Intro
Discover 5 gray zone facts, exploring moral ambiguity, ethical dilemmas, and controversial issues, shedding light on complex gray areas, nuances, and paradoxes.
The concept of gray zones has become increasingly relevant in various aspects of life, from ethics and morality to business and personal relationships. Gray zones refer to the ambiguous areas between clearly defined categories, where the boundaries are blurred, and the rules are not clearly established. Understanding gray zones is essential for making informed decisions and navigating complex situations. In this article, we will delve into the concept of gray zones, exploring their characteristics, implications, and practical applications.
Gray zones are ubiquitous, and we encounter them in our daily lives, often without realizing it. They can arise in personal relationships, professional settings, and even in our own thought processes. The gray zone is a metaphorical space where black-and-white thinking no longer applies, and we are forced to confront the nuances and complexities of reality. By acknowledging and embracing the gray zone, we can develop a more sophisticated and nuanced approach to decision-making and problem-solving.
The importance of understanding gray zones cannot be overstated. In a world where complexity and ambiguity are increasingly prevalent, being able to navigate gray zones effectively is a valuable skill. It requires a combination of critical thinking, emotional intelligence, and creativity. By developing these skills, we can better navigate the gray zones that arise in our personal and professional lives, making more informed decisions and achieving greater success.
Introduction to Gray Zones
Gray zones can be found in various domains, from ethics and morality to business and personal relationships. In ethics, gray zones refer to the areas where moral principles are not clearly defined, and different perspectives may lead to conflicting conclusions. In business, gray zones can arise in areas such as marketing, finance, and human resources, where the rules and regulations may be ambiguous or open to interpretation. In personal relationships, gray zones can occur in areas such as communication, boundaries, and conflict resolution.
Characteristics of Gray Zones
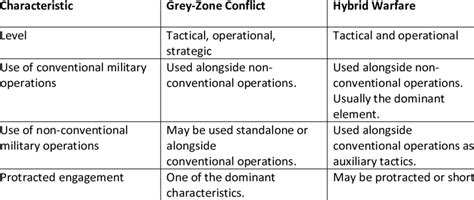
Gray zones have several key characteristics that distinguish them from more clearly defined areas. These characteristics include:
- Ambiguity: Gray zones are characterized by a lack of clear definitions or boundaries.
- Uncertainty: Gray zones often involve uncertain or unpredictable outcomes.
- Complexity: Gray zones typically involve multiple factors and variables, making them difficult to navigate.
- Nuance: Gray zones require a nuanced approach, taking into account multiple perspectives and context.
Types of Gray Zones
Gray zones can be categorized into different types, depending on the context and domain. Some common types of gray zones include: * Ethical gray zones: These refer to areas where moral principles are not clearly defined, and different perspectives may lead to conflicting conclusions. * Business gray zones: These refer to areas where the rules and regulations may be ambiguous or open to interpretation. * Personal gray zones: These refer to areas where personal relationships, communication, and boundaries may be unclear or ambiguous.Implications of Gray Zones

Gray zones have significant implications for individuals, organizations, and society as a whole. Some of the key implications include:
- Increased complexity: Gray zones can add complexity to decision-making and problem-solving, requiring a more nuanced and sophisticated approach.
- Uncertainty: Gray zones can create uncertainty, making it difficult to predict outcomes or make informed decisions.
- Conflict: Gray zones can lead to conflict, as different perspectives and interpretations may lead to conflicting conclusions.
Navigating Gray Zones
Navigating gray zones requires a combination of critical thinking, emotional intelligence, and creativity. Some strategies for navigating gray zones include: * Seeking multiple perspectives: Gathering information and insights from different sources can help to clarify the situation and identify potential solutions. * Analyzing context: Understanding the context and nuances of the situation can help to inform decision-making and problem-solving. * Developing a nuanced approach: Recognizing the complexity and ambiguity of gray zones can help to develop a more sophisticated and nuanced approach to decision-making and problem-solving.Practical Applications of Gray Zones

Gray zones have numerous practical applications in various domains, from business and ethics to personal relationships and decision-making. Some examples of practical applications include:
- Business ethics: Gray zones can arise in areas such as marketing, finance, and human resources, requiring a nuanced and sophisticated approach to decision-making and problem-solving.
- Personal relationships: Gray zones can occur in areas such as communication, boundaries, and conflict resolution, requiring a combination of critical thinking, emotional intelligence, and creativity.
- Decision-making: Gray zones can add complexity to decision-making, requiring a more nuanced and sophisticated approach to evaluating options and making informed decisions.
Real-World Examples of Gray Zones
Gray zones can be found in various real-world contexts, from business and ethics to personal relationships and decision-making. Some examples of real-world gray zones include: * The use of artificial intelligence in decision-making: As AI becomes increasingly prevalent, there are gray zones around its use, including issues of bias, transparency, and accountability. * The impact of social media on mental health: There are gray zones around the impact of social media on mental health, including issues of addiction, cyberbullying, and online harassment. * The ethics of gene editing: There are gray zones around the ethics of gene editing, including issues of consent, safety, and potential consequences.Benefits of Understanding Gray Zones
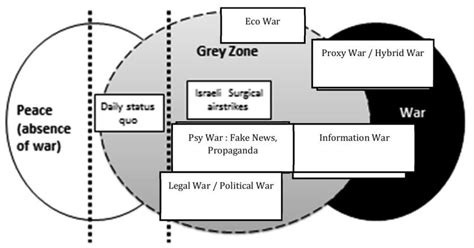
Understanding gray zones has numerous benefits, from improving decision-making and problem-solving to enhancing personal and professional relationships. Some of the key benefits include:
- Improved decision-making: By recognizing and navigating gray zones, individuals and organizations can make more informed decisions and avoid potential pitfalls.
- Enhanced relationships: Understanding gray zones can help to build trust, improve communication, and enhance personal and professional relationships.
- Increased creativity: Gray zones can stimulate creativity, as individuals and organizations are forced to think outside the box and develop innovative solutions.
Challenges of Navigating Gray Zones
Navigating gray zones can be challenging, requiring a combination of critical thinking, emotional intelligence, and creativity. Some of the key challenges include: * Ambiguity: Gray zones are characterized by ambiguity, making it difficult to define the situation or identify clear solutions. * Uncertainty: Gray zones can create uncertainty, making it difficult to predict outcomes or make informed decisions. * Conflict: Gray zones can lead to conflict, as different perspectives and interpretations may lead to conflicting conclusions.Gallery of Gray Zone Images
Gray Zone Image Gallery

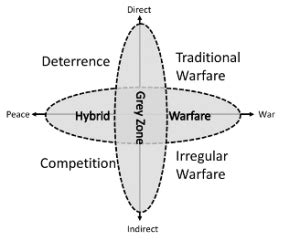





Frequently Asked Questions
What are gray zones?
+Gray zones refer to the ambiguous areas between clearly defined categories, where the boundaries are blurred, and the rules are not clearly established.
Why are gray zones important?
+Understanding gray zones is essential for making informed decisions and navigating complex situations. Gray zones can add complexity to decision-making, but they can also stimulate creativity and innovation.
How can I navigate gray zones effectively?
+Navigating gray zones requires a combination of critical thinking, emotional intelligence, and creativity. Seeking multiple perspectives, analyzing context, and developing a nuanced approach can help to navigate gray zones effectively.
What are some practical applications of gray zones?
+Gray zones have numerous practical applications in various domains, from business and ethics to personal relationships and decision-making. Understanding gray zones can help to improve decision-making, enhance relationships, and stimulate creativity.
How can I develop a nuanced approach to gray zones?
+Developing a nuanced approach to gray zones requires a combination of critical thinking, emotional intelligence, and creativity. Seeking multiple perspectives, analyzing context, and recognizing the complexity and ambiguity of gray zones can help to develop a nuanced approach.
In conclusion, gray zones are an inherent part of our personal and professional lives. By understanding and navigating these ambiguous areas, we can make more informed decisions, build stronger relationships, and stimulate creativity and innovation. We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with gray zones in the comments below. How do you navigate gray zones in your personal and professional life? What strategies do you use to make informed decisions and build strong relationships in the face of ambiguity and uncertainty? Share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about gray zones and how to navigate them effectively.
