Intro
Discover 5 ways job manufacturing works, leveraging production planning, supply chain management, and lean manufacturing techniques to optimize workflow, reduce costs, and increase efficiency in modern manufacturing processes and systems.
The manufacturing industry has undergone significant transformations over the years, driven by advances in technology, changes in consumer demand, and the need for increased efficiency. At the heart of this industry is job manufacturing, a process that involves the production of custom or specialty products in limited quantities. Understanding how job manufacturing works is crucial for businesses and individuals looking to navigate this complex and highly specialized field. In this article, we will delve into the world of job manufacturing, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and the steps involved in this process.
Job manufacturing is a critical component of the manufacturing sector, allowing companies to produce unique products that cater to specific customer needs. This approach is particularly useful for businesses that require small batches of customized products, such as aerospace components, medical devices, or precision instruments. By adopting job manufacturing techniques, companies can reduce production costs, improve product quality, and enhance their competitiveness in the global market. Furthermore, job manufacturing enables businesses to respond quickly to changing customer demands, making it an essential strategy for companies operating in dynamic and fast-paced industries.
The importance of job manufacturing cannot be overstated, as it plays a vital role in driving innovation and economic growth. By facilitating the production of custom products, job manufacturing helps to foster entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation, allowing companies to develop new products and services that meet the evolving needs of their customers. Additionally, job manufacturing creates employment opportunities, both directly and indirectly, contributing to the overall health and prosperity of local economies. As the manufacturing industry continues to evolve, job manufacturing is likely to remain a key driver of growth, innovation, and competitiveness.
Introduction to Job Manufacturing

Benefits of Job Manufacturing
The benefits of job manufacturing are numerous, ranging from improved product quality to increased competitiveness. Some of the key advantages of job manufacturing include: * Improved product quality: Job manufacturing allows companies to focus on producing high-quality products that meet the specific needs of their customers. * Increased flexibility: Job manufacturing enables businesses to respond quickly to changing customer demands, making it an essential strategy for companies operating in dynamic and fast-paced industries. * Reduced production costs: By producing products in limited quantities, companies can reduce their production costs and improve their profitability. * Enhanced competitiveness: Job manufacturing helps businesses to differentiate themselves from their competitors, improving their competitiveness in the global market. * Improved customer satisfaction: By producing custom products that meet the specific needs of their customers, businesses can improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.How Job Manufacturing Works
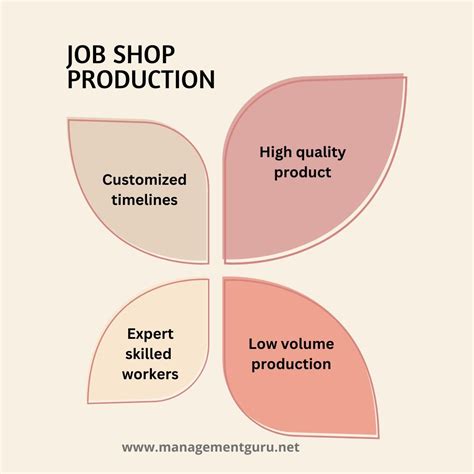
Steps Involved in Job Manufacturing
The steps involved in job manufacturing are critical to the success of the production process. The following are some of the key steps involved in job manufacturing: * Design and planning: Creating detailed specifications, selecting materials, and determining the production schedule. * Material selection: Sourcing raw materials, purchasing components, and ensuring that all materials meet the required quality standards. * Production: Manufacturing the product using specialized equipment and techniques, including machining, assembly, and testing. * Quality control: Inspecting the product, testing its performance, and ensuring that it meets the required quality standards. * Packaging and shipping: Preparing the product for shipping, including packaging, labeling, and documentation.Types of Job Manufacturing

Applications of Job Manufacturing
Job manufacturing has a wide range of applications, from aerospace and defense to medical devices and precision instruments. The following are some of the most common applications of job manufacturing: * Aerospace and defense: Job manufacturing is used to produce custom components and systems for the aerospace and defense industries. * Medical devices: Job manufacturing is used to produce custom medical devices, such as implants, prosthetics, and surgical instruments. * Precision instruments: Job manufacturing is used to produce precision instruments, such as watches, clocks, and scientific instruments. * Automotive: Job manufacturing is used to produce custom components and systems for the automotive industry.Challenges and Opportunities in Job Manufacturing

Future of Job Manufacturing
The future of job manufacturing is likely to be shaped by advances in technology, changes in consumer demand, and the need for increased efficiency. The following are some of the key trends and developments that are likely to shape the future of job manufacturing: * Increased use of automation and robotics: Automation and robotics are likely to play a major role in job manufacturing, improving efficiency and reducing production costs. * Greater emphasis on sustainability: Job manufacturing is likely to place a greater emphasis on sustainability, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact. * Increased use of advanced materials: Job manufacturing is likely to involve the use of advanced materials, such as composites and nanomaterials, to improve product performance and reduce production costs. * Greater focus on customer satisfaction: Job manufacturing is likely to place a greater focus on customer satisfaction, producing custom products that meet the specific needs of individual customers.Job Manufacturing Image Gallery
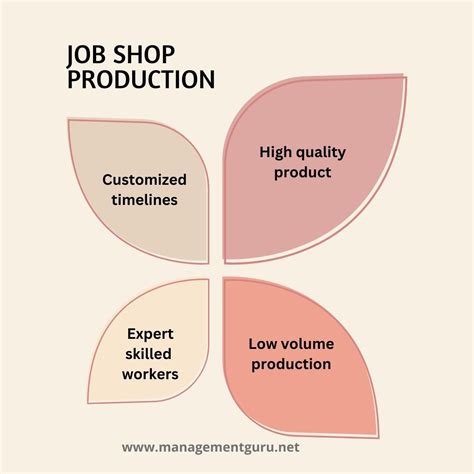









What is job manufacturing?
+Job manufacturing is a process that involves the production of custom or specialty products in limited quantities.
What are the benefits of job manufacturing?
+The benefits of job manufacturing include improved product quality, increased flexibility, reduced production costs, enhanced competitiveness, and improved customer satisfaction.
What are the steps involved in job manufacturing?
+The steps involved in job manufacturing include design and planning, material selection, production, quality control, and packaging and shipping.
What are the types of job manufacturing?
+The types of job manufacturing include custom manufacturing, specialty manufacturing, precision manufacturing, and batch manufacturing.
What is the future of job manufacturing?
+The future of job manufacturing is likely to be shaped by advances in technology, changes in consumer demand, and the need for increased efficiency, with a greater emphasis on sustainability, automation, and customer satisfaction.
In conclusion, job manufacturing is a critical component of the manufacturing industry, allowing companies to produce custom or specialty products in limited quantities. By understanding the benefits, working mechanisms, and steps involved in job manufacturing, businesses can improve their competitiveness, reduce production costs, and enhance their reputation for quality and reliability. As the manufacturing industry continues to evolve, job manufacturing is likely to remain a key driver of growth, innovation, and competitiveness. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with job manufacturing, and to explore the many resources and opportunities available in this exciting and dynamic field. Whether you are a business owner, entrepreneur, or simply interested in learning more about job manufacturing, we encourage you to join the conversation and contribute to the ongoing discussion about the future of this critical industry.
