Intro
Discover the comprehensive Army Officer Job List, featuring military careers, officer ranks, and specialties, including combat, logistics, and medical roles, to help you navigate army occupations and find your ideal military job.
The role of an army officer is multifaceted and demanding, requiring a unique blend of leadership, strategic thinking, and physical courage. Army officers are responsible for leading and managing teams of soldiers, making critical decisions in high-pressure situations, and executing complex military operations. With a wide range of specialties and career paths to choose from, army officers can pursue a variety of challenging and rewarding roles.
From combat and tactical operations to logistics and administration, army officers play a vital role in ensuring the effectiveness and efficiency of military operations. They must possess strong communication and interpersonal skills, as well as the ability to adapt to changing circumstances and make sound decisions under pressure. Whether serving in a combat zone or supporting military operations from behind the scenes, army officers are essential to the success of modern military forces.
With the increasing complexity of modern warfare and the evolving nature of global threats, the role of the army officer is more critical than ever. As military forces continue to adapt and evolve, army officers must be prepared to lead and manage teams in a rapidly changing environment, leveraging advanced technologies and innovative strategies to achieve strategic objectives. From special operations and counterterrorism to cybersecurity and intelligence, the career paths available to army officers are diverse and exciting, offering opportunities for professional growth, personal development, and service to one's country.
Army Officer Job List

The following is a list of some of the most common army officer jobs, including their responsibilities and requirements:
- Infantry Officer: Leads and manages infantry units, responsible for combat operations and tactical planning.
- Armor Officer: Commands and controls armor units, specializing in tank operations and mechanized warfare.
- Artillery Officer: Directs and coordinates artillery operations, including fire support and logistics planning.
- Engineer Officer: Oversees engineering projects and operations, including construction, demolition, and infrastructure development.
- Signal Officer: Manages communication systems and networks, ensuring secure and reliable communication for military operations.
- Intelligence Officer: Analyzes and interprets intelligence data, providing critical insights and recommendations to support military decision-making.
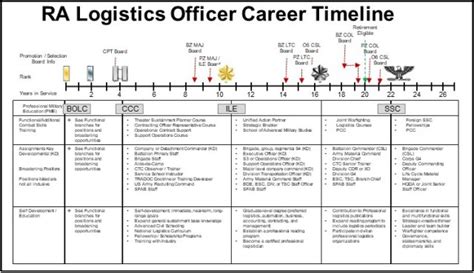
- Logistics Officer: Coordinates and manages supply chain operations, including procurement, transportation, and maintenance.
- Medical Officer: Provides medical care and support to military personnel, including emergency medicine, surgery, and preventive care.
- Military Police Officer: Maintains law and order, providing security and support for military operations and installations.
Combat Arms Jobs

Combat arms jobs are some of the most demanding and challenging roles in the army, requiring a high level of physical fitness, tactical expertise, and leadership ability. Some examples of combat arms jobs include:
- Infantry Officer: Leads and manages infantry units, responsible for combat operations and tactical planning.
- Armor Officer: Commands and controls armor units, specializing in tank operations and mechanized warfare.
- Artillery Officer: Directs and coordinates artillery operations, including fire support and logistics planning.
- Special Forces Officer: Leads and manages special forces units, specializing in unconventional warfare, counterterrorism, and direct action.
- Ranger Officer: Commands and controls ranger units, specializing in airborne operations, special reconnaissance, and direct action.
Combat Support Jobs

Combat support jobs provide critical support to combat arms units, ensuring the success and effectiveness of military operations. Some examples of combat support jobs include:
- Engineer Officer: Oversees engineering projects and operations, including construction, demolition, and infrastructure development.
- Signal Officer: Manages communication systems and networks, ensuring secure and reliable communication for military operations.
- Intelligence Officer: Analyzes and interprets intelligence data, providing critical insights and recommendations to support military decision-making.
- Logistics Officer: Coordinates and manages supply chain operations, including procurement, transportation, and maintenance.
- Military Police Officer: Maintains law and order, providing security and support for military operations and installations.
Combat Service Support Jobs
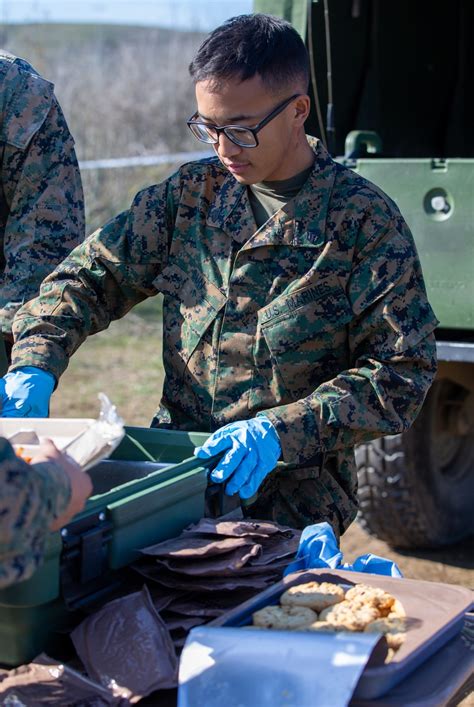

Combat service support jobs provide essential services and support to military personnel, ensuring their health, well-being, and effectiveness. Some examples of combat service support jobs include:
- Medical Officer: Provides medical care and support to military personnel, including emergency medicine, surgery, and preventive care.
- Chaplain: Provides spiritual support and guidance to military personnel, including counseling, worship services, and pastoral care.
- Adjutant General Officer: Manages personnel operations, including recruitment, training, and personnel management.
- Finance Officer: Manages financial operations, including budgeting, accounting, and financial planning.
- Judge Advocate General Officer: Provides legal support and advice to military personnel, including military justice, contracts, and administrative law.
Army Officer Ranks
Army officers are organized into a hierarchical structure, with each rank representing a level of authority, responsibility, and expertise. The following are the main army officer ranks, from lowest to highest: * Second Lieutenant (2LT): The entry-level rank for army officers, typically serving as platoon leaders or executive officers. * First Lieutenant (1LT): A junior officer rank, typically serving as platoon leaders or company executive officers. * Captain (CPT): A company-level rank, typically serving as company commanders or staff officers. * Major (MAJ): A field-grade rank, typically serving as battalion executive officers or staff officers. * Lieutenant Colonel (LTC): A senior field-grade rank, typically serving as battalion commanders or staff officers. * Colonel (COL): A senior officer rank, typically serving as brigade commanders or staff officers. * Brigadier General (BG): A one-star general officer rank, typically serving as brigade commanders or division staff officers. * Major General (MG): A two-star general officer rank, typically serving as division commanders or corps staff officers. * Lieutenant General (LTG): A three-star general officer rank, typically serving as corps commanders or army staff officers. * General (GEN): A four-star general officer rank, typically serving as army commanders or joint staff officers.Army Officer Image Gallery









What are the different types of army officer jobs?
+There are several types of army officer jobs, including combat arms, combat support, and combat service support. Combat arms jobs include infantry, armor, and artillery, while combat support jobs include engineering, signal, and intelligence. Combat service support jobs include medical, chaplain, and adjutant general.
What are the requirements to become an army officer?
+To become an army officer, one must meet certain requirements, including being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 35, and having a high school diploma or equivalent. Additionally, one must score well on the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test and complete Officer Candidate School (OCS) or the United States Military Academy (USMA).
What is the career path for an army officer?
+The career path for an army officer typically begins with commissioning as a second lieutenant, followed by promotion to first lieutenant, captain, and major. With experience and advanced education, one can be promoted to lieutenant colonel, colonel, and eventually general officer ranks. Army officers can also pursue specialized career paths, such as special forces, aviation, or cyber operations.
In conclusion, the role of an army officer is complex and demanding, requiring a unique blend of leadership, strategic thinking, and physical courage. With a wide range of specialties and career paths to choose from, army officers can pursue a variety of challenging and rewarding roles, from combat arms and combat support to combat service support and specialized fields. Whether serving in a combat zone or supporting military operations from behind the scenes, army officers are essential to the success of modern military forces. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences about army officer jobs, and to explore the many opportunities available to those who serve in this critical and rewarding profession.
