Intro
Discover the ultimate Wastewater Treatment Plant Operator Guide, covering water management, sewage systems, and effluent treatment, to ensure efficient wastewater processing and environmental sustainability.
The role of a wastewater treatment plant operator is crucial in maintaining the health and safety of both the environment and the community. These operators are responsible for ensuring that wastewater is treated and discharged in a manner that meets regulatory standards, protecting waterways and public health. The importance of their work cannot be overstated, as improper treatment can lead to environmental degradation and health hazards. As the global population grows, the demand for clean water increases, making the efficient operation of wastewater treatment plants more critical than ever.
The process of treating wastewater involves a series of physical, chemical, and biological processes designed to remove contaminants and pollutants. Operators must have a deep understanding of these processes, as well as the equipment and technology used in treatment plants. This knowledge enables them to troubleshoot issues, optimize treatment processes, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Moreover, the work of wastewater treatment plant operators is not limited to the technical aspects of treatment; they also play a key role in maintaining the plant's infrastructure, managing resources, and collaborating with other professionals in the field.
The complexity and importance of wastewater treatment plant operations underscore the need for comprehensive guidance and training for operators. This includes not only the technical aspects of wastewater treatment but also best practices in plant management, safety protocols, and environmental regulations. By equipping operators with the knowledge and skills necessary to perform their duties effectively, we can ensure that wastewater treatment plants operate efficiently, safely, and in compliance with regulatory standards. This, in turn, protects public health, preserves the environment, and supports sustainable development.
Introduction to Wastewater Treatment
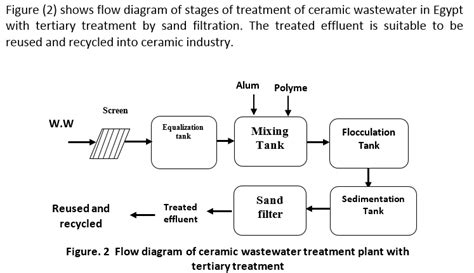
Wastewater treatment is a multi-step process that removes physical, chemical, and biological contaminants from wastewater. The primary goal of wastewater treatment is to produce an effluent that can be safely discharged into the environment without harming aquatic life or human health. The treatment process typically involves preliminary treatment, primary treatment, secondary treatment, and sometimes advanced or tertiary treatment, depending on the quality of the effluent required.
Preliminary Treatment
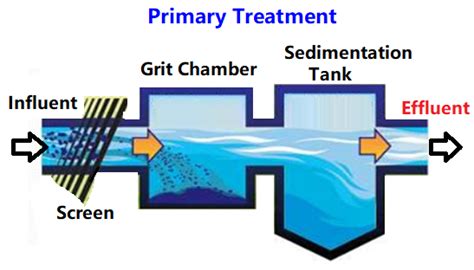
Preliminary treatment is the first step in the wastewater treatment process. It involves the removal of large objects and debris that could damage equipment or interfere with the treatment process. This is typically achieved through the use of screens and grit chambers. Screens catch large objects like sticks and rags, while grit chambers remove sand and other abrasive materials that could wear down equipment.Primary Treatment
Primary treatment follows preliminary treatment and involves the removal of suspended solids and organic matter from the wastewater. This is typically achieved through physical processes such as sedimentation and flotation. In sedimentation basins, also known as clarifiers, the wastewater is held for a period, allowing the heavier solids to settle to the bottom and the lighter materials to float to the surface. The settled solids, known as sludge, are removed and further treated, while the floating materials, such as grease and oils, are skimmed off.Secondary Treatment
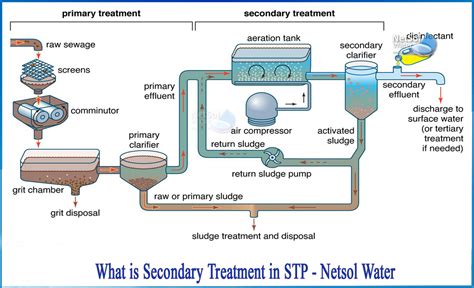
Secondary treatment is designed to remove the organic matter that was not removed during primary treatment. This is typically achieved through biological processes, where microorganisms break down the organic matter. The most common methods of secondary treatment are the activated sludge process, trickling filters, and rotating biological contactors. In the activated sludge process, for example, wastewater is mixed with a population of microorganisms, known as activated sludge, which breaks down the organic matter. The mixture is then held in a tank for a period, allowing the microorganisms to grow and consume the organic matter.
Advanced Treatment
Advanced or tertiary treatment is used to further improve the quality of the effluent, typically to meet specific regulatory requirements or to reuse the water for non-potable purposes such as irrigation or toilet flushing. Advanced treatment processes can include chemical treatment, filtration, and disinfection. Chemical treatment involves the addition of chemicals to remove specific contaminants, such as phosphorus or nitrogen. Filtration, often using sand or membrane filters, can remove remaining suspended solids, while disinfection, typically using chlorine or ultraviolet light, is used to kill any remaining pathogens.Wastewater Treatment Plant Operations

The operation of a wastewater treatment plant involves a range of activities, from monitoring and controlling the treatment processes to maintaining equipment and ensuring regulatory compliance. Operators must be able to analyze data from various sources, including laboratory tests and monitoring equipment, to assess the performance of the treatment processes and make adjustments as necessary. This might involve changing chemical dosages, adjusting flow rates, or identifying and resolving issues with equipment.
Plant Maintenance
Regular maintenance is critical to the efficient and effective operation of a wastewater treatment plant. This includes routine checks and repairs of equipment, replacement of worn-out parts, and preventive maintenance to avoid breakdowns. Operators must also ensure that the plant's infrastructure, including buildings, roads, and utilities, is well-maintained. Effective maintenance not only extends the life of equipment and reduces operational costs but also helps in preventing failures that could lead to environmental hazards and regulatory non-compliance.Regulatory Compliance and Safety

Wastewater treatment plant operators must ensure that their operations comply with all relevant regulations and standards. This includes meeting effluent quality standards, adhering to operational permits, and implementing safety protocols to protect workers and the public. Regulatory requirements can vary significantly depending on the location and type of treatment plant, making it essential for operators to stay updated on current laws, regulations, and best practices.
Safety Protocols
Safety is a paramount concern in wastewater treatment plant operations. Operators are exposed to a range of hazards, including toxic gases, hazardous chemicals, and the risk of infection from pathogens. Implementing robust safety protocols is essential to mitigate these risks. This includes providing personal protective equipment (PPE), conducting regular safety training, and ensuring that all operations are carried out in accordance with safety procedures. Emergency response plans should also be in place to address potential accidents or spills.Best Practices in Wastewater Treatment

Adopting best practices in wastewater treatment is crucial for optimizing plant operations, ensuring regulatory compliance, and protecting the environment. This includes implementing energy-efficient technologies, minimizing waste production, and promoting water conservation. Operators should also engage in continuous learning, staying abreast of the latest technologies and management strategies to improve plant performance.
Energy Efficiency
Wastewater treatment is an energy-intensive process, making energy efficiency a key consideration for plant operators. Implementing energy-efficient technologies and practices can significantly reduce operational costs and minimize the plant's carbon footprint. This might include the use of biogas generators, which convert wastewater sludge into energy, or the implementation of more efficient aeration systems in biological treatment processes.Gallery of Wastewater Treatment Processes
Wastewater Treatment Image Gallery








Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary goal of wastewater treatment?
+The primary goal of wastewater treatment is to remove contaminants from wastewater, producing an effluent that can be safely discharged into the environment without harming aquatic life or human health.
What are the main steps in the wastewater treatment process?
+The main steps include preliminary treatment to remove large objects and debris, primary treatment to remove suspended solids and organic matter, secondary treatment to remove remaining organic matter through biological processes, and sometimes advanced or tertiary treatment for further purification.
Why is regulatory compliance important in wastewater treatment?
+Regulatory compliance is crucial to ensure that wastewater is treated and discharged in a manner that protects public health and the environment. Non-compliance can result in legal penalties, environmental damage, and health risks.
How can wastewater treatment plants reduce their environmental impact?
+Wastewater treatment plants can reduce their environmental impact by implementing energy-efficient technologies, minimizing waste production, promoting water conservation, and adopting sustainable practices in their operations.
What role do operators play in wastewater treatment plant operations?
+Operators play a critical role in ensuring the efficient and safe operation of wastewater treatment plants. They are responsible for monitoring and controlling treatment processes, maintaining equipment, ensuring regulatory compliance, and implementing safety protocols.
In conclusion, the role of wastewater treatment plant operators is multifaceted and critical to protecting public health and the environment. By understanding the wastewater treatment process, adopting best practices, and ensuring regulatory compliance, operators can optimize plant operations and contribute to sustainable development. As the world continues to face challenges related to water scarcity and environmental protection, the importance of efficient and effective wastewater treatment will only continue to grow. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences on the importance of wastewater treatment and the role of operators in this process, and to explore further the many resources available for those interested in learning more about this vital field.

