Intro
Discover 5 key German Invasion facts, exploring WWII history, Nazi occupation, and European resistance, revealing pivotal moments in military strategy and war tactics.
The German invasion, which occurred during World War II, was a pivotal event in modern history. Understanding the intricacies of this period can provide valuable insights into the complexities of war, international relations, and the human experience. The importance of exploring this topic lies in its ability to educate us about the past, helping us navigate the present and future with greater wisdom. By delving into the key facts surrounding the German invasion, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the sacrifices made, the strategies employed, and the impact on global politics.
The German invasion, particularly the invasion of Poland in 1939, marked the beginning of World War II, drawing in multiple countries and resulting in one of the deadliest conflicts in human history. The events leading up to and following the invasion are complex, involving political maneuvers, military strategies, and the profound effects on civilian populations. The study of these events is not only a tribute to those who lived through them but also a cautionary tale about the dangers of unchecked aggression and the importance of diplomacy.
As we explore the German invasion, it's essential to consider the broader context, including the political climate of the time, the role of key figures such as Adolf Hitler, and the responses of other nations to the aggression. This period in history is a rich tapestry of political, military, and social dynamics, offering lessons that can inform our understanding of international relations, conflict resolution, and the pursuit of peace. By examining the facts surrounding the German invasion, we can better comprehend the complexities of the past and apply these lessons to the challenges of the present.
Introduction to the German Invasion

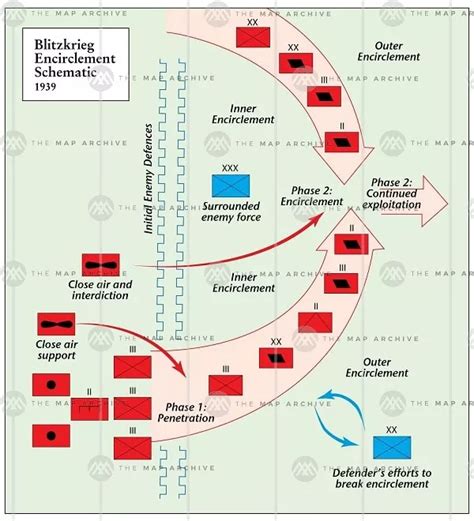
The German invasion refers to the military actions taken by Nazi Germany during World War II, starting with the invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. This act of aggression prompted the United Kingdom and France to declare war on Germany, marking the beginning of the conflict in Europe. The invasion was characterized by its swift and decisive nature, employing a new form of warfare known as the Blitzkrieg, or "lightning war," which combined air power, armor, and infantry to quickly overwhelm enemy defenses.
Key Players and Their Roles
The German invasion was orchestrated by Adolf Hitler, the leader of Nazi Germany, who had a vision for expanding German territory and establishing the country as a dominant world power. Hitler's aggressive foreign policy, coupled with his racist and nationalist ideologies, set the stage for the conflict. Other key players included Benito Mussolini of Italy, who allied with Hitler, and the leaders of the United Kingdom and France, who initially adopted a policy of appeasement before finally declaring war.The Blitzkrieg Strategy

The Blitzkrieg strategy was a crucial element of the German invasion, allowing for rapid advances into enemy territory. This strategy involved:
- Air Superiority: The use of air power to destroy enemy air forces and disrupt command and control structures.
- Armor: The deployment of tanks and other armored vehicles to break through enemy lines and exploit weaknesses.
- Infantry: The use of infantry to secure gains and hold territory.
This combination of forces enabled the German military to achieve significant victories in the early years of the war, including the invasion of Poland, Denmark, Norway, Belgium, the Netherlands, and France.
Impact on Civilian Populations
The German invasion had a profound impact on civilian populations, leading to widespread displacement, suffering, and loss of life. The invasion of Poland, for example, resulted in the deaths of millions of civilians, including the systematic persecution and murder of Jews and other minority groups. The use of Blitzkrieg tactics also led to significant destruction of infrastructure and cities, exacerbating the humanitarian crisis.Major Battles and Campaigns

Several major battles and campaigns marked the German invasion, including:
- The Battle of Poland: The initial invasion of Poland in September 1939.
- The Battle of Britain: The air campaign fought between the German Luftwaffe and the British Royal Air Force in the summer of 1940.
- The Invasion of the Soviet Union: Operation Barbarossa, launched in June 1941, which marked a significant turning point in the war as it opened up a vast new front for Germany.
These battles and campaigns highlight the expansive nature of the conflict and the significant challenges faced by the Axis powers as they sought to expand their territories.
Turning Points and Outcomes
The German invasion ultimately ended in defeat for Nazi Germany, with several turning points marking the shift in momentum. These included: - **The Battle of Stalingrad:** A major defeat for German forces in the Soviet Union, marking a significant turning point on the Eastern Front. - **The D-Day Invasion:** The Allied invasion of Normandy on June 6, 1944, which opened up a new front in Western Europe. - **The Soviet Advance:** The gradual push of Soviet forces towards Berlin, culminating in the capture of the city in April 1945.These events, along with the entry of the United States into the war following the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, contributed to the eventual defeat of Germany and the end of World War II in Europe.
Legacy of the German Invasion

The legacy of the German invasion is complex and far-reaching, involving:
- Reconstruction and Reconciliation: Efforts to rebuild and reconcile in the aftermath of the war.
- International Relations: The establishment of new international bodies and agreements aimed at preventing future conflicts.
- Historical Memory: The preservation of the history of the war and its impact, serving as a reminder of the dangers of aggression and the importance of peace.
Understanding this legacy is crucial for navigating the modern world, as it informs our approaches to conflict resolution, international cooperation, and the protection of human rights.
Lessons Learned
The study of the German invasion and World War II offers several key lessons, including: - **The Dangers of Unchecked Aggression:** The importance of addressing aggression early to prevent larger conflicts. - **The Value of Diplomacy:** The role of diplomacy in preventing and resolving conflicts. - **The Importance of Human Rights:** The need to protect human rights and prevent atrocities.These lessons are timeless, providing guidance for policymakers, diplomats, and individuals seeking to promote peace and stability in the world.
German Invasion Image Gallery









What were the main factors that led to the German invasion of Poland in 1939?
+The main factors included the policy of appeasement by the United Kingdom and France, the aggressive expansionist policies of Nazi Germany under Adolf Hitler, and the strategic importance of Poland in Central Europe.
How did the Blitzkrieg strategy contribute to the initial successes of the German invasion?
+The Blitzkrieg strategy, combining air power, armor, and infantry, allowed for rapid and decisive victories, enabling the German military to quickly overwhelm enemy defenses and achieve significant territorial gains in the early years of the war.
What were the significant turning points that led to the defeat of Nazi Germany?
+Key turning points included the Battle of Stalingrad, the D-Day invasion of Normandy, and the Soviet advance towards Berlin, which collectively marked a shift in momentum against Germany and ultimately led to its defeat.
In conclusion, the German invasion of World War II was a pivotal moment in history, marked by aggression, conflict, and profound human suffering. Understanding the complexities of this period, including the strategies employed, the key players involved, and the outcomes of the war, is essential for navigating the challenges of the modern world. By reflecting on the past, we can work towards a future characterized by peace, cooperation, and the protection of human rights. We invite readers to share their thoughts on the significance of this historical event and its relevance to contemporary international relations, and to explore further the many lessons that can be learned from this critical period in human history.
