Intro
Discover the Selective Reserve definition, a military concept involving part-time soldiers, reserve forces, and national defense strategies, utilizing mobilization and deployment tactics.
The concept of a selective reserve is crucial in various fields, including finance, human resources, and environmental conservation. It refers to the practice of setting aside a portion of resources, assets, or personnel for specific purposes, often to ensure their availability when needed most. This approach allows for the efficient management of resources, minimizing waste and optimizing their utilization. In this article, we will delve into the importance of selective reserve, its benefits, and its applications across different sectors.
The selective reserve concept is essential in today's fast-paced world, where uncertainty and unpredictability are inherent. By allocating a portion of resources as a reserve, individuals, organizations, and governments can mitigate risks, respond to emergencies, and capitalize on opportunities as they arise. This strategic approach enables entities to adapt to changing circumstances, ensuring their resilience and competitiveness in an ever-evolving environment. Whether it's a financial safety net, a talent pool, or a natural resource reserve, the selective reserve concept plays a vital role in achieving long-term sustainability and success.
The significance of selective reserve cannot be overstated, as it offers numerous benefits, including enhanced flexibility, improved risk management, and increased efficiency. By maintaining a reserve, entities can respond promptly to unexpected events, such as economic downturns, natural disasters, or talent shortages. This proactive approach enables them to stay ahead of the curve, minimizing the impact of disruptions and maximizing opportunities for growth. Moreover, a selective reserve can serve as a buffer against uncertainties, providing a sense of security and stability in an unpredictable world.
Understanding Selective Reserve
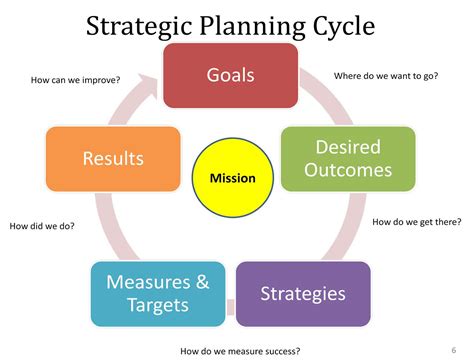
To grasp the concept of selective reserve, it's essential to understand its underlying principles and mechanisms. A selective reserve is created by allocating a portion of resources, which can be financial, human, or natural, for specific purposes. This allocation is based on a thorough analysis of needs, risks, and opportunities, ensuring that the reserve is tailored to address potential challenges and capitalize on prospects. The selective reserve is then managed and maintained to ensure its availability and effectiveness when needed.
Key Characteristics of Selective Reserve
The selective reserve concept is characterized by several key features, including: * Strategic allocation: Resources are allocated based on a thorough analysis of needs, risks, and opportunities. * Proactive management: The reserve is managed and maintained to ensure its availability and effectiveness. * Flexibility: The reserve can be adjusted and adapted to respond to changing circumstances. * Efficiency: The reserve is optimized to minimize waste and maximize utilization.Applications of Selective Reserve

The selective reserve concept has numerous applications across various sectors, including:
- Finance: A financial reserve can provide a safety net against economic downturns, enabling individuals and organizations to weather financial storms.
- Human Resources: A talent pool or reserve can help organizations respond to talent shortages, ensuring they have the skills and expertise needed to drive growth.
- Environmental Conservation: A natural resource reserve can help conserve and protect vital resources, such as water, land, and biodiversity.
Benefits of Selective Reserve
The benefits of selective reserve are numerous, including: * Enhanced flexibility: A reserve provides the ability to respond to changing circumstances and capitalize on opportunities. * Improved risk management: A reserve can mitigate risks and minimize the impact of disruptions. * Increased efficiency: A reserve can optimize resource utilization, minimizing waste and maximizing effectiveness.Implementing Selective Reserve

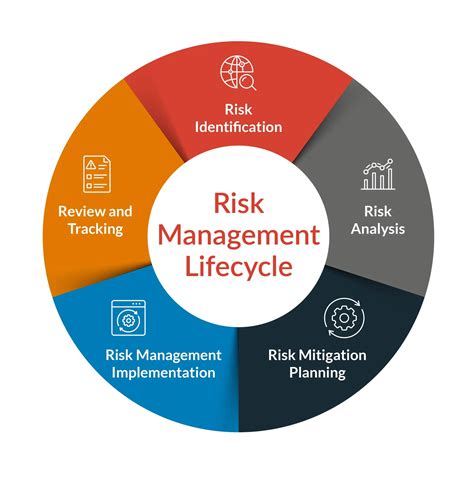
Implementing a selective reserve requires a thorough analysis of needs, risks, and opportunities. This involves:
- Identifying resources: Determining which resources to allocate to the reserve.
- Assessing risks: Evaluating potential risks and challenges to determine the optimal size and composition of the reserve.
- Establishing goals: Defining the objectives and purposes of the reserve.
- Managing the reserve: Ensuring the reserve is maintained and optimized to ensure its availability and effectiveness.
Best Practices for Selective Reserve
To ensure the effectiveness of a selective reserve, it's essential to follow best practices, including: * Regular review and assessment: Periodically reviewing and assessing the reserve to ensure it remains relevant and effective. * Adaptive management: Adjusting and adapting the reserve to respond to changing circumstances. * Transparency and accountability: Ensuring transparency and accountability in the management and maintenance of the reserve.Challenges and Limitations of Selective Reserve
While the selective reserve concept offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges and limitations, including:
- Opportunity costs: Allocating resources to a reserve may mean forgoing other opportunities or investments.
- Maintenance and management: Ensuring the reserve remains effective and relevant requires ongoing management and maintenance.
- Uncertainty: The selective reserve concept is based on predictions and assumptions, which may not always be accurate.
Overcoming Challenges and Limitations
To overcome the challenges and limitations of selective reserve, it's essential to: * Conduct thorough analysis: Ensuring that the reserve is based on a thorough analysis of needs, risks, and opportunities. * Monitor and adjust: Regularly monitoring and adjusting the reserve to respond to changing circumstances. * Diversify: Diversifying the reserve to minimize risks and maximize opportunities.Real-World Examples of Selective Reserve
The selective reserve concept has numerous real-world applications, including:
- Financial reserves: Individuals and organizations maintaining financial reserves to weather economic downturns.
- Talent pools: Companies establishing talent pools to respond to talent shortages.
- Natural resource reserves: Governments and organizations establishing natural resource reserves to conserve and protect vital resources.
Case Studies
Case studies of selective reserve include: * A company establishing a financial reserve to weather an economic downturn. * A government establishing a natural resource reserve to conserve and protect biodiversity. * An individual establishing a talent pool to respond to talent shortages.Future of Selective Reserve

The future of selective reserve is promising, with emerging trends and technologies enabling more efficient and effective management of reserves. These include:
- Advanced analytics: Utilizing advanced analytics to optimize reserve management and maintenance.
- Artificial intelligence: Leveraging artificial intelligence to predict and respond to changing circumstances.
- Blockchain: Utilizing blockchain technology to ensure transparency and accountability in reserve management.
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in selective reserve include: * Increased focus on sustainability: Ensuring that reserves are managed and maintained in a sustainable and responsible manner. * Growing importance of technology: Leveraging technology to optimize reserve management and maintenance. * Evolving regulatory landscape: Responding to changing regulatory requirements and standards.Gallery of Selective Reserve







What is selective reserve?
+Selective reserve refers to the practice of setting aside a portion of resources, assets, or personnel for specific purposes, often to ensure their availability when needed most.
What are the benefits of selective reserve?
+The benefits of selective reserve include enhanced flexibility, improved risk management, and increased efficiency.
How is selective reserve implemented?
+Implementing selective reserve requires a thorough analysis of needs, risks, and opportunities, followed by the allocation and management of resources.
What are the challenges and limitations of selective reserve?
+The challenges and limitations of selective reserve include opportunity costs, maintenance and management, and uncertainty.
What is the future of selective reserve?
+The future of selective reserve is promising, with emerging trends and technologies enabling more efficient and effective management of reserves.
In conclusion, the selective reserve concept is a vital strategy for managing resources, mitigating risks, and capitalizing on opportunities. By understanding the principles, benefits, and applications of selective reserve, individuals, organizations, and governments can optimize their resource allocation, ensure their resilience, and drive growth. As the world becomes increasingly complex and unpredictable, the importance of selective reserve will only continue to grow, making it an essential tool for achieving success and sustainability in various fields. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and insights on the selective reserve concept, and we look forward to continuing the conversation on this critical topic.
