Intro
Discover the crucial infantry role in army operations, including combat tactics, military strategy, and ground warfare, highlighting the importance of foot soldiers in modern warfare and national defense.
The infantry is the backbone of any army, playing a crucial role in achieving military objectives. Infantry units are responsible for engaging enemy forces on the ground, using a variety of tactics and techniques to outmaneuver and defeat their opponents. The importance of infantry in modern warfare cannot be overstated, as they provide the necessary boots on the ground to secure territory, protect civilians, and conduct reconnaissance missions.
Throughout history, infantry has been the largest and most diverse branch of the military, with soldiers serving in a wide range of roles and specialties. From frontline combat troops to support personnel, infantry units rely on teamwork, discipline, and strategy to accomplish their missions. The infantry's versatility and adaptability make them an essential component of any military force, capable of operating in various environments and contexts.
In modern armies, the infantry is often organized into specialized units, each with its own unique capabilities and areas of expertise. These units may include light infantry, mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, and special forces, among others. Light infantry units, for example, are designed to be highly mobile and flexible, using speed and agility to outmaneuver enemy forces. Mechanized infantry units, on the other hand, rely on armored vehicles and heavy firepower to break through enemy lines and secure key terrain.
Infantry Tactics and Techniques
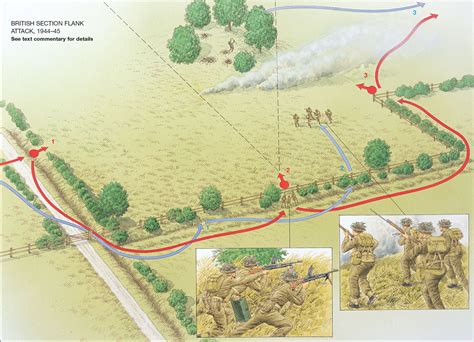
Infantry tactics and techniques are constantly evolving, as military forces adapt to new technologies, enemy strategies, and operational environments. Some of the key tactics and techniques used by infantry units include patrolling, ambushing, and flanking maneuvers. Patrolling involves sending small teams of soldiers into enemy territory to gather intelligence, conduct reconnaissance, and disrupt enemy supply lines. Ambushing involves setting up hidden positions to attack enemy forces as they move through a specific area, while flanking maneuvers involve attacking the enemy from the sides or rear to exploit vulnerabilities in their defenses.
Types of Infantry Units
Infantry units can be broadly categorized into several types, each with its own unique characteristics and capabilities. These include:- Light infantry: Designed to be highly mobile and flexible, using speed and agility to outmaneuver enemy forces.
- Mechanized infantry: Rely on armored vehicles and heavy firepower to break through enemy lines and secure key terrain.
- Airborne infantry: Trained to conduct parachute assaults and airland operations, using airborne insertion to rapidly deploy into enemy territory.
- Special forces: Elite units trained to conduct unconventional warfare, counterterrorism, and special reconnaissance missions.
Infantry Equipment and Weapons

Infantry equipment and weapons are designed to provide soldiers with the necessary tools to accomplish their missions. These may include small arms, such as rifles and machine guns, as well as heavier weapons, such as mortars and anti-tank missiles. Infantry units may also use a variety of specialized equipment, such as night vision goggles, body armor, and communication devices.
Some of the key infantry equipment and weapons include:
- Assault rifles: Designed for close-quarters combat, these rifles are highly versatile and effective in a variety of environments.
- Machine guns: Provide suppressive fire to pin down enemy forces and prevent them from returning fire.
- Mortars: Used to attack enemy positions and fortifications, mortars are highly effective in urban and mountainous terrain.
- Body armor: Designed to protect soldiers from small arms fire and shrapnel, body armor is an essential component of infantry equipment.
Infantry Training and Doctrine
Infantry training and doctrine are critical components of military effectiveness, as they provide soldiers with the necessary skills and knowledge to accomplish their missions. Infantry training typically includes basic combat skills, such as marksmanship and first aid, as well as more advanced skills, such as tactics and leadership.Some of the key aspects of infantry training and doctrine include:
- Basic combat skills: Marksmanship, first aid, and combat tactics.
- Advanced skills: Leadership, tactics, and operational planning.
- Unit training: Squad, platoon, and company-level training to develop teamwork and coordination.
- Joint training: Training with other branches and units to develop interoperability and coordination.
Infantry Operations in Modern Warfare

Infantry operations in modern warfare are highly complex and dynamic, involving a wide range of tactics, techniques, and technologies. Infantry units must be able to adapt to rapidly changing environments and operational contexts, using their training and experience to make quick decisions and take effective action.
Some of the key aspects of infantry operations in modern warfare include:
- Urban warfare: Fighting in cities and towns, where the enemy may be embedded among civilians.
- Counterinsurgency: Conducting operations to defeat insurgent or guerrilla forces, often in rural or mountainous terrain.
- Peacekeeping: Maintaining order and stability in post-conflict environments, often in cooperation with other military forces and civilian agencies.
- Humanitarian assistance: Providing aid and support to civilians affected by conflict or natural disasters.
Challenges Facing Infantry Units
Infantry units face a wide range of challenges in modern warfare, from enemy firepower and maneuverability to logistical and operational complexities. Some of the key challenges facing infantry units include:- Enemy firepower: The increasing use of precision-guided munitions and other advanced technologies has made the battlefield more lethal than ever before.
- Logistical challenges: Infantry units must often operate in remote or austere environments, where logistical support may be limited or unreliable.
- Operational complexity: Modern warfare often involves multiple branches and units, as well as coalition partners and civilian agencies, which can create operational complexities and challenges.
Future of Infantry Warfare

The future of infantry warfare is likely to be shaped by a wide range of technological, operational, and strategic factors. Some of the key trends and developments that are likely to shape the future of infantry warfare include:
- Increased use of autonomous systems: Autonomous vehicles, drones, and other systems are likely to play an increasingly important role in infantry operations.
- Advanced sensors and communications: The use of advanced sensors and communications systems will enable infantry units to gather and share information more quickly and effectively.
- Cyber warfare: Infantry units will need to be able to operate in a cyber-enabled environment, using cyber tools and techniques to disrupt enemy command and control systems.
Implications for Infantry Units
The future of infantry warfare will have significant implications for infantry units, from the way they train and operate to the equipment and technologies they use. Some of the key implications for infantry units include:- Increased emphasis on technological proficiency: Infantry soldiers will need to be proficient in the use of advanced technologies, including autonomous systems, sensors, and communications systems.
- Changing nature of combat: The increasing use of autonomous systems and cyber warfare will change the nature of combat, with infantry units needing to adapt to new threats and operational contexts.
- Greater emphasis on joint operations: Infantry units will need to be able to operate effectively with other branches and units, as well as coalition partners and civilian agencies.
Infantry Image Gallery










What is the role of infantry in modern warfare?
+The infantry plays a crucial role in modern warfare, providing the necessary boots on the ground to secure territory, protect civilians, and conduct reconnaissance missions.
What are the different types of infantry units?
+Infantry units can be broadly categorized into several types, including light infantry, mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, and special forces.
What are the key challenges facing infantry units in modern warfare?
+Infantry units face a wide range of challenges in modern warfare, including enemy firepower, logistical complexities, and operational complexities.
What is the future of infantry warfare?
+The future of infantry warfare is likely to be shaped by a wide range of technological, operational, and strategic factors, including the increasing use of autonomous systems, advanced sensors and communications, and cyber warfare.
How will infantry units need to adapt to the changing nature of combat?
+Infantry units will need to adapt to the changing nature of combat by developing new tactics, techniques, and procedures, as well as leveraging new technologies and capabilities.
In conclusion, the infantry plays a vital role in modern warfare, providing the necessary boots on the ground to secure territory, protect civilians, and conduct reconnaissance missions. As the nature of combat continues to evolve, infantry units will need to adapt to new challenges and operational contexts, leveraging new technologies and capabilities to remain effective. By understanding the importance of infantry in modern warfare, we can better appreciate the sacrifices and contributions of these brave men and women, and work to support and enable their success in the years to come. We invite you to share your thoughts and comments on the role of infantry in modern warfare, and to explore the many resources and references available on this topic.
