesel engines to generate electricity that powers an electric motor.
What is the purpose of a submarine's ballast tanks?
+The purpose of a submarine's ballast tanks is to control the submarine's buoyancy and depth by filling or emptying the tanks with water or air.
How do submarines communicate with the surface?
+Submarines communicate with the surface using a variety of methods, including radio communication, satellite communication, and acoustic communication.
What is the average length of a submarine?
+The average length of a submarine can vary greatly, depending on the type and purpose of the vessel. However, most submarines are between 100 and 300 meters (330 and 1,000 feet) in length.
In conclusion, the world of submarines is a fascinating and complex one, with a wide range of technologies and innovations that have enabled these vessels to operate at incredible speeds and depths. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that submarines will become even faster and more efficient, with new propulsion systems and materials being developed to improve their performance. Whether you are interested in the military, scientific, or recreational applications of submarines, there is no doubt that these incredible machines will continue to play a major role in our world for years to come. We hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of submarine speed and the fascinating world of underwater exploration. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more, please don't hesitate to comment or share this article with others.
