Intro
The importance of naval warfare during World War I cannot be overstated. The war at sea played a crucial role in the ultimate outcome of the conflict, with various types of ships contributing to the efforts of the Allied and Central Powers. Among these, destroyers emerged as a key component of naval fleets, providing a unique combination of speed, maneuverability, and firepower. The development and deployment of World War I destroyers not only reflected the technological advancements of the time but also significantly influenced the nature of naval combat.
As the war began, the major naval powers, including Britain, Germany, and the United States, found themselves in a race to build and deploy the most advanced destroyers. These ships were designed to perform a variety of tasks, from escorting convoys and capital ships to engaging in torpedo attacks against enemy vessels. The versatility of destroyers made them invaluable assets, capable of operating in both offensive and defensive roles. Their ability to swiftly respond to changing battlefield conditions and their capacity to inflict significant damage with their torpedoes and guns made them a critical component of naval strategy.
The evolution of destroyer design during World War I was marked by significant improvements in speed, armament, and endurance. Early destroyers were relatively small, lightly armed, and prone to instability in rough seas. However, as the war progressed, newer classes of destroyers were built with larger displacements, more powerful engines, and enhanced armament, including the introduction of depth charges for anti-submarine warfare. These advancements were driven by the lessons learned from early naval engagements and the need to counter the growing threat of German U-boats, which were wreaking havoc on Allied shipping.
Development of World War I Destroyers

The development of World War I destroyers was a complex process, involving the integration of new technologies and the adaptation of existing designs to meet the changing demands of naval warfare. Shipbuilders and naval architects worked tirelessly to improve the performance and capabilities of destroyers, often drawing upon lessons learned from actual combat experiences. The introduction of new materials, such as steel, and the development of more efficient propulsion systems allowed for the construction of larger, faster, and more heavily armed destroyers.
Key Features of World War I Destroyers
Some of the key features of World War I destroyers included their high speed, which often exceeded 30 knots, making them among the fastest ships at sea. Their armament typically consisted of guns, ranging from 3-inch to 4.7-inch calibers, and torpedo tubes, usually 18-inch or 21-inch. The crew sizes varied but were generally around 80 to 100 sailors, who had to be highly trained to manage the complex systems and weaponry of these ships. Destroyers also played a crucial role in anti-submarine warfare, equipped with depth charges and, later in the war, hydrophones for detecting submarines.Tactical Roles of Destroyers in World War I
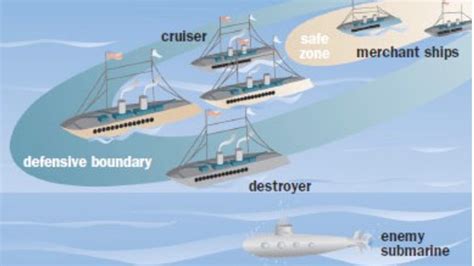
Destroyers in World War I fulfilled a variety of tactical roles, reflecting their versatility and the evolving nature of naval warfare. Initially, they were used primarily for offensive operations, such as torpedo attacks against capital ships and raids on enemy ports. However, as the war progressed and the threat from German U-boats increased, destroyers found themselves increasingly engaged in defensive tasks, such as escorting convoys and patrols aimed at detecting and destroying enemy submarines.
Convoy Escort and Anti-Submarine Warfare
The role of destroyers in convoy escort and anti-submarine warfare became particularly critical as the war entered its later stages. The introduction of the convoy system, where merchant ships were grouped together and escorted by warships, significantly reduced the losses to U-boat attacks. Destroyers, with their speed and maneuverability, were ideal for this role, able to quickly respond to submarine threats and protect the slower and more vulnerable merchant vessels.Notable Destroyer Classes of World War I

Several destroyer classes from World War I are notable for their design innovations, operational performance, or the significant roles they played in key naval battles. The British Tribal-class destroyers, for example, were known for their large size and heavy armament, making them among the most powerful destroyers of their time. The German G101-class destroyers were recognized for their speed and maneuverability, while the American Clemson-class destroyers were notable for their large numbers and the role they played in the final stages of the war.
Legacy of World War I Destroyers
The legacy of World War I destroyers extends beyond their immediate impact on the outcome of the conflict. They paved the way for the development of future destroyer classes, influencing naval architecture and tactics for decades to come. The lessons learned from their operations, both successes and failures, were instrumental in shaping the destroyer designs of World War II, where these ships would again play a critical role in naval warfare.Gallery of World War I Destroyers
World War I Destroyers Image Gallery









Frequently Asked Questions About World War I Destroyers
What was the primary role of destroyers in World War I?
+The primary role of destroyers in World War I was to protect larger ships from torpedo boat attacks, to escort convoys, and to engage in anti-submarine warfare.
How did the design of destroyers evolve during World War I?
+The design of destroyers evolved significantly during World War I, with improvements in speed, armament, and endurance. Newer classes of destroyers were built with larger displacements, more powerful engines, and enhanced armament, including depth charges for anti-submarine warfare.
What impact did World War I destroyers have on the outcome of the war?
+World War I destroyers played a critical role in the outcome of the war, particularly in the Battle of the Atlantic, where they helped to counter the German U-boat threat and protect Allied shipping. Their success in anti-submarine warfare and convoy escort duties was instrumental in ensuring the supply lines remained open, which was crucial for the Allied victory.
What legacy did World War I destroyers leave for future naval warfare?
+World War I destroyers left a significant legacy for future naval warfare, influencing the design and tactical employment of destroyers in World War II and beyond. The lessons learned from their operations, including the importance of convoy escort and anti-submarine warfare, continue to shape naval doctrine and ship design to this day.
How did the development of destroyers reflect technological advancements during World War I?
+The development of destroyers during World War I reflected significant technological advancements, including improvements in propulsion systems, materials, and weaponry. The introduction of new technologies, such as hydrophones for detecting submarines, also played a crucial role in enhancing the capabilities of destroyers.
In conclusion, the story of World War I destroyers is one of rapid evolution, technological innovation, and critical operational importance. Their impact on the outcome of the war and their legacy for future naval warfare are undeniable. As we reflect on the history of naval combat and the development of warships, the role of World War I destroyers stands out as a testament to human ingenuity, strategic adaptability, and the enduring importance of naval power. We invite readers to share their thoughts on the significance of destroyers in World War I and how their development influenced the course of naval history. Your insights and perspectives are invaluable in enriching our understanding of this pivotal moment in world history.
