Intro
Discover Mach 2 speed, a supersonic velocity twice the speed of sound, exploring aerodynamics, sonic booms, and high-speed flight, with insights into aircraft design and performance optimization.
The concept of speed has always fascinated humans, and achieving high speeds has been a constant pursuit in various fields, including aviation, automotive, and space exploration. One term that is often used to describe extremely high speeds is "Mach 2." But what exactly does Mach 2 speed mean, and how is it achieved? In this article, we will delve into the world of high-speed flight and explore the significance of Mach 2 speed.
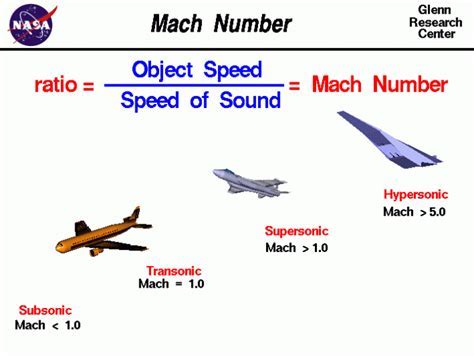
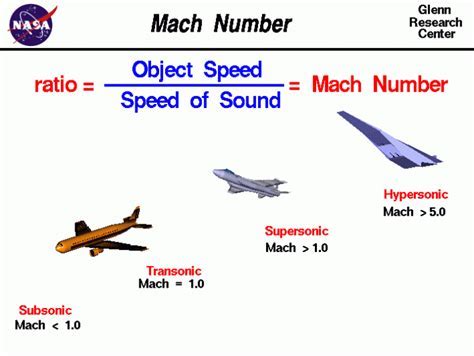
Mach 2 speed refers to an object moving at twice the speed of sound, which is approximately 1,472 miles per hour (2,370 kilometers per hour) at sea level in dry air at a temperature of 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius). To put this in perspective, the speed of sound is the fastest speed at which any object can travel in the atmosphere, and it is the speed at which sound waves propagate through the air. When an object breaks the sound barrier, it is said to be traveling at supersonic speeds. Mach 2 speed is a significant milestone in the field of aerodynamics, as it represents a major achievement in designing and building vehicles that can withstand the intense forces and heat generated by traveling at such high speeds.
The study of high-speed flight has led to numerous breakthroughs in our understanding of aerodynamics and the development of new materials and technologies. For instance, the design of supersonic aircraft requires careful consideration of the aerodynamic forces that act upon the vehicle, including drag, lift, and thrust. Additionally, the materials used in the construction of these aircraft must be able to withstand the extreme temperatures and stresses generated by high-speed flight. The pursuit of Mach 2 speed has driven innovation in fields such as materials science, computer simulations, and wind tunnel testing.
Introduction to Mach 2 Speed

The concept of Mach 2 speed is closely related to the speed of sound, which is a fundamental constant in physics. The speed of sound is the fastest speed at which any object can travel in the atmosphere, and it is the speed at which sound waves propagate through the air. When an object breaks the sound barrier, it is said to be traveling at supersonic speeds. The speed of sound is approximately 768 miles per hour (1,236 kilometers per hour) at sea level in dry air at a temperature of 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius). However, this speed can vary depending on factors such as altitude, temperature, and air pressure.
History of Mach 2 Speed
The history of Mach 2 speed dates back to the early 20th century, when scientists and engineers began to explore the possibilities of supersonic flight. One of the pioneers in this field was Chuck Yeager, an American test pilot who became the first person to break the sound barrier in 1947. Yeager flew a Bell X-1 rocket-powered aircraft at a speed of Mach 1.06, which is approximately 700 miles per hour (1,127 kilometers per hour). Since then, numerous aircraft have been designed and built to achieve Mach 2 speed, including the Lockheed F-104 Starfighter, the McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II, and the Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-25.Benefits of Mach 2 Speed
The benefits of Mach 2 speed are numerous and significant. For instance, supersonic aircraft can travel long distances in a relatively short period, making them ideal for military and reconnaissance missions. Additionally, Mach 2 speed can be used to launch satellites and spacecraft into orbit, reducing the time and energy required for these missions. Furthermore, the study of high-speed flight has led to numerous breakthroughs in our understanding of aerodynamics and the development of new materials and technologies.
Some of the key benefits of Mach 2 speed include:
- Reduced travel time: Supersonic aircraft can travel long distances in a relatively short period, making them ideal for military and reconnaissance missions.
- Increased efficiency: Mach 2 speed can be used to launch satellites and spacecraft into orbit, reducing the time and energy required for these missions.
- Improved safety: Supersonic aircraft can avoid hostile territory and enemy fire, reducing the risk of damage or loss.
- Enhanced reconnaissance: Mach 2 speed enables aircraft to gather intelligence and conduct surveillance missions quickly and efficiently.
Challenges of Mach 2 Speed
Despite the numerous benefits of Mach 2 speed, there are several challenges associated with achieving and maintaining such high speeds. For instance, supersonic aircraft must be designed to withstand the intense forces and heat generated by high-speed flight. Additionally, the materials used in the construction of these aircraft must be able to withstand the extreme temperatures and stresses generated by high-speed flight. Furthermore, the control systems and avionics of supersonic aircraft must be highly advanced to ensure stable and controlled flight.Some of the key challenges of Mach 2 speed include:
- Aerodynamic forces: Supersonic aircraft must be designed to withstand the intense forces generated by high-speed flight, including drag, lift, and thrust.
- Heat generation: High-speed flight generates intense heat, which can damage the aircraft's structure and systems.
- Materials science: The materials used in the construction of supersonic aircraft must be able to withstand the extreme temperatures and stresses generated by high-speed flight.
- Control systems: The control systems and avionics of supersonic aircraft must be highly advanced to ensure stable and controlled flight.
Applications of Mach 2 Speed
The applications of Mach 2 speed are numerous and varied. For instance, supersonic aircraft can be used for military and reconnaissance missions, launching satellites and spacecraft into orbit, and conducting scientific research. Additionally, Mach 2 speed can be used in the development of high-speed transportation systems, such as supersonic business jets and hypersonic vehicles.
Some of the key applications of Mach 2 speed include:
- Military and reconnaissance missions: Supersonic aircraft can be used to conduct surveillance and reconnaissance missions, as well as to launch missiles and bombs.
- Space exploration: Mach 2 speed can be used to launch satellites and spacecraft into orbit, reducing the time and energy required for these missions.
- Scientific research: Supersonic aircraft can be used to conduct scientific research, such as studying the upper atmosphere and the effects of high-speed flight on materials and systems.
- High-speed transportation: Mach 2 speed can be used in the development of high-speed transportation systems, such as supersonic business jets and hypersonic vehicles.
Future of Mach 2 Speed
The future of Mach 2 speed is exciting and promising. With advances in materials science, computer simulations, and wind tunnel testing, it is likely that supersonic aircraft will become faster, more efficient, and more affordable. Additionally, the development of new technologies, such as scramjets and hypersonic vehicles, will enable aircraft to travel at even higher speeds, potentially exceeding Mach 5 or Mach 10.Some of the key trends and developments in the future of Mach 2 speed include:
- Advances in materials science: New materials and technologies will enable the construction of supersonic aircraft that are stronger, lighter, and more efficient.
- Computer simulations: Advanced computer simulations will enable engineers to design and test supersonic aircraft more efficiently and effectively.
- Wind tunnel testing: Advances in wind tunnel testing will enable engineers to test and evaluate supersonic aircraft more accurately and reliably.
- Scramjets and hypersonic vehicles: The development of scramjets and hypersonic vehicles will enable aircraft to travel at even higher speeds, potentially exceeding Mach 5 or Mach 10.
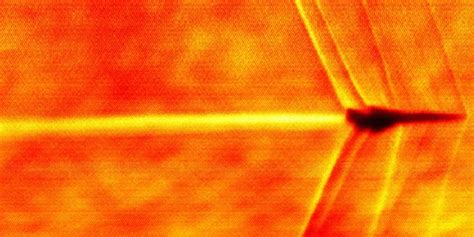
Gallery of Mach 2 Speed
Mach 2 Speed Image Gallery








Frequently Asked Questions
What is Mach 2 speed?
+Mach 2 speed refers to an object moving at twice the speed of sound, which is approximately 1,472 miles per hour (2,370 kilometers per hour) at sea level in dry air at a temperature of 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius).
What are the benefits of Mach 2 speed?
+The benefits of Mach 2 speed include reduced travel time, increased efficiency, improved safety, and enhanced reconnaissance capabilities.
What are the challenges of Mach 2 speed?
+The challenges of Mach 2 speed include aerodynamic forces, heat generation, materials science, and control systems.
What are the applications of Mach 2 speed?
+The applications of Mach 2 speed include military and reconnaissance missions, space exploration, scientific research, and high-speed transportation.
What is the future of Mach 2 speed?
+The future of Mach 2 speed is exciting and promising, with advances in materials science, computer simulations, and wind tunnel testing enabling the development of faster, more efficient, and more affordable supersonic aircraft.
In conclusion, Mach 2 speed is a significant milestone in the field of aerodynamics, representing a major achievement in designing and building vehicles that can withstand the intense forces and heat generated by traveling at such high speeds. The benefits of Mach 2 speed are numerous and significant, including reduced travel time, increased efficiency, improved safety, and enhanced reconnaissance capabilities. As research and development continue to advance, it is likely that supersonic aircraft will become faster, more efficient, and more affordable, enabling new applications and opportunities in fields such as military and reconnaissance missions, space exploration, scientific research, and high-speed transportation. We invite you to share your thoughts and comments on the topic of Mach 2 speed and its applications, and to explore the numerous resources and references available on this fascinating subject.
