Intro
Discover how age impacts financial reserves, including retirement savings, emergency funds, and investment strategies, affecting long-term wealth and financial security.
As people age, their bodies undergo a series of changes that can impact their physical and mental health. One often overlooked aspect of aging is its effect on reserves, including financial, emotional, and physical reserves. Understanding how age affects these reserves is crucial for maintaining overall well-being and quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the five ways age affects reserves, exploring the benefits, working mechanisms, and key information related to this topic.
Aging is a natural process that affects everyone, and its impact on reserves can be significant. As people grow older, they may experience a decline in their physical health, emotional stability, and financial security. This can lead to a decrease in their overall reserves, making it challenging to cope with life's challenges. However, by understanding the effects of aging on reserves, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain and even increase their reserves, ensuring a more comfortable and secure life.
The importance of reserves cannot be overstated. Reserves provide a safety net, allowing individuals to navigate life's uncertainties with confidence. Whether it's a financial emergency, a health crisis, or an emotional setback, having sufficient reserves can make all the difference. As people age, their reserves can be depleted, leaving them vulnerable to stress, anxiety, and other negative consequences. By recognizing the impact of aging on reserves, individuals can take measures to mitigate these effects and maintain their overall well-being.
Physical Reserves

To maintain physical reserves, older adults can engage in regular exercise, such as walking, swimming, or yoga. These activities can help improve mobility, balance, and flexibility, reducing the risk of falls and other age-related health issues. Additionally, a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide essential nutrients for maintaining physical health. By prioritizing physical activity and healthy eating, individuals can help preserve their physical reserves and maintain their independence as they age.
Emotional Reserves

To maintain emotional reserves, older adults can engage in activities that promote social connection, such as volunteering, joining a club or organization, or participating in group therapy. These activities can help reduce feelings of loneliness and isolation, improving emotional well-being. Additionally, practices like meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness can help manage stress and anxiety, preserving emotional reserves. By prioritizing social connection and stress management, individuals can help maintain their emotional reserves and overall mental health as they age.
Financial Reserves

To maintain financial reserves, older adults can prioritize saving and investing, creating a sustainable income stream for retirement. They can also explore ways to reduce expenses, such as downsizing their living situation or negotiating with service providers. Additionally, seeking professional advice from a financial advisor can help individuals create a personalized plan for maintaining their financial reserves and achieving their long-term goals. By prioritizing financial planning and management, individuals can help preserve their financial reserves and maintain their standard of living as they age.
Cognitive Reserves
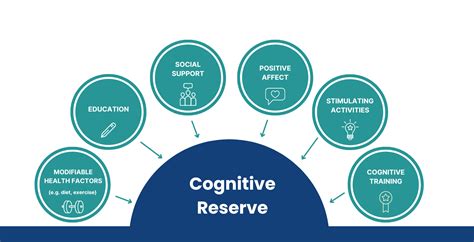
To maintain cognitive reserves, older adults can engage in activities that challenge their minds, such as learning a new language, playing musical instruments, or participating in strategy games. These activities can help build cognitive reserve, reducing the risk of age-related cognitive decline. Additionally, practices like meditation, mindfulness, and yoga can help improve cognitive function, promoting overall brain health. By prioritizing cognitive stimulation and mental wellness, individuals can help preserve their cognitive reserves and maintain their mental abilities as they age.
Social Reserves

To maintain social reserves, older adults can prioritize social engagement, participating in activities that promote social connection, such as volunteering, joining a club or organization, or attending community events. These activities can help reduce feelings of loneliness and isolation, improving social well-being. Additionally, technologies like video conferencing, social media, and messaging apps can help individuals stay connected with friends and family, maintaining social reserves. By prioritizing social connection and community engagement, individuals can help preserve their social reserves and overall well-being as they age.
Reserves Image Gallery










What are the key factors that affect reserves as we age?
+The key factors that affect reserves as we age include physical health, emotional well-being, financial security, cognitive function, and social connections.
How can I maintain my physical reserves as I age?
+You can maintain your physical reserves by engaging in regular exercise, eating a healthy diet, and getting enough sleep.
What are some strategies for building cognitive reserves?
+Strategies for building cognitive reserves include engaging in cognitively stimulating activities, such as reading, puzzles, and learning new skills, as well as practicing mindfulness and meditation.
How can I maintain my social reserves as I age?
+You can maintain your social reserves by prioritizing social engagement, participating in activities that promote social connection, and staying connected with friends and family through technology.
What are some common challenges that can impact reserves as we age?
+Common challenges that can impact reserves as we age include chronic health conditions, social isolation, financial insecurity, and cognitive decline.
In conclusion, aging can have a significant impact on reserves, including physical, emotional, financial, cognitive, and social reserves. By understanding the effects of aging on these reserves, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain and even increase their reserves, ensuring a more comfortable and secure life. Whether it's prioritizing physical activity, emotional wellness, financial planning, cognitive stimulation, or social connection, there are many strategies that can help individuals build and maintain their reserves as they age. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on this topic, and to explore the resources and strategies outlined in this article to help you maintain your reserves and thrive as you age.
