Intro
Discover welders work places, including welding shops, factories, and construction sites, requiring safety gear and equipment for shielded metal arc welding, gas metal arc welding, and gas tungsten arc welding processes.
Welding is a crucial process in various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and repair. Welders play a vital role in joining metals and other materials together to create structures, machines, and other essential products. The work environment of welders can vary greatly, depending on the industry, location, and specific job requirements. In this article, we will explore the different workplaces where welders can be found, the challenges they face, and the importance of their work.
Welders can work in a variety of settings, from small workshops to large industrial facilities. Some welders may work outdoors, while others may be confined to a specific area or room. The type of welding process used, the materials being worked with, and the level of precision required can all impact the work environment. For example, welders working in the automotive industry may work in a production line setting, while those in the construction industry may work on-site, outdoors, and in varying weather conditions.
The work of welders is essential to many industries, and their skills are in high demand. Without welders, many of the products and structures we use today would not be possible. From the cars we drive to the buildings we live and work in, welding plays a critical role in their construction and maintenance. As technology continues to evolve, the demand for skilled welders is likely to increase, making it an exciting and rewarding career path for those interested in working with their hands and creating something from raw materials.
Types of Welding Workplaces

There are several types of workplaces where welders can be found, including manufacturing facilities, construction sites, repair shops, and fabrication shops. Each of these environments presents unique challenges and requires specific skills and knowledge. Manufacturing facilities, for example, may require welders to work on production lines, following strict quality control guidelines and meeting tight deadlines. Construction sites, on the other hand, may require welders to work at heights, in confined spaces, or in extreme weather conditions.
Manufacturing Facilities
Manufacturing facilities are one of the most common workplaces for welders. These facilities produce a wide range of products, from automotive parts to aerospace components. Welders in manufacturing facilities may work on production lines, assembling and welding parts together to create finished products. They may also work in quality control, inspecting welded joints and ensuring that they meet strict quality standards.Construction Sites
Construction sites are another common workplace for welders. These sites can be found in urban, suburban, and rural areas, and may involve working on buildings, bridges, roads, and other infrastructure projects. Welders on construction sites may work at heights, in confined spaces, or in extreme weather conditions, requiring specialized training and equipment to ensure their safety.Repair Shops
Repair shops are also an important workplace for welders. These shops repair and maintain equipment, vehicles, and other machinery, often using welding techniques to fix damaged or worn-out parts. Welders in repair shops may work on a wide range of projects, from repairing farm equipment to fixing industrial machinery.Fabrication Shops
Fabrication shops are specialized workplaces where welders create custom parts and products from raw materials. These shops may produce anything from metal artwork to industrial equipment, requiring welders to have a high level of skill and creativity. Fabrication shops may also involve working with a variety of materials, including steel, aluminum, and stainless steel.Challenges Faced by Welders

Welders face a variety of challenges in their workplaces, including physical demands, safety risks, and technical complexities. The physical demands of welding can be significant, requiring welders to work in awkward positions, lift heavy equipment, and endure extreme temperatures. Safety risks are also a major concern, as welders may be exposed to hazardous materials, electrical shock, and other hazards.
Physical Demands
The physical demands of welding can be significant, requiring welders to have good hand-eye coordination, manual dexterity, and physical strength. Welders may work in awkward positions, such as bending, kneeling, or standing for long periods, which can lead to fatigue and injury. They may also be required to lift heavy equipment, such as welding machines or metal parts, which can strain their backs and other muscles.Safety Risks
Safety risks are a major concern for welders, as they may be exposed to hazardous materials, electrical shock, and other hazards. Welders may work with flammable materials, such as gasoline or propane, which can ignite and cause fires or explosions. They may also be exposed to electrical shock, as welding equipment can be faulty or improperly maintained. Additionally, welders may be exposed to toxic fumes, such as those emitted by welding rods or fluxes, which can cause respiratory problems and other health issues.Technical Complexities
The technical complexities of welding can be significant, requiring welders to have a high level of skill and knowledge. Welders must understand the properties of different metals, including their melting points, thermal conductivity, and tensile strength. They must also be familiar with various welding techniques, such as shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), gas metal arc welding (GMAW), and gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW). Additionally, welders must be able to read blueprints and diagrams, understand quality control procedures, and troubleshoot problems with welding equipment and processes.Importance of Welding

Welding is a critical process in many industries, and its importance cannot be overstated. Without welding, many of the products and structures we use today would not be possible. Welding allows us to join metals and other materials together, creating strong and durable bonds that can withstand a wide range of stresses and loads. This is particularly important in industries such as construction, where welded joints are used to create buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
Construction Industry
The construction industry is one of the largest users of welding, as it relies heavily on welded joints to create buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure projects. Welding is used to join steel beams, columns, and other structural elements together, creating strong and durable frames that can support heavy loads. Welding is also used to create pipes, fittings, and other components used in plumbing, HVAC, and other systems.Manufacturing Industry
The manufacturing industry is another major user of welding, as it relies on welding to create a wide range of products, from automotive parts to aerospace components. Welding is used to join metals and other materials together, creating strong and durable bonds that can withstand a wide range of stresses and loads. This is particularly important in industries such as automotive, where welded joints are used to create car bodies, engines, and other critical components.Repair and Maintenance
Welding is also critical in repair and maintenance, as it allows us to fix damaged or worn-out parts and equipment. This can be particularly important in industries such as agriculture, where equipment is subject to heavy use and wear. Welding can be used to repair broken or damaged parts, such as tractor axles or plows, allowing farmers to quickly return to work and minimize downtime.Welding Image Gallery
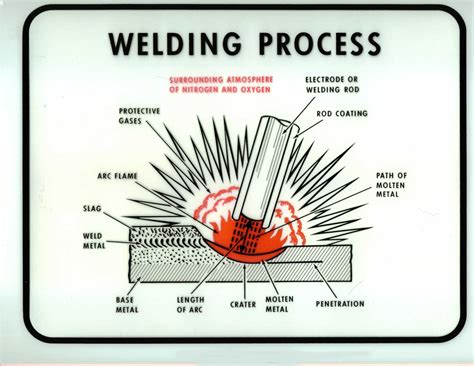

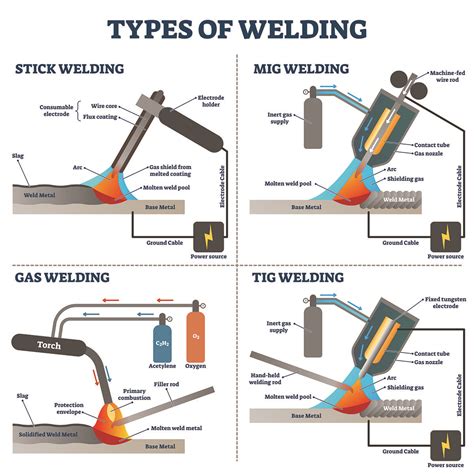







What is welding?
+Welding is a process of joining two metal pieces together by applying heat, pressure, or both, with or without filler metal.
What are the different types of welding?
+There are several types of welding, including shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), gas metal arc welding (GMAW), gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), and flux cored arc welding (FCAW).
What are the benefits of welding?
+The benefits of welding include the ability to join metals and other materials together, creating strong and durable bonds that can withstand a wide range of stresses and loads.
What are the challenges faced by welders?
+The challenges faced by welders include physical demands, safety risks, and technical complexities, such as working in awkward positions, lifting heavy equipment, and dealing with hazardous materials.
What is the importance of welding in the construction industry?
+Welding is critical in the construction industry, as it allows us to join steel beams, columns, and other structural elements together, creating strong and durable frames that can support heavy loads.
In conclusion, welders play a vital role in many industries, and their work is essential to the construction, manufacturing, and repair of a wide range of products and structures. The challenges faced by welders, including physical demands, safety risks, and technical complexities, require specialized training and equipment to ensure their safety and success. As technology continues to evolve, the demand for skilled welders is likely to increase, making it an exciting and rewarding career path for those interested in working with their hands and creating something from raw materials. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with welding, and to explore the many resources available for those interested in pursuing a career in this field.
