Intro
Discover what a reservist is, exploring military reserve roles, benefits, and requirements, including part-time service, deployment, and veteran advantages.
The role of a reservist is often misunderstood, yet it is a vital component of a country's defense and security strategy. Reservists are individuals who have chosen to serve their country on a part-time basis, balancing their military obligations with civilian careers and personal lives. In this article, we will delve into the world of reservists, exploring their importance, benefits, and the various ways they contribute to national defense.
Reservists are essential to the military's ability to respond to crises and conflicts. They bring a unique set of skills and experiences to the table, having developed expertise in their civilian careers that can be applied to military operations. This blend of military and civilian expertise enables reservists to provide valuable support to active-duty personnel, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the military. Moreover, reservists often serve as a link between the military and the community, fostering greater understanding and cooperation between the two.
The benefits of being a reservist are numerous. Not only do reservists have the opportunity to serve their country and make a meaningful contribution to national defense, but they also gain valuable skills and experiences that can be applied to their civilian careers. Reservists receive training and education in areas such as leadership, communication, and problem-solving, which can be highly beneficial in the civilian workforce. Additionally, reservists are entitled to certain benefits, such as education assistance and healthcare, which can be a significant advantage for those seeking to balance their military and civilian lives.
Introduction to Reservist Roles

Reservists can serve in a variety of roles, depending on their skills, interests, and civilian careers. Some reservists may serve in combat positions, such as infantry or artillery, while others may work in support roles, such as logistics or administration. There are also reservists who serve in specialized fields, such as medicine, engineering, or intelligence. Regardless of their role, reservists are an integral part of the military team, providing critical support and expertise to active-duty personnel.
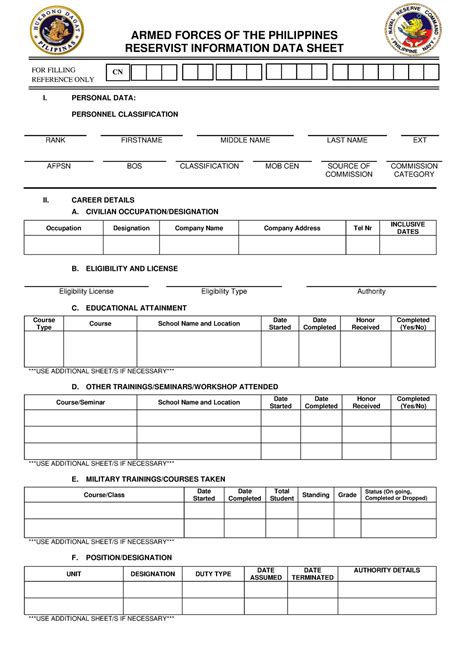
The process of becoming a reservist typically involves several steps. First, individuals must meet the basic eligibility requirements, which include being a citizen of the country, being between the ages of 17 and 35, and meeting certain physical and educational standards. Once these requirements are met, individuals can enlist in the reserves, either through a recruiter or online. After enlisting, reservists will attend basic training, where they will learn the fundamentals of military service and begin their training in their chosen specialty.
Benefits of Being a Reservist
The benefits of being a reservist are numerous and can have a significant impact on an individual's life. One of the most significant benefits is the opportunity to serve one's country and make a meaningful contribution to national defense. Reservists also gain valuable skills and experiences that can be applied to their civilian careers, such as leadership, communication, and problem-solving. Additionally, reservists are entitled to certain benefits, such as education assistance and healthcare, which can be a significant advantage for those seeking to balance their military and civilian lives.
Reservists also have the opportunity to develop a sense of camaraderie and esprit de corps with their fellow soldiers. The bonds formed through shared experiences and challenges can last a lifetime, providing a sense of belonging and connection that is hard to find in civilian life. Furthermore, reservists have the opportunity to travel and experience new cultures, both within their own country and abroad. This can be a valuable experience, broadening one's perspective and understanding of the world.
Types of Reservists

There are several types of reservists, each with their own unique role and responsibilities. The most common type of reservist is the traditional reservist, who serves one weekend a month and two weeks a year. These reservists typically work in support roles, such as logistics or administration, and provide critical support to active-duty personnel. There are also reservists who serve in specialized fields, such as medicine or engineering, and provide expertise in these areas.
Another type of reservist is the individual ready reserve (IRR) member. These individuals have previously served in the military and have agreed to remain on active status, but are not currently assigned to a unit. IRR members can be called back to active duty in times of crisis or conflict, providing a valuable source of experienced personnel. There are also reservists who serve in the national guard, which is a reserve component of the military that is organized at the state level. National guard members can be called upon to respond to natural disasters or other emergencies, as well as to support military operations.
Reservist Training and Education

Reservists receive training and education in a variety of areas, depending on their role and responsibilities. This training can include basic military skills, such as first aid and combat techniques, as well as specialized training in areas such as logistics or administration. Reservists also have the opportunity to attend advanced training courses, such as leadership or language training, which can be beneficial for their civilian careers.
The training and education provided to reservists are designed to prepare them for the challenges of military service, as well as to enhance their skills and knowledge in their chosen specialty. Reservists typically attend training one weekend a month and two weeks a year, although this can vary depending on their role and responsibilities. This training can be physically and mentally demanding, but it provides reservists with the skills and confidence they need to perform their duties effectively.
Reservist Deployment and Mobilization

Reservists can be deployed or mobilized in times of crisis or conflict, providing critical support to active-duty personnel. This can be a challenging and demanding experience, requiring reservists to leave their civilian careers and families behind. However, it also provides reservists with the opportunity to make a meaningful contribution to national defense and to serve their country in a time of need.
The process of deployment or mobilization typically involves several steps. First, reservists are notified of their deployment or mobilization, which can occur with little warning. They are then required to report to their unit, where they will receive further instructions and training. Once deployed or mobilized, reservists will perform their assigned duties, which can include combat, logistics, or administration. They will also have the opportunity to work with active-duty personnel and other reservists, providing critical support and expertise.
Reservist Support and Resources

Reservists have access to a variety of support and resources, designed to help them balance their military and civilian lives. This can include education assistance, healthcare, and financial support, as well as counseling and other forms of support. Reservists also have the opportunity to connect with other reservists and veterans, providing a sense of community and camaraderie.
The support and resources provided to reservists are designed to recognize the challenges and sacrifices they make in serving their country. Reservists often have to balance their military obligations with civilian careers and personal lives, which can be demanding and stressful. However, with the right support and resources, reservists can thrive in their roles and make a meaningful contribution to national defense.
Gallery of Reservist Images
Reservist Image Gallery










Frequently Asked Questions
What is a reservist?
+A reservist is an individual who serves in the military on a part-time basis, balancing their military obligations with civilian careers and personal lives.
What are the benefits of being a reservist?
+The benefits of being a reservist include education assistance, healthcare, and financial support, as well as the opportunity to develop valuable skills and experiences that can be applied to civilian careers.
How do I become a reservist?
+To become a reservist, individuals must meet the basic eligibility requirements, which include being a citizen of the country, being between the ages of 17 and 35, and meeting certain physical and educational standards. They can then enlist in the reserves, either through a recruiter or online.
What kind of training do reservists receive?
+Reservists receive training and education in a variety of areas, depending on their role and responsibilities. This can include basic military skills, specialized training, and advanced courses.
Can reservists be deployed or mobilized?
+Yes, reservists can be deployed or mobilized in times of crisis or conflict, providing critical support to active-duty personnel.
In conclusion, being a reservist is a rewarding and challenging experience that provides individuals with the opportunity to serve their country, develop valuable skills and experiences, and connect with others who share similar values and goals. Whether you are interested in serving in a combat role or providing support in a specialized field, the reserves offer a unique and fulfilling way to make a difference. If you are considering joining the reserves, we encourage you to explore the many benefits and opportunities that this path has to offer. Share your thoughts and experiences with us, and let's work together to build a stronger and more resilient community of reservists.
