Intro
Explore 5 ways gray zone warfare persists, involving hybrid threats, cyber warfare, and asymmetric tactics, blurring traditional conflict lines and testing national security strategies.
The concept of gray zone warfare has become increasingly relevant in today's global security landscape. It refers to the use of ambiguous, indirect, and often unconventional tactics by state and non-state actors to achieve their strategic objectives without resorting to traditional forms of warfare. The importance of understanding gray zone warfare lies in its ability to challenge the traditional notions of war and peace, making it essential for nations and organizations to develop effective countermeasures. In this article, we will delve into the world of gray zone warfare, exploring its various facets, and discussing five ways it remains a significant concern for global security.
Gray zone warfare is characterized by its ambiguity, making it difficult to distinguish between military and non-military actions. This ambiguity is deliberately created by the actors involved, who often use proxy forces, cyberattacks, and disinformation campaigns to achieve their objectives. The lack of clear attribution and the use of plausible deniability make it challenging for nations to respond effectively to gray zone threats. As a result, gray zone warfare has become a preferred tactic for many state and non-state actors, allowing them to pursue their interests without facing significant consequences.
The use of gray zone warfare is not limited to any particular region or conflict. It has been employed in various forms and contexts, from the Ukraine-Russia conflict to the South China Sea disputes. The versatility of gray zone warfare makes it an attractive option for actors seeking to challenge the status quo without resorting to traditional forms of warfare. However, the consequences of gray zone warfare can be severe, ranging from destabilization of entire regions to the erosion of trust in international institutions.
Introduction to Gray Zone Warfare

Gray zone warfare is often described as a "competition short of war," where actors engage in a range of activities designed to undermine their opponents without crossing the threshold of traditional warfare. These activities can include cyberattacks, disinformation campaigns, economic coercion, and the use of proxy forces. The aim of gray zone warfare is to create a situation where the opponent is forced to respond, thereby escalating the situation and creating a pretext for further action.
The concept of gray zone warfare is not new, but its significance has increased in recent years due to the changing nature of conflict. The rise of non-state actors, the proliferation of technology, and the increasing importance of information operations have all contributed to the growth of gray zone warfare. As a result, nations and organizations must develop new strategies and capabilities to counter gray zone threats, which often require a combination of military, diplomatic, and economic measures.
Characteristics of Gray Zone Warfare

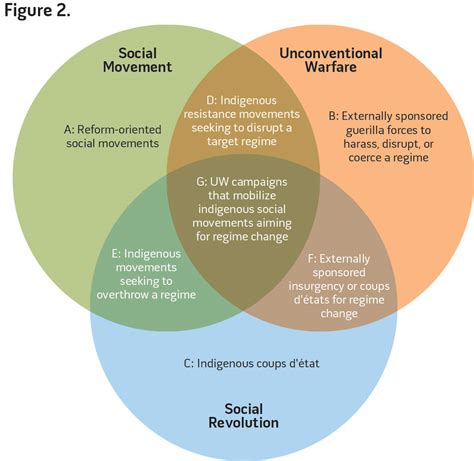
Gray zone warfare has several key characteristics that distinguish it from traditional forms of warfare. These include:
- Ambiguity: Gray zone warfare is often characterized by ambiguity, making it difficult to determine the identity and intentions of the actors involved.
- Indirect action: Gray zone warfare involves the use of indirect action, such as proxy forces, cyberattacks, and disinformation campaigns.
- Unconventional tactics: Gray zone warfare often involves the use of unconventional tactics, such as economic coercion, sabotage, and terrorism.
- Deniability: Gray zone warfare is often designed to provide plausible deniability, making it difficult for nations to respond effectively.
These characteristics make gray zone warfare a challenging and complex phenomenon to counter. Nations and organizations must develop new strategies and capabilities to address the ambiguities and uncertainties of gray zone warfare, which often require a combination of military, diplomatic, and economic measures.
Types of Gray Zone Warfare
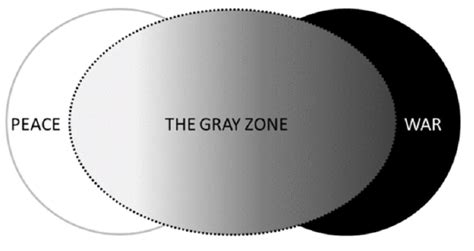
Gray zone warfare can take many forms, depending on the context and the actors involved. Some common types of gray zone warfare include:
- Cyber gray zone warfare: This involves the use of cyberattacks, hacking, and other forms of cyber exploitation to disrupt or destroy an opponent's critical infrastructure.
- Information gray zone warfare: This involves the use of disinformation, propaganda, and other forms of information operations to influence public opinion and undermine an opponent's legitimacy.
- Economic gray zone warfare: This involves the use of economic coercion, sanctions, and other forms of economic pressure to weaken an opponent's economy and undermine their ability to respond.
- Proxy gray zone warfare: This involves the use of proxy forces, such as militias, insurgents, or terrorists, to conduct attacks on an opponent's territory or interests.
Each type of gray zone warfare presents unique challenges and opportunities for nations and organizations seeking to counter these threats. By understanding the different types of gray zone warfare, nations can develop effective countermeasures and strategies to mitigate the risks and consequences of these activities.
Examples of Gray Zone Warfare

Gray zone warfare has been employed in various contexts and regions, often with significant consequences. Some examples of gray zone warfare include:
- The Ukraine-Russia conflict: This conflict has involved the use of gray zone warfare, including cyberattacks, disinformation campaigns, and the use of proxy forces.
- The South China Sea disputes: This conflict has involved the use of gray zone warfare, including the use of coast guard vessels, fishing boats, and other forms of maritime coercion.
- The Middle East: This region has seen the use of gray zone warfare, including the use of proxy forces, cyberattacks, and disinformation campaigns.
These examples illustrate the versatility and complexity of gray zone warfare, which can be employed in various contexts and regions to achieve strategic objectives. By understanding these examples, nations and organizations can develop effective countermeasures and strategies to mitigate the risks and consequences of gray zone warfare.
Countering Gray Zone Warfare

Countering gray zone warfare requires a combination of military, diplomatic, and economic measures. Some strategies for countering gray zone warfare include:
- Developing effective countermeasures: Nations must develop effective countermeasures to gray zone threats, including cyber defenses, information operations, and economic sanctions.
- Building international cooperation: International cooperation is essential for countering gray zone warfare, which often involves the use of proxy forces and other forms of indirect action.
- Enhancing situational awareness: Nations must enhance their situational awareness to detect and respond to gray zone threats, which often involve ambiguous and unconventional tactics.
By developing effective countermeasures, building international cooperation, and enhancing situational awareness, nations can mitigate the risks and consequences of gray zone warfare. However, countering gray zone warfare is a complex and challenging task that requires a sustained effort and commitment from nations and organizations.
Gallery of Gray Zone Warfare
Gray Zone Warfare Image Gallery




What is gray zone warfare?
+Gray zone warfare refers to the use of ambiguous, indirect, and often unconventional tactics by state and non-state actors to achieve their strategic objectives without resorting to traditional forms of warfare.
What are the characteristics of gray zone warfare?
+The characteristics of gray zone warfare include ambiguity, indirect action, unconventional tactics, and deniability.
How can nations counter gray zone warfare?
+Nations can counter gray zone warfare by developing effective countermeasures, building international cooperation, and enhancing situational awareness.
In conclusion, gray zone warfare remains a significant concern for global security, and nations must develop effective countermeasures to mitigate its risks and consequences. By understanding the characteristics, types, and examples of gray zone warfare, nations can develop strategies to counter these threats and protect their interests. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences on gray zone warfare, and to continue the conversation on this critical topic.
