Intro
Discover the 5 key differences, highlighting crucial distinctions, comparisons, and contrasts, to make informed decisions with expert analysis and insights.
The world of technology and innovation is constantly evolving, and with it, the ways in which we approach various aspects of our lives. One area that has seen significant growth and development is the realm of digital tools and software. Among the numerous options available, two concepts have garnered considerable attention: open-source and proprietary solutions. Understanding the differences between these two is crucial for individuals and organizations looking to make informed decisions about the tools they use. In this article, we will delve into the 5 key differences between open-source and proprietary solutions, exploring their implications, benefits, and drawbacks.
As we navigate the complex landscape of digital technologies, it's essential to recognize the significance of choosing the right tools for our needs. The choice between open-source and proprietary solutions can have far-reaching consequences, affecting not only the functionality and cost of the tools but also the security, flexibility, and community support associated with them. By examining the core differences between these two types of solutions, we can better equip ourselves to make decisions that align with our goals, whether personal or professional.
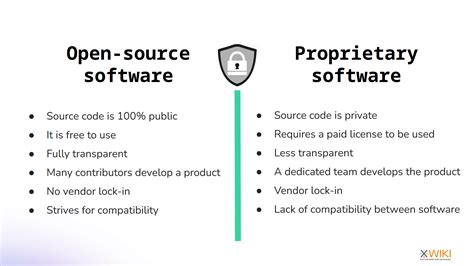
The distinction between open-source and proprietary solutions lies at the heart of how software is developed, distributed, and maintained. Open-source software is characterized by its transparent and collaborative approach, where the source code is freely available for anyone to view, modify, and distribute. This openness fosters a community-driven environment, encouraging contributions from a wide range of developers and users. On the other hand, proprietary software is owned and controlled by a single entity, which retains the rights to the source code and dictates how the software can be used and distributed. This fundamental difference in approach sets the stage for the various distinctions between open-source and proprietary solutions.
Introduction to Open-Source Solutions

Benefits of Open-Source Solutions
The benefits of open-source solutions are multifaceted, including lower costs, increased security, and the potential for community-driven innovation. By leveraging the collective expertise of a global community, open-source projects can address complex challenges and evolve more quickly than proprietary alternatives. Furthermore, the transparent nature of open-source software development can foster trust among users, as the code is openly available for review and audit. This transparency is particularly valuable in applications where security and reliability are paramount.Introduction to Proprietary Solutions
Benefits of Proprietary Solutions
Proprietary solutions offer several benefits, including professional technical support, comprehensive documentation, and a polished user interface designed to enhance user experience. Since proprietary software is developed with commercial objectives in mind, it often comes with dedicated customer support, which can be invaluable for businesses and individuals who require reliable assistance. Additionally, proprietary solutions are frequently designed with user-friendliness as a priority, making them accessible to a wide range of users, regardless of their technical expertise.Difference in Cost
Implications of Cost Difference
The difference in cost between open-source and proprietary solutions has significant implications for individuals and organizations. For those with limited budgets, open-source solutions can provide an affordable entry point into the world of digital tools. However, the cost savings of open-source software must be weighed against the potential need for specialized knowledge to customize and maintain the software. On the other hand, the higher cost of proprietary solutions is often offset by the provision of professional support and the assurance of compatibility and reliability.Difference in Customization and Flexibility

Importance of Customization
The ability to customize software is crucial in today's fast-paced technological landscape. As businesses and individuals seek to differentiate themselves and address specific challenges, the need for tailored solutions grows. Open-source solutions, with their inherent customizability, can provide a competitive edge by allowing for the creation of unique tools that precisely match user requirements. In contrast, the limitations on customization in proprietary software can sometimes hinder innovation and force users into a "one-size-fits-all" approach.Difference in Security

Security Considerations
When considering the security of open-source versus proprietary solutions, it's essential to weigh the risks and benefits. The transparent and community-driven nature of open-source software can lead to more secure solutions over time, as vulnerabilities are identified and addressed by a broad community of developers. On the other hand, proprietary solutions place the burden of security solely on the vendor, which can be both a blessing and a curse, depending on the vendor's capabilities and priorities.Difference in Community Support

Value of Community Support
The support provided by the community in open-source solutions and by vendors in proprietary solutions plays a crucial role in the user experience. For open-source software, community support can be a powerful resource, offering diverse perspectives and solutions. However, it may lack the consistency and reliability of professional support. Proprietary solutions, with their vendor-provided support, can offer a higher level of reliability and accountability, which is essential for mission-critical applications.Difference in Licensing and Ownership

Implications of Licensing and Ownership
The licensing and ownership models of open-source and proprietary solutions have profound implications for users. Open-source licensing promotes freedom and collaboration, allowing software to evolve rapidly and adapt to new needs. However, it can also lead to fragmentation and inconsistencies across different versions and implementations. Proprietary licensing, while restrictive, provides a clear legal framework and ensures that the software is maintained and updated by a single, accountable entity.Open-Source and Proprietary Solutions Image Gallery








What is the primary difference between open-source and proprietary solutions?
+The primary difference lies in the accessibility and modifiability of the source code, with open-source solutions being openly available for modification and distribution, and proprietary solutions having restricted access and use governed by a license agreement.
Which type of solution is more secure, open-source or proprietary?
+Security depends on various factors, including community involvement, vendor priorities, and the specific software in question. Open-source solutions benefit from community audits, while proprietary solutions rely on the vendor for security updates and patches.
Can open-source solutions be customized to meet specific needs?
+Yes, one of the key benefits of open-source solutions is their customizability. Users can modify the source code to add new features, fix bugs, or adapt the software to unique environments.
In conclusion, the choice between open-source and proprietary solutions depends on a variety of factors, including cost considerations, the need for customization, security requirements, and the importance of community versus professional support. By understanding the 5 key differences outlined in this article, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions that best align with their goals and needs. Whether the preference is for the collaborative, customizable nature of open-source solutions or the polished, professionally supported experience of proprietary solutions, recognizing the strengths and weaknesses of each can lead to more effective and satisfying outcomes. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with open-source and proprietary solutions, and to explore the vast array of options available in the world of digital technologies.
