Intro
Irans geopolitical tensions spark WW3 fears, driven by nuclear threats, Middle East conflicts, and global alliances, escalating into a potentially catastrophic war scenario.
The prospect of a third world war is a daunting one, and various global events and tensions have led to speculation about the potential sparks that could ignite such a conflict. Iran, with its complex geopolitical position and often tense relationships with other nations, is frequently mentioned in discussions about potential flashpoints for global conflict. Understanding the reasons behind this involves examining Iran's role in regional and global politics, its military capabilities, and the diplomatic tensions it faces, especially with Western countries and its neighbors.
Iran's position in the Middle East, its nuclear program, support for militia groups, disputes over territorial waters, and the impact of economic sanctions all contribute to the complex web of tensions that could potentially escalate into a wider conflict. The country's strategic importance, both geographically and in terms of energy resources, means that any significant conflict involving Iran could have far-reaching consequences.
The international community, including the United Nations, the European Union, and various countries, has been involved in diplomatic efforts to address these issues, aiming to prevent escalation and promote peace and stability in the region. However, the path forward is fraught with challenges, and the risk of miscalculation or unforeseen events leading to conflict remains.
In recent years, the situation has been further complicated by shifts in global politics, changes in leadership in key countries, and the ongoing impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on international relations and economies. As the world navigates these challenges, understanding the specific ways in which Iran could potentially spark a wider conflict is crucial for policymakers, scholars, and the general public alike.
Introduction to the Geopolitical Landscape
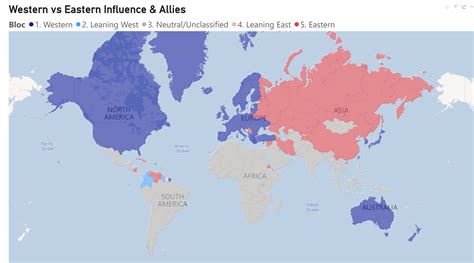
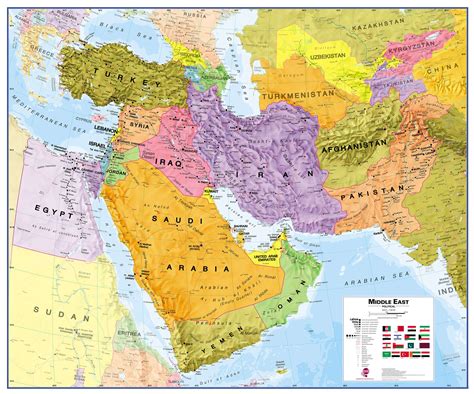
The geopolitical landscape surrounding Iran is complex and multifaceted. The country is located in a critical region, bordering several important countries and bodies of water, including the Persian Gulf and the Caspian Sea. This strategic location makes Iran a key player in regional and global energy markets, as well as a crucial actor in Middle Eastern politics.
Iran's relations with its neighbors and with global powers are influenced by a variety of factors, including historical grievances, religious and ethnic affiliations, and competition for resources and influence. The country's Islamic Revolution in 1979 marked a significant turning point in its relations with the West, particularly the United States, and has since been a point of contention in international relations.
Nuclear Program and International Tensions
One of the most significant sources of tension involving Iran is its nuclear program. The program, which Iran claims is for peaceful purposes such as energy production and medical research, has been the subject of intense international scrutiny and concern. Many countries, particularly in the West, fear that Iran's ultimate goal is to develop nuclear weapons, which would significantly alter the balance of power in the Middle East and pose a direct threat to regional and global security.
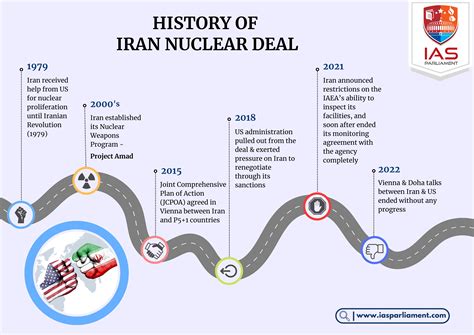
The Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), also known as the Iran nuclear deal, was negotiated in 2015 between Iran, the United States, the United Kingdom, Russia, France, China, and Germany. The agreement placed limits on Iran's nuclear program in exchange for relief from economic sanctions. However, the deal's future has been uncertain since the United States withdrew from it in 2018 and reimposed sanctions on Iran, leading to a significant escalation of tensions between the two countries.
Support for Militia Groups

Iran's support for various militia groups and proxies across the Middle East is another factor contributing to regional instability and international concern. These groups, which operate in countries such as Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, and Yemen, are seen as extensions of Iranian influence and are often involved in conflicts that align with Iran's strategic interests.
The support provided by Iran to these groups includes military training, financial backing, and the supply of weapons, which has been documented in various reports and analyses. This proxy warfare allows Iran to exert influence beyond its borders without directly engaging in conflicts, although it also contributes to the destabilization of the region and the exacerbation of sectarian tensions.
Disputes Over Territorial Waters
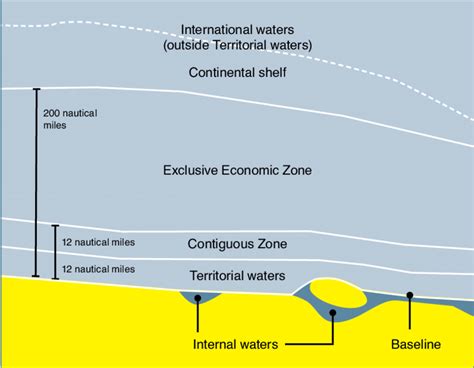
Disputes over territorial waters, particularly in the Strait of Hormuz, are a significant point of contention involving Iran. The Strait of Hormuz is a critical waterway through which a substantial portion of the world's oil passes, making it a vital chokepoint for global energy supplies.
Iran has periodically threatened to close the Strait of Hormuz in response to sanctions or military threats, which would have profound implications for global oil markets and could lead to a significant escalation of conflict. The United States and other countries have pledged to keep the waterway open, setting the stage for potential naval confrontations.
Economic Sanctions and Their Impact

Economic sanctions imposed on Iran by the United States and other countries have had a profound impact on the Iranian economy and the livelihoods of its citizens. These sanctions, which target various sectors including oil exports, banking, and trade, are designed to pressure Iran into changing its behavior on issues such as its nuclear program and support for militia groups.
However, sanctions also have humanitarian consequences, affecting the availability of food, medicine, and other essential goods. The economic hardship caused by sanctions can increase internal tensions within Iran and potentially destabilize the region further, as countries and factions vie for influence and resources.
Steps Towards De-escalation
To mitigate the risks of conflict and work towards a more stable and peaceful region, several steps can be taken: - Diplomatic Engagement: Encouraging dialogue between Iran and other countries, particularly the United States, to address areas of contention and work towards mutually beneficial agreements. - Economic Incentives: Offering economic incentives for Iran to comply with international demands, such as lifting sanctions in exchange for verifiable changes in behavior. - Regional Security Initiatives: Promoting regional security initiatives that involve all stakeholders, aiming to reduce tensions and prevent miscalculations that could lead to conflict.Iran and Global Politics Image Gallery






What are the main issues causing tension between Iran and the West?
+The main issues include Iran's nuclear program, its support for militia groups in the Middle East, disputes over territorial waters, and the impact of economic sanctions.
How does Iran's location contribute to its geopolitical importance?
+Iran's strategic location near critical waterways and its position in the Middle East make it a key player in regional and global energy markets, as well as a crucial actor in Middle Eastern politics.
What are the potential consequences of a conflict involving Iran?
+The potential consequences include a significant disruption to global oil supplies, escalation of regional conflicts, and the potential for the conflict to draw in other global powers, leading to a wider war.
As the situation involving Iran continues to evolve, it's essential for the international community to remain vigilant and committed to finding peaceful solutions to the challenges posed by Iran's actions. Through diplomatic engagement, economic incentives, and a focus on regional stability, it may be possible to mitigate the risks of conflict and work towards a more peaceful and secure future for all nations involved. We invite readers to share their thoughts and insights on this critical issue, and we hope that this discussion can contribute to a deeper understanding of the complexities at play and the paths forward that prioritize peace, stability, and cooperation.
