Intro
Discover 5 ways medics get paid, including salary, benefits, and incentives, to understand medical compensation, physician pay, and healthcare revenue streams.
The medical field is one of the most respected and rewarding careers, with medics playing a crucial role in saving lives and improving healthcare outcomes. While the primary motivation for becoming a medic is often the desire to help others, it's also essential to consider the financial aspects of this profession. Medics, including doctors, nurses, and other healthcare professionals, can earn a good income through various payment methods. In this article, we will explore the different ways medics get paid, highlighting the benefits and challenges associated with each method.
Medics are essential members of the healthcare team, and their compensation reflects their importance. The payment methods for medics vary depending on factors such as their specialization, location, experience, and employer. Understanding these payment methods can help aspiring medics make informed decisions about their career paths and financial futures. Moreover, knowing how medics get paid can also help patients and healthcare organizations appreciate the value of these professionals and the importance of fair compensation.
The payment methods for medics have evolved over time, with some methods becoming more prevalent than others. For instance, the traditional fee-for-service model is still widely used, but value-based payment models are gaining popularity. These changes reflect the shifting landscape of the healthcare industry, with a growing emphasis on quality, affordability, and patient satisfaction. As the healthcare system continues to evolve, it's likely that the payment methods for medics will also change, with a focus on rewarding high-quality care and improving health outcomes.
Introduction to Medic Payment Methods

Fee-for-Service Payment Method
The fee-for-service payment method is one of the most common ways medics get paid. In this model, medics charge patients or their insurance providers a fee for each service provided, such as consultations, procedures, or treatments. The fee-for-service model is widely used in primary care, specialty care, and hospital settings. Medics who work in private practices or are self-employed often use this payment method, as it allows them to charge patients directly for their services.Salary Payment Method

Value-Based Payment Method
The value-based payment method is a relatively new approach to paying medics. In this model, medics receive payment based on the quality and value of care they provide, rather than the volume of services. The value-based payment method is designed to incentivize medics to provide high-quality, cost-effective care that improves patient outcomes. This payment method is gaining popularity, particularly in the United States, where healthcare organizations are seeking to reduce costs and improve quality.Contract Payment Method

Bonus Payment Method
The bonus payment method is used by some healthcare organizations to incentivize medics to provide high-quality care. In this model, medics receive bonuses or incentives for meeting specific performance targets, such as improving patient satisfaction or reducing hospital readmissions. The bonus payment method can be used in conjunction with other payment methods, such as salary or fee-for-service.Benefits and Challenges of Medic Payment Methods

Key Considerations for Medics
When considering payment methods, medics must think about several key factors, including their financial goals, practice settings, and patient needs. Medics must also stay up-to-date with changes in the healthcare industry, including shifts in payment policies and reimbursement rates. By understanding the different payment methods and their benefits and challenges, medics can make informed decisions about their careers and financial futures.Conclusion and Future Directions
Final Thoughts
Medics play a vital role in the healthcare system, and their compensation reflects their importance. By understanding the different payment methods and their benefits and challenges, medics can make informed decisions about their careers and financial futures. As the healthcare industry continues to shift towards value-based care, it's essential for medics to stay up-to-date with changes in payment policies and reimbursement rates.Medic Payment Methods Image Gallery

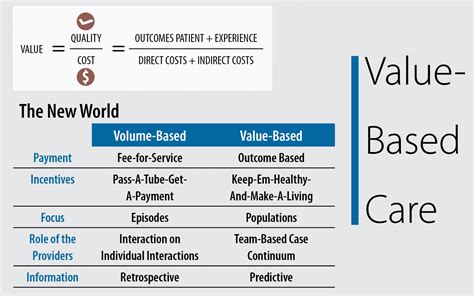

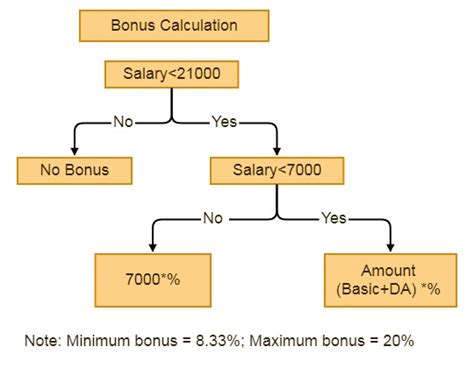





What are the different payment methods for medics?
+The different payment methods for medics include fee-for-service, salary, value-based payment, contract payment, and bonus payment.
What is the fee-for-service payment method?
+The fee-for-service payment method is a payment model in which medics charge patients or their insurance providers a fee for each service provided.
What is the value-based payment method?
+The value-based payment method is a payment model in which medics receive payment based on the quality and value of care they provide, rather than the volume of services.
What are the benefits and challenges of the different payment methods for medics?
+The benefits and challenges of the different payment methods for medics vary, but generally include factors such as autonomy, flexibility, and financial stability, as well as administrative burdens and challenges in measuring quality.
How do medics choose a payment method?
+Medics choose a payment method based on factors such as their financial goals, practice settings, and patient needs, as well as their personal preferences and values.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the different ways medics get paid. Whether you're a medic, a patient, or simply interested in the healthcare industry, understanding these payment methods can help you navigate the complex healthcare system and make informed decisions about your care and career. If you have any further questions or comments, please don't hesitate to reach out. Share this article with others who may be interested, and let's continue the conversation about the importance of fair compensation for medics and high-quality care for patients.
