Intro
Discover 5 crucial nuclear deterrent facts, exploring strategic defense, atomic warfare, and global security measures to prevent catastrophic conflicts.
The concept of nuclear deterrents has been a cornerstone of international relations and global security for decades. The idea that a country's possession of nuclear weapons can deter other nations from attacking it has been a topic of debate among scholars, policymakers, and the general public. In this article, we will delve into the world of nuclear deterrents and explore some fascinating facts about this complex and sensitive topic.
Nuclear deterrents have played a crucial role in maintaining global stability, particularly during the Cold War era. The threat of mutually assured destruction (MAD) was a significant factor in preventing direct conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union. However, the landscape of global security has changed significantly since the end of the Cold War, and the role of nuclear deterrents has evolved accordingly. Today, nuclear deterrents continue to be an essential component of a country's defense strategy, and their significance cannot be overstated.
The development and maintenance of nuclear deterrents are intricate and costly endeavors. The process involves significant investments in research and development, infrastructure, and personnel. Moreover, the possession of nuclear weapons comes with tremendous responsibilities, including ensuring the safety and security of these weapons, as well as complying with international non-proliferation agreements. As we explore the world of nuclear deterrents, it is essential to consider the complexities and challenges associated with these powerful weapons.
Nuclear Deterrent Basics

Types of Nuclear Deterrents
Nuclear deterrents can be categorized into two primary types: strategic and tactical. Strategic nuclear deterrents are designed to target an adversary's vital interests, such as its capital city, major population centers, or critical infrastructure. These weapons are typically characterized by their long range and high yield. Tactical nuclear deterrents, on the other hand, are designed for use on the battlefield and are typically characterized by their shorter range and lower yield.Nuclear Deterrent Strategies

Nuclear Deterrent Doctrine
A country's nuclear deterrent doctrine refers to its official policy regarding the use of nuclear weapons. This doctrine outlines the circumstances under which a country would consider using nuclear weapons, as well as the types of targets that would be prioritized. Nuclear deterrent doctrine can be influenced by a range of factors, including a country's strategic culture, its relationships with other nations, and its perceptions of the threat environment.Nuclear Deterrent Systems
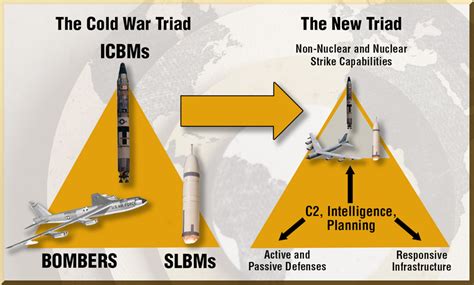
Nuclear Deterrent Modernization
The modernization of nuclear deterrent systems is an ongoing process, driven by advances in technology and changing threat environments. The development of new nuclear weapons, such as hypersonic missiles and advanced submarine-launched cruise missiles, has significant implications for global security. Moreover, the integration of emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and cyber capabilities, into nuclear deterrent systems raises important questions about the future of nuclear deterrence.Nuclear Deterrent Challenges

Nuclear Deterrent Ethics
The ethics of nuclear deterrence are complex and contentious, with some arguing that the possession of nuclear weapons is morally justifiable as a means of preventing war, while others contend that these weapons are inherently immoral. The use of nuclear weapons would have catastrophic consequences, including widespread death and destruction, as well as long-term environmental damage. As such, the development and deployment of nuclear deterrents raise important ethical questions about the morality of threatening to use these weapons.Nuclear Deterrent Future

Nuclear Deterrent Implications
The implications of nuclear deterrence are far-reaching, with significant consequences for global security, international relations, and human well-being. The possession of nuclear weapons by a growing number of countries increases the risk of nuclear conflict, while the development of advanced missile defense systems raises questions about the effectiveness of nuclear deterrents. As such, it is essential to consider the potential consequences of nuclear deterrence, including the risk of proliferation, the threat of terrorism, and the impact of emerging technologies.Nuclear Deterrent Gallery
Nuclear Deterrent Image Gallery










What is the purpose of nuclear deterrents?
+The purpose of nuclear deterrents is to prevent an adversary from attacking by threatening to inflict unacceptable damage in response.
What are the different types of nuclear deterrents?
+Nuclear deterrents can be categorized into two primary types: strategic and tactical. Strategic nuclear deterrents are designed to target an adversary's vital interests, while tactical nuclear deterrents are designed for use on the battlefield.
What are the challenges facing nuclear deterrents?
+Nuclear deterrents face a range of challenges, including the risk of proliferation, the threat of terrorism, and the impact of emerging technologies. The spread of nuclear weapons to new countries or non-state actors increases the risk of nuclear conflict, while the development of advanced missile defense systems raises questions about the effectiveness of nuclear deterrents.
What is the future of nuclear deterrence?
+The future of nuclear deterrence is uncertain, with a range of factors influencing the trajectory of these systems. The development of new technologies, such as hypersonic missiles and advanced submarine-launched cruise missiles, will likely play a significant role in shaping the future of nuclear deterrence.
What are the implications of nuclear deterrence?
+The implications of nuclear deterrence are far-reaching, with significant consequences for global security, international relations, and human well-being. The possession of nuclear weapons by a growing number of countries increases the risk of nuclear conflict, while the development of advanced missile defense systems raises questions about the effectiveness of nuclear deterrents.
As we conclude our exploration of nuclear deterrents, it is essential to consider the complexities and challenges associated with these powerful weapons. The development and maintenance of nuclear deterrents require significant investments in research and development, infrastructure, and personnel. Moreover, the possession of nuclear weapons comes with tremendous responsibilities, including ensuring the safety and security of these weapons, as well as complying with international non-proliferation agreements. We invite you to share your thoughts on the role of nuclear deterrents in maintaining global security and to consider the potential consequences of these systems. By engaging in a nuanced and informed discussion about nuclear deterrence, we can work towards a more stable and secure world for all.
