Intro
Discover the role of linking verbs in sentence structure, including types like be, seem, and appear, to improve grammar and verb usage skills.
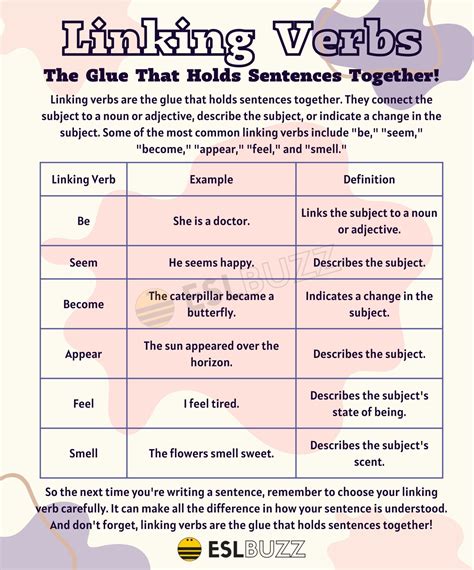
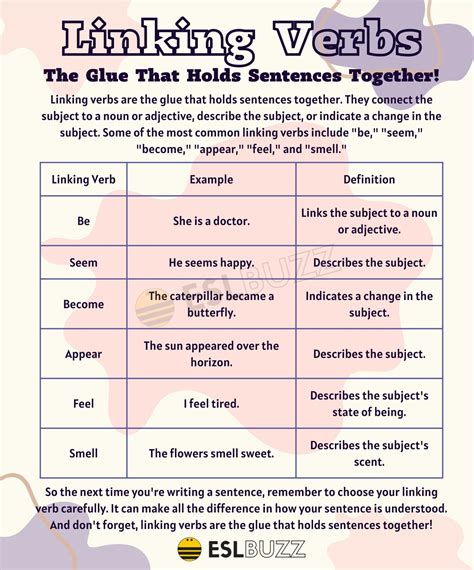
Verbs are a crucial part of the English language, and understanding their different types is essential for effective communication. Among the various types of verbs, linking verbs play a significant role in connecting the subject of a sentence to additional information. In this article, we will delve into the world of linking verbs, exploring their definition, examples, and usage.
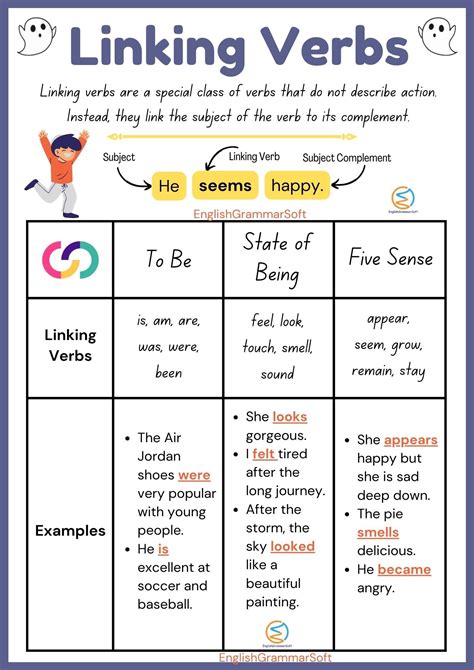
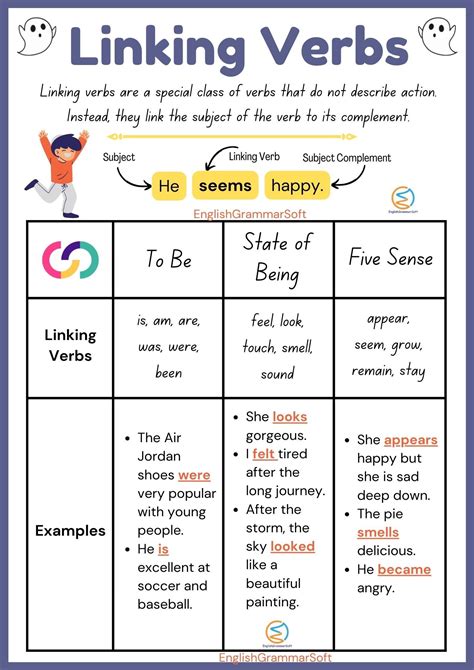
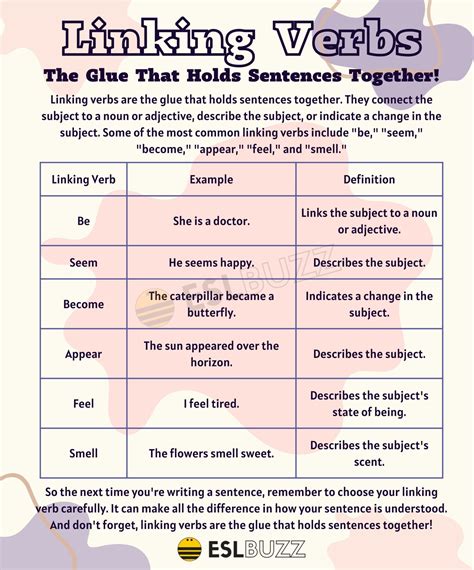
Linking verbs, also known as copular verbs, are verbs that connect the subject of a sentence to a predicate, which is the part of the sentence that contains additional information about the subject. The primary function of a linking verb is to link the subject to a predicate nominative, a predicate adjective, or an adverb. This connection helps to provide more information about the subject, making the sentence more descriptive and informative.
The most common linking verb is "to be," which includes various forms such as "is," "are," "am," "be," "been," and "being." Other examples of linking verbs include "seem," "appear," "become," "feel," "look," "sound," and "taste." These verbs help to create a connection between the subject and the predicate, allowing for a more detailed description of the subject.
For instance, in the sentence "She is a doctor," the verb "is" is a linking verb that connects the subject "she" to the predicate nominative "a doctor." Similarly, in the sentence "He seems happy," the verb "seems" is a linking verb that connects the subject "he" to the predicate adjective "happy." In both cases, the linking verb helps to provide additional information about the subject, making the sentence more descriptive and engaging.
Definition and Examples of Linking Verbs

Linking verbs can be used in various contexts to create different effects. For example, in the sentence "The cake tastes delicious," the verb "tastes" is a linking verb that connects the subject "cake" to the predicate adjective "delicious." In this case, the linking verb helps to describe the subject's quality or characteristic. In contrast, in the sentence "The music sounds beautiful," the verb "sounds" is a linking verb that connects the subject "music" to the predicate adjective "beautiful," creating a more subjective description.
Types of Linking Verbs

There are several types of linking verbs, each with its own unique characteristics and usage. Some common types of linking verbs include:
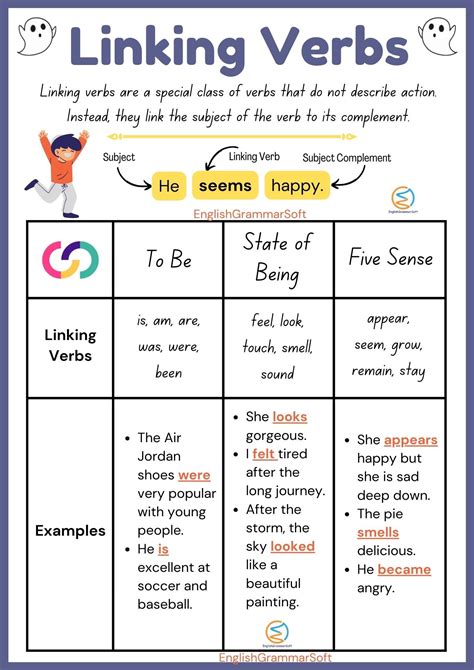
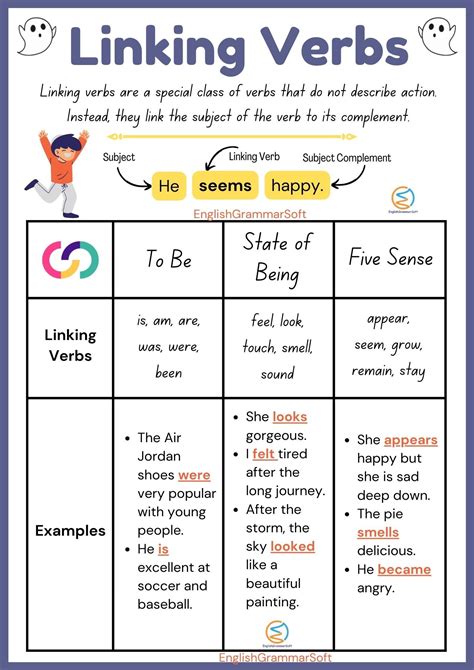
- Verbs of sensation, such as "feel," "taste," "smell," "hear," and "see"
- Verbs of appearance, such as "seem," "appear," and "look"
- Verbs of being, such as "be," "is," "are," "am," "been," and "being"
- Verbs of becoming, such as "become," "grow," and "turn"
Each type of linking verb has its own specific usage and context, and understanding these differences is essential for effective communication.
How Linking Verbs Work
Linking verbs work by connecting the subject of a sentence to a predicate, which can be a noun, an adjective, or an adverb. The linking verb helps to create a relationship between the subject and the predicate, allowing for a more detailed description of the subject. For example, in the sentence "The book is interesting," the verb "is" is a linking verb that connects the subject "book" to the predicate adjective "interesting."
In this case, the linking verb helps to describe the subject's quality or characteristic, making the sentence more engaging and informative. Similarly, in the sentence "The city seems crowded," the verb "seems" is a linking verb that connects the subject "city" to the predicate adjective "crowded," creating a more subjective description.
Benefits of Using Linking Verbs
Using linking verbs can have several benefits, including:
- Creating more descriptive sentences that provide additional information about the subject
- Allowing for a more nuanced and subjective description of the subject
- Helping to connect the subject to a predicate, which can be a noun, an adjective, or an adverb
- Enabling the use of predicate nominatives, predicate adjectives, and adverbs to provide more information about the subject
By using linking verbs effectively, writers and speakers can create more engaging and informative sentences that provide a more detailed description of the subject.
Common Mistakes with Linking Verbs

While linking verbs can be powerful tools for creating more descriptive sentences, there are several common mistakes that can occur when using them. Some common mistakes include:
- Using the wrong form of the linking verb, such as using "is" instead of "are"
- Forgetting to use a linking verb, resulting in a sentence that lacks connection between the subject and the predicate
- Using a linking verb incorrectly, such as using "seem" instead of "seems"
By being aware of these common mistakes, writers and speakers can avoid errors and create more effective sentences that use linking verbs correctly.
Best Practices for Using Linking Verbs
To use linking verbs effectively, there are several best practices to follow, including:
- Using the correct form of the linking verb, such as using "is" instead of "are"
- Choosing the right type of linking verb, such as using "seem" instead of "seems"
- Using linking verbs to create more descriptive sentences that provide additional information about the subject
- Avoiding common mistakes, such as using the wrong form of the linking verb or forgetting to use a linking verb
By following these best practices, writers and speakers can create more effective sentences that use linking verbs correctly and provide a more detailed description of the subject.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, linking verbs are a powerful tool for creating more descriptive sentences that provide additional information about the subject. By understanding the different types of linking verbs, their usage, and common mistakes, writers and speakers can create more effective sentences that use linking verbs correctly. Whether you are a writer, speaker, or simply someone who wants to improve your communication skills, mastering the use of linking verbs can help you to create more engaging and informative sentences that provide a more detailed description of the subject.
Linking Verbs Image Gallery






What is a linking verb?
+A linking verb is a verb that connects the subject of a sentence to a predicate, which can be a noun, an adjective, or an adverb.
What are some examples of linking verbs?
+Some examples of linking verbs include "is," "are," "seem," "appear," "become," "feel," "look," "sound," and "taste."
How do linking verbs work?
+Linking verbs work by connecting the subject of a sentence to a predicate, which can be a noun, an adjective, or an adverb, helping to create a more detailed description of the subject.
What are some common mistakes with linking verbs?
+Some common mistakes with linking verbs include using the wrong form of the linking verb, forgetting to use a linking verb, and using a linking verb incorrectly.
How can I use linking verbs effectively?
+To use linking verbs effectively, choose the right type of linking verb, use the correct form of the linking verb, and use linking verbs to create more descriptive sentences that provide additional information about the subject.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of linking verbs and how to use them effectively. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to share them with us. We'd love to hear from you and help you improve your communication skills. Share this article with your friends and family to help them learn more about linking verbs and how to use them correctly.
