Intro
Discover the EOD military definition, exploring Explosive Ordnance Disposal techniques, bomb disposal methods, and military demining procedures, highlighting the crucial role of EOD specialists in ensuring military safety and security.
The term "EOD" is an acronym that stands for Explosive Ordnance Disposal, which refers to the process of safely disposing of or neutralizing explosive devices, such as bombs, grenades, and other types of munitions. In a military context, EOD is a critical function that requires specialized training and equipment to ensure the safety of personnel and the public.
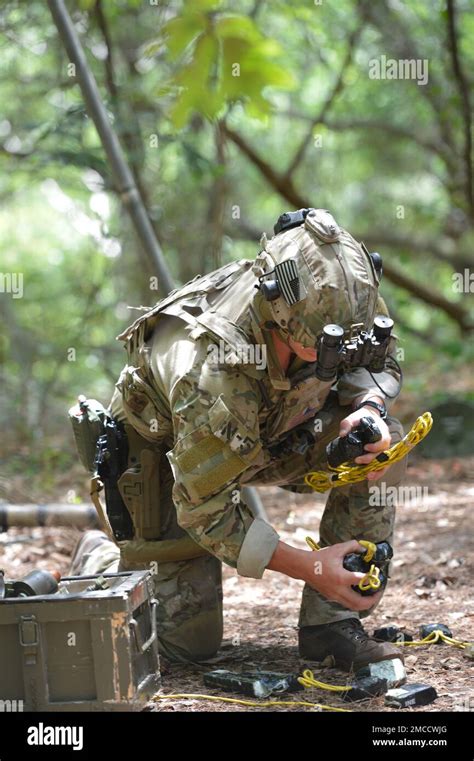
EOD teams are typically composed of highly trained military personnel who are experts in the identification, rendering safe, and disposal of explosive devices. These teams are often called upon to respond to a wide range of situations, including bomb threats, improvised explosive device (IED) attacks, and the discovery of unexploded ordnance (UXO). The primary goal of EOD teams is to prevent harm to people and property by safely disposing of explosive devices, and to gather intelligence on the devices and their manufacturers.
The importance of EOD in military operations cannot be overstated. Explosive devices are a major threat to military personnel and civilians, and the ability to safely dispose of them is critical to maintaining security and stability in conflict zones. EOD teams play a vital role in supporting military operations, and their work is often carried out in high-risk environments, such as combat zones and disaster areas.
EOD Military Operations

EOD military operations involve a range of activities, including the identification and rendering safe of explosive devices, the disposal of UXO, and the provision of training and support to other military units. EOD teams use a variety of techniques and equipment to perform their duties, including bomb suits, robotic systems, and explosive detection equipment. These teams are also responsible for investigating the scene of an explosion, gathering evidence, and providing intelligence on the device and its manufacturer.
The work of EOD teams is highly specialized and requires a great deal of training and expertise. EOD technicians must be able to identify and render safe a wide range of explosive devices, including bombs, grenades, and other types of munitions. They must also be able to work in high-stress environments, often with limited resources and under intense pressure.
EOD Equipment and Techniques
EOD teams use a variety of equipment and techniques to perform their duties, including: * Bomb suits: These are specialized suits that provide protection against explosive blasts and shrapnel. * Robotic systems: These are remotely controlled robots that can be used to inspect and dispose of explosive devices. * Explosive detection equipment: This includes equipment such as metal detectors and explosive sniffing dogs. * Disruptors: These are devices that can be used to disrupt or destroy explosive devices. * Explosive ordnance disposal tools: These are specialized tools that are used to render safe and dispose of explosive devices.EOD Training and Certification

EOD training and certification are critical components of the EOD program. EOD technicians must undergo extensive training and certification before they are qualified to perform EOD duties. This training includes classroom instruction, hands-on training, and field exercises, and covers a range of topics, including explosive theory, bomb construction, and render safe procedures.
The certification process for EOD technicians typically involves a series of tests and evaluations, including written exams, practical exercises, and performance evaluations. EOD technicians must also complete regular training and certification updates to ensure that they remain current and proficient in their skills.
EOD Career Paths
There are several career paths available to EOD technicians, including: * Military service: EOD technicians can serve in the military, where they can work in a variety of roles, including EOD team leader, EOD technician, and instructor. * Law enforcement: EOD technicians can work in law enforcement, where they can provide EOD support to police departments and other law enforcement agencies. * Private industry: EOD technicians can work in private industry, where they can provide EOD services to companies and organizations. * Government agencies: EOD technicians can work in government agencies, such as the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF).EOD Safety Protocols

EOD safety protocols are critical to ensuring the safety of EOD technicians and the public. These protocols include:
- Risk assessment: EOD technicians must conduct a thorough risk assessment before attempting to render safe or dispose of an explosive device.
- Safety equipment: EOD technicians must wear safety equipment, including bomb suits and protective gear, when working with explosive devices.
- Communication: EOD technicians must maintain clear communication with other team members and with command centers during EOD operations.
- Contingency planning: EOD technicians must have a contingency plan in place in case of an emergency or unexpected event.
EOD Challenges and Future Directions
The EOD field is constantly evolving, with new challenges and threats emerging all the time. Some of the current challenges facing EOD teams include: * Improvised explosive devices (IEDs): IEDs are a major threat to military personnel and civilians, and require specialized training and equipment to detect and dispose of. * Unexploded ordnance (UXO): UXO is a major problem in many parts of the world, and requires specialized training and equipment to detect and dispose of. * Cyber threats: Cyber threats are a growing concern for EOD teams, who must be able to detect and mitigate cyber attacks on EOD systems and equipment.In terms of future directions, the EOD field is likely to continue to evolve and adapt to new challenges and threats. Some of the potential future directions for EOD include:
- Increased use of robotics and autonomous systems: Robotics and autonomous systems are likely to play an increasingly important role in EOD operations, allowing EOD technicians to work more safely and efficiently.
- Improved explosive detection equipment: New technologies, such as advanced sensors and detection systems, are likely to improve the ability of EOD teams to detect and dispose of explosive devices.
- Enhanced training and certification: The EOD field is likely to continue to require highly specialized training and certification, with a focus on emerging threats and technologies.
EOD Image Gallery









What is EOD?
+EOD stands for Explosive Ordnance Disposal, which refers to the process of safely disposing of or neutralizing explosive devices.
What do EOD technicians do?
+EOD technicians are responsible for identifying, rendering safe, and disposing of explosive devices, as well as providing training and support to other military units.
What kind of training do EOD technicians receive?
+EOD technicians receive extensive training and certification, including classroom instruction, hands-on training, and field exercises, to ensure that they are qualified to perform EOD duties.
What are some of the challenges facing EOD teams?
+Some of the challenges facing EOD teams include improvised explosive devices (IEDs), unexploded ordnance (UXO), and cyber threats, which require specialized training and equipment to detect and dispose of.
What is the future of EOD?
+The future of EOD is likely to involve increased use of robotics and autonomous systems, improved explosive detection equipment, and enhanced training and certification, as well as a focus on emerging threats and technologies.
In conclusion, the EOD field is a critical component of military operations, requiring specialized training and equipment to ensure the safety of personnel and the public. EOD technicians play a vital role in supporting military operations, and their work is often carried out in high-risk environments. As the EOD field continues to evolve, it is likely to involve increased use of technology, improved training and certification, and a focus on emerging threats and challenges. If you have any questions or comments about EOD, please feel free to share them below.
