Intro
Discover the 5 ways Active Reserve works, leveraging military training, part-time service, and reserve benefits to enhance career flexibility, skill development, and national security through reserve component, veteran support, and force readiness initiatives.
The concept of active reserve has gained significant attention in recent years, particularly in the context of military operations and disaster response. However, its application extends beyond these areas, and it can be a valuable strategy in various aspects of life. In this article, we will delve into the world of active reserve, exploring its importance, benefits, and working mechanisms. We will also discuss the steps to implement an active reserve system and provide practical examples to illustrate its effectiveness.
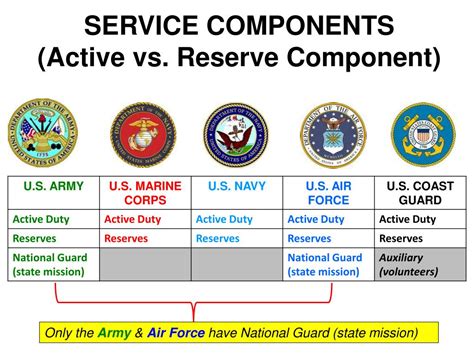
Active reserve refers to a pool of resources, including personnel, equipment, and facilities, that can be quickly mobilized to respond to emergencies, support ongoing operations, or enhance overall capabilities. The key characteristic of active reserve is its readiness to be deployed at short notice, allowing for rapid response and flexibility in the face of changing circumstances. This concept has far-reaching implications, from military and disaster response to business and personal development.
The importance of active reserve cannot be overstated. In today's fast-paced and unpredictable world, being able to respond quickly to emerging challenges is crucial for success. Whether it's a natural disaster, a cyber attack, or a sudden change in market conditions, having a robust active reserve in place can make all the difference. By maintaining a pool of readily available resources, organizations and individuals can reduce their vulnerability to unexpected events, minimize downtime, and gain a competitive edge.
Benefits of Active Reserve
The benefits of active reserve are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant advantages include:
- Enhanced responsiveness: Active reserve enables rapid response to emerging challenges, reducing the time it takes to mobilize resources and react to changing circumstances.
- Improved flexibility: By maintaining a pool of readily available resources, organizations and individuals can adapt quickly to shifting priorities and unexpected events.
- Increased efficiency: Active reserve can help reduce downtime, minimize waste, and optimize resource utilization, leading to significant cost savings and improved productivity.
- Better risk management: By having a robust active reserve in place, organizations and individuals can reduce their vulnerability to unexpected events, mitigate risks, and enhance their overall resilience.
Key Components of Active Reserve
The key components of active reserve include:- Personnel: Trained and experienced individuals who can be quickly mobilized to respond to emergencies or support ongoing operations.
- Equipment: Specialized gear and machinery that can be rapidly deployed to enhance capabilities or respond to emerging challenges.
- Facilities: Infrastructure and assets that can be quickly activated to support operations, provide shelter, or serve as a hub for response efforts.
- Systems and processes: Established protocols and procedures that enable rapid mobilization, coordination, and deployment of active reserve resources.
Working Mechanisms of Active Reserve

The working mechanisms of active reserve involve a combination of planning, preparation, and execution. Some of the key steps include:
- Identification of resources: Organizations and individuals must identify the resources they need to maintain in their active reserve, including personnel, equipment, facilities, and systems.
- Training and preparation: Active reserve resources must be trained and prepared to respond quickly and effectively to emerging challenges.
- Maintenance and upkeep: Active reserve resources must be regularly maintained and updated to ensure they remain functional and effective.
- Mobilization and deployment: Active reserve resources must be rapidly mobilized and deployed in response to emerging challenges or changing circumstances.
- Coordination and communication: Effective coordination and communication are critical to the successful deployment of active reserve resources, ensuring that all stakeholders are informed and aligned.
Steps to Implement Active Reserve
Implementing an active reserve system requires careful planning, preparation, and execution. Some of the key steps include:- Conducting a thorough risk assessment to identify potential challenges and emerging threats.
- Developing a comprehensive plan for active reserve, including the identification of resources, training, and maintenance.
- Establishing clear protocols and procedures for mobilization, deployment, and coordination.
- Conducting regular exercises and drills to test the effectiveness of the active reserve system.
- Continuously monitoring and evaluating the active reserve system, making adjustments as needed to ensure its effectiveness and relevance.
Practical Examples of Active Reserve
There are many practical examples of active reserve in action, across various domains and industries. Some notable examples include:
- Military reserve forces, which can be quickly mobilized to support ongoing operations or respond to emerging threats.
- Emergency response teams, which can be rapidly deployed to respond to natural disasters, accidents, or other emergencies.
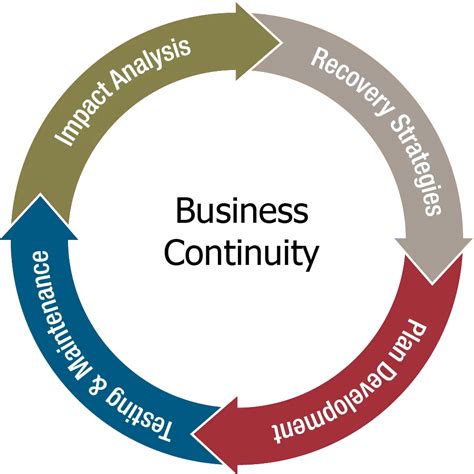
- Business continuity plans, which enable organizations to quickly respond to disruptions, minimize downtime, and maintain operations.
- Personal emergency funds, which provide individuals with a financial safety net to respond to unexpected expenses or income disruptions.
Challenges and Limitations of Active Reserve
While active reserve offers many benefits, there are also challenges and limitations to consider. Some of the key challenges include:- Maintaining readiness: Active reserve resources must be regularly maintained and updated to ensure they remain functional and effective.
- Managing costs: Maintaining an active reserve can be costly, requiring significant investments in resources, training, and equipment.
- Ensuring coordination: Effective coordination and communication are critical to the successful deployment of active reserve resources, requiring careful planning and execution.
- Addressing scalability: Active reserve systems must be scalable, able to adapt to changing circumstances and emerging challenges.
Best Practices for Active Reserve

To ensure the effectiveness of active reserve, it's essential to follow best practices, including:
- Regularly reviewing and updating the active reserve plan to ensure its relevance and effectiveness.
- Conducting thorough risk assessments to identify potential challenges and emerging threats.
- Providing ongoing training and preparation for active reserve resources.
- Establishing clear protocols and procedures for mobilization, deployment, and coordination.
- Continuously monitoring and evaluating the active reserve system, making adjustments as needed.
Future Directions for Active Reserve
As the world becomes increasingly complex and unpredictable, the importance of active reserve will only continue to grow. Some potential future directions for active reserve include:- Increased use of technology, such as artificial intelligence and automation, to enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of active reserve systems.
- Greater emphasis on sustainability and environmental considerations, ensuring that active reserve systems are environmentally friendly and sustainable.
- More focus on community-based active reserve systems, leveraging local resources and expertise to respond to emerging challenges.
- Greater integration of active reserve systems across domains and industries, enabling more effective coordination and collaboration.
Gallery of Active Reserve Images
Active Reserve Image Gallery








What is active reserve?
+Active reserve refers to a pool of resources, including personnel, equipment, and facilities, that can be quickly mobilized to respond to emergencies, support ongoing operations, or enhance overall capabilities.
What are the benefits of active reserve?
+The benefits of active reserve include enhanced responsiveness, improved flexibility, increased efficiency, and better risk management.
How can I implement an active reserve system?
+To implement an active reserve system, conduct a thorough risk assessment, develop a comprehensive plan, establish clear protocols and procedures, and provide ongoing training and preparation for active reserve resources.
What are some common challenges and limitations of active reserve?
+Some common challenges and limitations of active reserve include maintaining readiness, managing costs, ensuring coordination, and addressing scalability.
What are some best practices for active reserve?
+Some best practices for active reserve include regularly reviewing and updating the active reserve plan, conducting thorough risk assessments, providing ongoing training and preparation, and establishing clear protocols and procedures.
In conclusion, active reserve is a powerful strategy that can help organizations and individuals respond quickly and effectively to emerging challenges. By understanding the benefits, working mechanisms, and key components of active reserve, you can develop a robust system that enhances your responsiveness, flexibility, and overall resilience. Whether you're a business leader, a military commander, or an individual looking to enhance your personal preparedness, active reserve is an essential concept to explore and implement. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with active reserve, and to explore the many resources and examples available to help you get started.
