Intro
Discover the location of naval carriers with our guide, featuring aircraft carrier deployments, fleet movements, and maritime operations, including carrier strike groups and ship tracking.
The world of telecommunications has undergone significant transformations over the years, with various carriers emerging to provide a wide range of services to consumers. In today's digital age, it's essential to understand the role of carriers and how they operate. The term "carriers" refers to companies that provide telecommunications services, such as phone, internet, and television, to individuals and businesses. These carriers play a vital role in connecting people and facilitating communication across the globe.
The importance of carriers cannot be overstated, as they enable us to stay in touch with family and friends, access information, and conduct business transactions. With the rise of smartphones and other mobile devices, carriers have become an integral part of our daily lives. They offer various plans and services, including data, voice, and text messaging, to cater to different needs and preferences. Moreover, carriers are constantly investing in infrastructure and technology to improve network coverage, speed, and reliability.
As the demand for telecommunications services continues to grow, carriers are facing increasing competition and regulatory pressures. To stay ahead in the market, carriers must innovate and adapt to changing consumer needs and technological advancements. This includes investing in emerging technologies like 5G, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT). By doing so, carriers can provide faster, more reliable, and more secure services to their customers.
Types of Carriers
There are several types of carriers operating in the telecommunications industry, each with its unique characteristics and services. These include:
- Wireless carriers: Provide mobile phone services, including voice, data, and text messaging.
- Wireline carriers: Offer fixed-line telephone and internet services to homes and businesses.
- Cable carriers: Provide television, internet, and phone services through cable networks.
- Satellite carriers: Offer telecommunications services through satellite technology, often used in remote or underserved areas.
- Virtual carriers: Also known as mobile virtual network operators (MVNOs), these carriers lease network capacity from other providers and resell services to customers.
How Carriers Operate

Carriers operate complex networks that require significant investments in infrastructure, technology, and personnel. Their operations involve several key components, including:
- Network infrastructure: Carriers build and maintain networks of cell towers, fiber optic cables, and other equipment to provide services to customers.
- Spectrum management: Carriers manage radio frequency spectrum to ensure efficient use and minimize interference.
- Customer service: Carriers provide customer support through various channels, including call centers, online portals, and retail stores.
- Billing and payment: Carriers manage billing and payment processes, including invoicing, payment processing, and collections.
Benefits of Carriers

Carriers offer numerous benefits to consumers and businesses, including:
- Convenience: Carriers provide a range of services that can be accessed from anywhere, at any time.
- Connectivity: Carriers enable people to stay connected with family, friends, and colleagues, regardless of location.
- Economic growth: Carriers contribute to economic growth by creating jobs, stimulating innovation, and facilitating business transactions.
- Access to information: Carriers provide access to a vast amount of information, including news, education, and entertainment.
Challenges Facing Carriers

Despite the importance of carriers, they face several challenges, including:
- Increasing competition: The telecommunications industry is highly competitive, with many carriers vying for market share.
- Regulatory pressures: Carriers must comply with various regulations, including those related to net neutrality, data privacy, and spectrum management.
- Technological advancements: Carriers must invest in emerging technologies, such as 5G and IoT, to stay ahead in the market.
- Cybersecurity threats: Carriers must protect their networks and customers from cyber threats, including hacking and data breaches.
Future of Carriers

The future of carriers is exciting and uncertain, with several trends and technologies likely to shape the industry. These include:
- 5G networks: The rollout of 5G networks will enable faster, more reliable, and more secure services.
- IoT: The growth of IoT will create new opportunities for carriers to provide services and solutions to businesses and consumers.
- Artificial intelligence: Carriers will leverage AI to improve network management, customer service, and cybersecurity.
- Cloud computing: Carriers will increasingly adopt cloud computing to reduce costs, improve scalability, and enhance flexibility.
Carrier Services

Carriers offer a wide range of services to consumers and businesses, including:
- Voice services: Carriers provide voice services, including local, long-distance, and international calling.
- Data services: Carriers offer data services, including internet access, email, and file transfer.
- Text messaging: Carriers provide text messaging services, including SMS and MMS.
- Television services: Carriers offer television services, including cable, satellite, and streaming.
Carrier Plans
Carriers offer various plans to cater to different needs and preferences, including:
- Prepaid plans: Carriers offer prepaid plans, which require customers to pay for services in advance.
- Postpaid plans: Carriers offer postpaid plans, which require customers to pay for services after they are used.
- Unlimited plans: Carriers offer unlimited plans, which provide unlimited data, voice, and text messaging.
- Shared plans: Carriers offer shared plans, which allow multiple users to share a single plan.
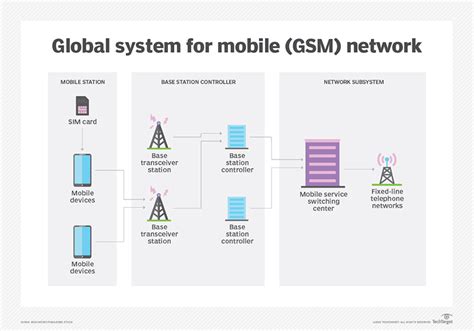
Carrier Networks
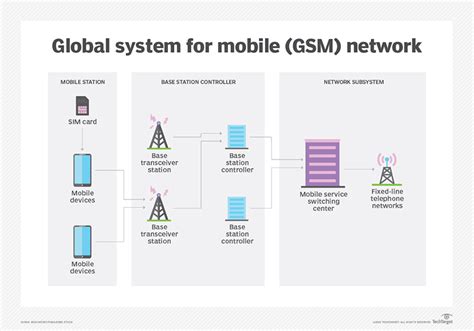
Carrier networks are complex systems that require significant investments in infrastructure and technology. These networks include:
- Cell towers: Carriers build and maintain cell towers to provide wireless services.
- Fiber optic cables: Carriers use fiber optic cables to provide high-speed internet and other services.
- Satellite technology: Carriers use satellite technology to provide services in remote or underserved areas.
- Network equipment: Carriers use network equipment, including routers, switches, and servers, to manage and maintain their networks.
Carrier Image Gallery
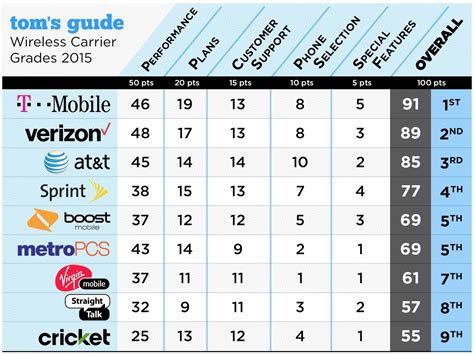

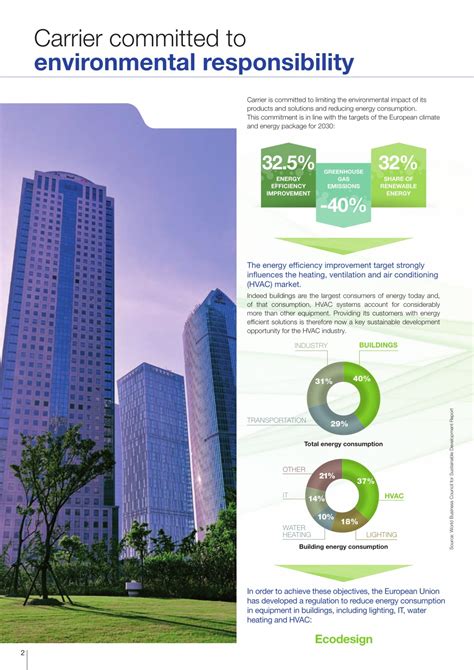

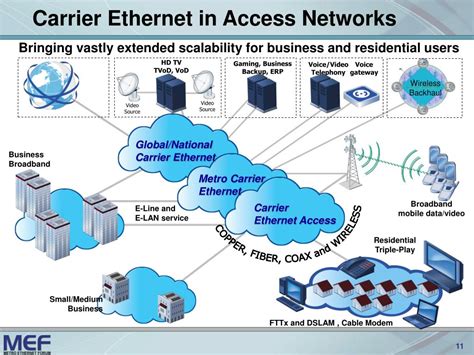


What is a carrier in the telecommunications industry?
+A carrier is a company that provides telecommunications services, including phone, internet, and television, to individuals and businesses.
What types of carriers are there in the telecommunications industry?
+There are several types of carriers, including wireless carriers, wireline carriers, cable carriers, satellite carriers, and virtual carriers.
What services do carriers offer to consumers and businesses?
+Carriers offer a wide range of services, including voice, data, text messaging, television, and internet access.
What is the future outlook for carriers in the telecommunications industry?
+The future outlook for carriers is exciting and uncertain, with several trends and technologies likely to shape the industry, including 5G networks, IoT, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing.
How do carriers contribute to economic growth and development?
+Carriers contribute to economic growth and development by creating jobs, stimulating innovation, and facilitating business transactions.
In conclusion, carriers play a vital role in the telecommunications industry, providing a wide range of services to consumers and businesses. As the industry continues to evolve, carriers must adapt to changing consumer needs and technological advancements. By understanding the importance of carriers and the challenges they face, we can appreciate the complex systems and networks that enable us to stay connected and access information. We invite you to share your thoughts and comments on the role of carriers in the telecommunications industry and how they can continue to innovate and improve their services.
