Intro
Discover the Infantry MOS, a military occupational specialty requiring combat skills, tactical training, and leadership, with related roles like rifleman, infantryman, and combat specialist.
The world of military operations is complex and multifaceted, involving various branches and specialties that work together to achieve strategic objectives. Among these, the infantry plays a crucial role, serving as the backbone of ground forces in combat and peacekeeping missions. Within the infantry, different Military Occupational Specialties (MOS) define the specific roles and responsibilities of soldiers, ensuring that each unit operates with precision and effectiveness. One such critical MOS is the Infantry MOS, which is the focus of our discussion.
The Infantry MOS is designed for soldiers who will be engaged in direct combat, reconnaissance, and other frontline duties. These individuals are trained to operate in a variety of environments, from urban settings to wilderness and desert terrains, utilizing a range of weapons, tactics, and strategies to accomplish their missions. The role of an infantry soldier is demanding, both physically and mentally, requiring a high level of fitness, discipline, and teamwork.
Infantry soldiers are involved in a broad spectrum of activities, including offensive and defensive operations, patrols, ambushes, and raids. They must be adept at using various weapons systems, including rifles, machine guns, mortars, and grenade launchers, as well as being skilled in hand-to-hand combat and first aid. The ability to navigate, communicate effectively, and make swift decisions under pressure are also essential skills for infantry personnel.
The training for Infantry MOS is rigorous and comprehensive, aiming to prepare soldiers for the challenges they will face in the field. This training includes basic combat skills, advanced infantry training, and specialized courses depending on the specific role within the infantry, such as sniper, reconnaissance, or heavy weapons specialist. The curriculum is designed to foster leadership, initiative, and adaptability, as these qualities are vital for success in dynamic and unpredictable combat environments.

Roles and Responsibilities
The roles and responsibilities of infantry soldiers can vary widely depending on their specific MOS, unit, and the nature of their deployment. However, some common duties include engaging enemy forces, securing and defending positions, conducting reconnaissance to gather intelligence, and participating in peacekeeping or humanitarian missions. Infantry soldiers must also be prepared to work in conjunction with other military branches and specialties, such as artillery, armor, and air support, to achieve strategic objectives.
In addition to combat duties, infantry soldiers are often involved in non-combat roles, such as training local security forces, providing security for convoys and patrols, and assisting in disaster relief efforts. The versatility and adaptability of infantry personnel make them invaluable in a wide range of scenarios, from conventional warfare to counterinsurgency and peacekeeping operations.
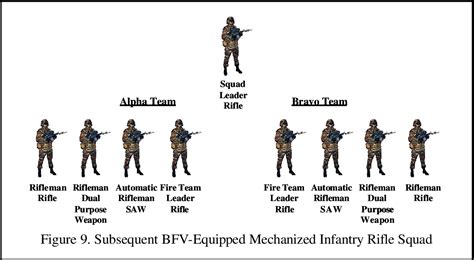
Specializations Within Infantry MOS
Within the Infantry MOS, there are several specializations that soldiers can pursue, each with its unique set of skills and responsibilities. These include:
- Rifleman: The most common infantry MOS, riflemen are the frontline soldiers who engage the enemy, conduct patrols, and secure positions.
- Machine Gunner: Responsible for the operation and maintenance of machine guns, these soldiers provide suppressive fire to support infantry operations.
- Mortarman: Mortarmen operate indirect fire weapons, such as mortars, to provide supporting fire for infantry units.
- Sniper: Snipers are trained to engage targets from concealed positions, using specialized rifles and tactics to achieve precision shots.
- Reconnaissance: Reconnaissance soldiers conduct missions to gather intelligence on enemy positions, movements, and activities.
Each of these specializations requires unique training and skills, but all are integral to the effectiveness of infantry units in achieving their objectives.

Training and Education
The training for infantry soldiers is among the most rigorous and demanding in the military. It begins with Basic Combat Training (BCT), where recruits learn the fundamental skills of soldiering, including first aid, map reading, and combat techniques. Following BCT, infantry soldiers attend Advanced Individual Training (AIT), also known as One Station Unit Training (OSUT) for infantry, which focuses on the specific skills required for their MOS.
In addition to initial training, infantry soldiers may attend specialized courses to enhance their skills, such as the Army Ranger School, Sniper School, or the School of Infantry. These courses are designed to prepare soldiers for more complex and challenging roles within the infantry.

Career Progression and Opportunities
Infantry soldiers have a variety of career paths and opportunities available to them, both within and outside the military. As they gain experience and advance in rank, they may take on leadership roles, such as squad or platoon leader, or specialize in a particular area, such as intelligence or communications.
After leaving the military, infantry veterans often find that their skills and experience are highly valued in the civilian job market. Many go on to careers in law enforcement, security, or emergency services, where their training and discipline are directly applicable. Others may pursue careers in fields such as business, education, or government, leveraging the leadership, teamwork, and problem-solving skills they developed during their military service.

Challenges and Rewards
Serving as an infantry soldier comes with its share of challenges, including the physical and mental demands of combat, the risk of injury or death, and the strain on personal and family life. However, for those who choose this path, the rewards can be immense. Infantry soldiers have the opportunity to serve their country, to be part of a proud and storied tradition, and to develop skills and qualities that will benefit them for the rest of their lives.
The camaraderie and esprit de corps among infantry soldiers are also unique and lasting. The bonds formed in the shared experiences of training and combat create lifelong friendships and a sense of belonging to a special fraternity.

Conclusion and Future Outlook
In conclusion, the Infantry MOS is a critical and respected role within the military, requiring soldiers who are brave, adaptable, and skilled. As the nature of warfare and global conflicts continues to evolve, the importance of well-trained and effective infantry forces will only continue to grow. For those considering a career as an infantry soldier, it is essential to understand the challenges and rewards involved and to be prepared for the rigors of training and the realities of combat.
The future outlook for infantry soldiers is dynamic, with ongoing advancements in technology, tactics, and equipment aimed at enhancing their capabilities and protecting them from harm. As the world becomes increasingly complex and interconnected, the role of infantry soldiers in defending national interests and contributing to global security will remain vital.

Infantry Image Gallery









What is the primary role of an infantry soldier?
+The primary role of an infantry soldier is to engage in direct combat with the enemy, conduct reconnaissance, and secure positions.
What kind of training do infantry soldiers receive?
+Infantry soldiers receive rigorous training that includes Basic Combat Training, Advanced Individual Training, and specialized courses depending on their specific role within the infantry.
What are some of the challenges faced by infantry soldiers?
+Infantry soldiers face a range of challenges, including the physical and mental demands of combat, the risk of injury or death, and the strain on personal and family life.
What are some career paths available to infantry soldiers after they leave the military?
+Infantry veterans often pursue careers in law enforcement, security, emergency services, business, education, or government, leveraging the skills and qualities they developed during their military service.
How does the infantry contribute to national security and global stability?
+The infantry plays a critical role in defending national interests and contributing to global security through their participation in combat operations, peacekeeping missions, and humanitarian efforts.
We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, or questions about the Infantry MOS and its significance in modern military operations. Your input can provide valuable insights and contribute to a deeper understanding of this critical role. Whether you are a veteran, a current service member, or simply someone interested in the military, your perspective is welcome. Let's engage in a constructive dialogue that honors the service and sacrifice of infantry soldiers and explores the complexities and challenges of their profession.
