Intro
Discover how signals intelligence works through interception, decryption, and analysis of communications, leveraging electronic intelligence, communications intelligence, and cybersecurity to inform strategic decisions.
The world of signals intelligence is a complex and fascinating one, filled with intrigue and secrecy. Signals intelligence, or SIGINT, is a crucial component of modern espionage and military operations, allowing governments and organizations to gather vital information about their adversaries. In this article, we will delve into the world of SIGINT, exploring its importance, methods, and applications. We will also examine the benefits and challenges of SIGINT, as well as its role in shaping global events.
Signals intelligence is the interception, analysis, and dissemination of signals, which can include communications, radar emissions, and other forms of electromagnetic radiation. SIGINT is used to gather information about an adversary's military capabilities, intentions, and operations, as well as to identify potential security threats. The importance of SIGINT cannot be overstated, as it provides critical insights that can inform decision-making at the highest levels of government and military command.
The use of SIGINT has been instrumental in shaping the course of modern history, from the Allied victory in World War II to the present day. By intercepting and analyzing enemy communications, governments and military commanders can gain a strategic advantage, anticipating and preparing for potential threats. SIGINT has also played a key role in counterterrorism efforts, helping to identify and disrupt terrorist networks and operations.
Introduction to Signals Intelligence

Signals intelligence is a highly specialized field, requiring advanced technical expertise and sophisticated equipment. SIGINT operations involve the use of specialized sensors and systems to intercept and analyze signals, which can be transmitted via a variety of means, including radio, microwave, and satellite communications. The analysis of these signals can provide valuable insights into an adversary's capabilities and intentions, as well as identify potential security threats.
Types of Signals Intelligence

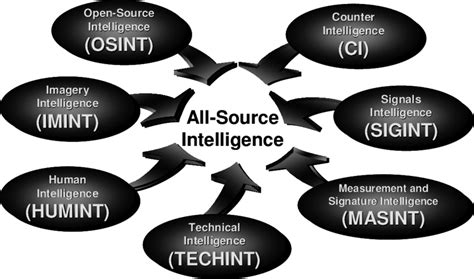
There are several types of SIGINT, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. These include:
- Communications intelligence (COMINT): the interception and analysis of communications signals, such as phone calls, emails, and text messages.
- Electronic intelligence (ELINT): the interception and analysis of electronic signals, such as radar emissions and electronic countermeasures.
- Foreign instrumentation signals intelligence (FISINT): the interception and analysis of signals emitted by foreign instrumentation, such as telemetry and beacon systems.
Communications Intelligence
COMINT is a critical component of SIGINT, providing valuable insights into an adversary's communications networks and patterns. COMINT involves the interception and analysis of communications signals, which can be transmitted via a variety of means, including radio, microwave, and satellite communications. The analysis of these signals can provide valuable insights into an adversary's capabilities and intentions, as well as identify potential security threats.Signals Intelligence Collection Methods

SIGINT collection methods involve the use of specialized sensors and systems to intercept and analyze signals. These methods can include:
- Ground-based collection: the use of ground-based sensors and systems to intercept and analyze signals.
- Airborne collection: the use of airborne sensors and systems, such as aircraft and drones, to intercept and analyze signals.
- Space-based collection: the use of space-based sensors and systems, such as satellites, to intercept and analyze signals.
Ground-Based Collection
Ground-based collection involves the use of ground-based sensors and systems to intercept and analyze signals. This can include the use of fixed and mobile sensors, as well as specialized systems designed to intercept and analyze specific types of signals.Signals Intelligence Analysis and Dissemination

SIGINT analysis and dissemination involve the examination and interpretation of intercepted signals, as well as the dissemination of intelligence products to authorized recipients. This can include the use of specialized software and systems to analyze and visualize signals, as well as the creation of intelligence reports and briefings.
Signals Intelligence Reporting
SIGINT reporting involves the creation and dissemination of intelligence products, such as reports and briefings, to authorized recipients. These products can provide valuable insights into an adversary's capabilities and intentions, as well as identify potential security threats.Challenges and Limitations of Signals Intelligence

Despite its importance and effectiveness, SIGINT is not without its challenges and limitations. These can include:
- The increasing use of secure communications protocols and encryption, which can make it difficult to intercept and analyze signals.
- The proliferation of advanced electronic countermeasures, which can disrupt or destroy SIGINT collection systems.
- The need for specialized technical expertise and equipment, which can be costly and difficult to maintain.
Future of Signals Intelligence
The future of SIGINT is likely to be shaped by advances in technology, as well as evolving geopolitical and security trends. This can include the increasing use of artificial intelligence and machine learning to analyze and interpret signals, as well as the development of new SIGINT collection systems and methods.Signals Intelligence Image Gallery








What is signals intelligence?
+Signals intelligence is the interception, analysis, and dissemination of signals, which can include communications, radar emissions, and other forms of electromagnetic radiation.
What are the types of signals intelligence?
+There are several types of SIGINT, including communications intelligence (COMINT), electronic intelligence (ELINT), and foreign instrumentation signals intelligence (FISINT).
What are the challenges and limitations of signals intelligence?
+Despite its importance and effectiveness, SIGINT is not without its challenges and limitations, including the increasing use of secure communications protocols and encryption, the proliferation of advanced electronic countermeasures, and the need for specialized technical expertise and equipment.
In conclusion, signals intelligence is a complex and fascinating field that plays a critical role in modern espionage and military operations. By intercepting and analyzing signals, governments and organizations can gather vital information about their adversaries, informing decision-making at the highest levels of government and military command. As the world of SIGINT continues to evolve, it is likely that new technologies and methods will emerge, providing even greater insights into the capabilities and intentions of adversaries. Whether you are a seasoned intelligence professional or simply interested in the world of espionage, signals intelligence is a topic that is sure to captivate and intrigue. We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about SIGINT in the comments below, and to explore the many resources and references available on this fascinating topic.
