Intro
Learn about the GI Bill expiration date and its education benefits, including eligibility, application, and veteran benefits, to maximize your Post-9/11 GI Bill benefits before they expire.
The GI Bill is a valuable education benefit that helps veterans, service members, and their families pay for college, vocational training, and other educational expenses. However, many beneficiaries are concerned about the GI Bill expiration date and how it may affect their ability to use their benefits. In this article, we will delve into the details of the GI Bill expiration date, its implications, and what beneficiaries can do to make the most of their benefits.
The GI Bill has undergone several changes over the years, and its expiration date has been a topic of discussion among veterans and education officials. The Post-9/11 GI Bill, which is the most commonly used version of the benefit, does not have a traditional expiration date. Instead, it has a delimiting date, which is the date by which beneficiaries must use their benefits. The delimiting date for the Post-9/11 GI Bill is typically 15 years from the date of discharge or separation from active duty.
For example, a veteran who was discharged from active duty on January 1, 2010, would have until January 1, 2025, to use their Post-9/11 GI Bill benefits. This means that beneficiaries have a significant amount of time to pursue their educational goals, and they can use their benefits to pay for a variety of educational programs, including college degrees, vocational training, and apprenticeships.
Understanding the GI Bill Expiration Date

It's essential to note that the GI Bill expiration date is not the same as the benefit's eligibility period. The eligibility period refers to the time frame during which beneficiaries can apply for and receive GI Bill benefits. The eligibility period for the Post-9/11 GI Bill is typically 36 months, but it can be extended in certain circumstances, such as if the beneficiary is pursuing a graduate degree or is using their benefits to pay for a vocational training program.
Factors Affecting the GI Bill Expiration Date
Several factors can affect the GI Bill expiration date, including the type of benefit, the beneficiary's eligibility status, and any changes to the benefit program. For instance, the Forever GI Bill, which was signed into law in 2017, eliminated the 15-year delimiting date for beneficiaries who were discharged or separated from active duty after January 1, 2013. This means that beneficiaries who are eligible for the Forever GI Bill have more time to use their benefits and can pursue their educational goals without worrying about an expiration date.GI Bill Benefits and Eligibility

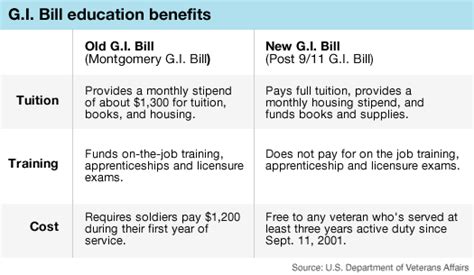
The GI Bill provides a range of benefits to eligible beneficiaries, including tuition and fees, housing allowances, and book stipends. The amount of benefits received depends on the type of benefit, the beneficiary's eligibility status, and the educational program being pursued. For example, the Post-9/11 GI Bill pays up to 100% of tuition and fees for public colleges and universities, while the Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR) pays a monthly stipend to beneficiaries who are pursuing a degree or vocational training program.
To be eligible for GI Bill benefits, beneficiaries must meet specific requirements, such as having served in the military for a certain period, being discharged or separated from active duty under honorable conditions, and pursuing an approved educational program. Beneficiaries can apply for GI Bill benefits online or by mail, and they must provide documentation, such as their DD Form 214, to support their application.
Types of GI Bill Benefits
There are several types of GI Bill benefits, each with its own eligibility requirements and benefits. The most common types of GI Bill benefits include:- Post-9/11 GI Bill: This benefit provides up to 36 months of education benefits to beneficiaries who have served in the military since September 11, 2001.
- Montgomery GI Bill Active Duty (MGIB-AD): This benefit provides up to 36 months of education benefits to beneficiaries who have served in the military on active duty.
- Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR): This benefit provides up to 36 months of education benefits to beneficiaries who are members of the Selected Reserve.
- Vocational Rehabilitation and Employment (VR&E) program: This benefit provides education and training benefits to beneficiaries who have a service-connected disability.
Using GI Bill Benefits
Beneficiaries can use their GI Bill benefits to pursue a variety of educational programs, including college degrees, vocational training, and apprenticeships. To use their benefits, beneficiaries must first apply for and receive approval from the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). They must then certify their enrollment with the VA each semester or term to receive their benefits.
Beneficiaries can also use their GI Bill benefits to pay for educational expenses, such as tuition and fees, housing allowances, and book stipends. The amount of benefits received depends on the type of benefit, the beneficiary's eligibility status, and the educational program being pursued.
GI Bill Benefits and Employment
The GI Bill can also provide employment benefits to beneficiaries, such as job training and placement assistance. The VR&E program, for example, provides employment benefits to beneficiaries who have a service-connected disability. This program helps beneficiaries find and maintain employment, and it provides support services, such as counseling and job training, to help them achieve their employment goals.GI Bill Expiration Date and Transferability
The GI Bill expiration date can also affect the transferability of benefits. The Post-9/11 GI Bill, for example, allows beneficiaries to transfer their benefits to their spouses or dependents. However, the transferability of benefits is subject to certain restrictions, such as the beneficiary's eligibility status and the type of benefit.
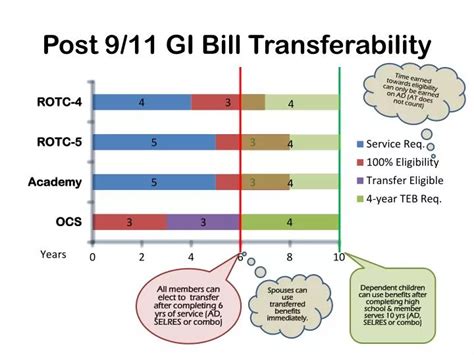
To transfer their benefits, beneficiaries must meet specific requirements, such as having served in the military for a certain period and being eligible for the Post-9/11 GI Bill. They must also apply for and receive approval from the Department of Defense (DoD) to transfer their benefits.
GI Bill Transferability and Eligibility
The eligibility requirements for GI Bill transferability vary depending on the type of benefit and the beneficiary's eligibility status. For example, the Post-9/11 GI Bill requires beneficiaries to have served in the military for at least six years to be eligible to transfer their benefits. The Montgomery GI Bill Active Duty (MGIB-AD) requires beneficiaries to have served in the military for at least two years to be eligible to transfer their benefits.GI Bill Expiration Date and Delimiting Date

The GI Bill expiration date and delimiting date are two separate concepts that can affect a beneficiary's ability to use their benefits. The expiration date refers to the date by which beneficiaries must use their benefits, while the delimiting date refers to the date by which beneficiaries must complete their educational program.
The delimiting date for the Post-9/11 GI Bill is typically 15 years from the date of discharge or separation from active duty. This means that beneficiaries have a significant amount of time to pursue their educational goals and use their benefits.
GI Bill Delimiting Date and Eligibility
The eligibility requirements for the GI Bill delimiting date vary depending on the type of benefit and the beneficiary's eligibility status. For example, the Post-9/11 GI Bill requires beneficiaries to have served in the military for at least 90 days to be eligible for the delimiting date. The Montgomery GI Bill Active Duty (MGIB-AD) requires beneficiaries to have served in the military for at least two years to be eligible for the delimiting date.GI Bill Image Gallery









What is the GI Bill expiration date?
+The GI Bill expiration date is the date by which beneficiaries must use their benefits. The expiration date varies depending on the type of benefit and the beneficiary's eligibility status.
How do I apply for GI Bill benefits?
+To apply for GI Bill benefits, beneficiaries must submit an application to the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). The application can be submitted online or by mail, and it must be accompanied by supporting documentation, such as the beneficiary's DD Form 214.
Can I transfer my GI Bill benefits to my spouse or dependents?
+Yes, beneficiaries can transfer their GI Bill benefits to their spouses or dependents. However, the transferability of benefits is subject to certain restrictions, such as the beneficiary's eligibility status and the type of benefit.
What is the delimiting date for the Post-9/11 GI Bill?
+The delimiting date for the Post-9/11 GI Bill is typically 15 years from the date of discharge or separation from active duty. This means that beneficiaries have a significant amount of time to pursue their educational goals and use their benefits.
How do I certify my enrollment to receive GI Bill benefits?
+To certify their enrollment, beneficiaries must submit a certification request to the VA each semester or term. The certification request can be submitted online or by mail, and it must be accompanied by supporting documentation, such as the beneficiary's enrollment verification.
In conclusion, the GI Bill expiration date is an important consideration for beneficiaries who are pursuing their educational goals. By understanding the expiration date and the delimiting date, beneficiaries can make informed decisions about their education and career plans. If you have any further questions or concerns about the GI Bill expiration date or any other aspect of the benefit, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others who may be interested. Additionally, you can take specific actions, such as applying for GI Bill benefits or certifying your enrollment, to make the most of your benefits and achieve your educational goals.
