Intro
Boost defense industry success with 5 military contract tips, covering procurement, bidding, and negotiation strategies, to secure lucrative government contracts and subcontracting opportunities.
The world of military contracting is complex and highly regulated, with numerous rules and guidelines that must be followed to ensure compliance and success. For businesses looking to enter this field, understanding the intricacies of military contracting is crucial. Whether you're a seasoned contractor or just starting out, navigating the landscape of military contracts can be daunting. However, with the right approach and knowledge, companies can not only comply with the stringent requirements but also thrive in this sector.
Military contracts are a significant source of revenue for many businesses, offering opportunities for growth and expansion. However, the process of securing and executing these contracts is highly competitive and subject to rigorous oversight. Companies must demonstrate a deep understanding of the military's needs, adhere to strict quality and security standards, and navigate a complex bureaucratic process. Despite these challenges, the rewards can be substantial, making it an attractive option for companies willing to invest the time and effort required to succeed.
The military contracting process involves several key stages, from initial bidding and proposal submission to contract award and execution. Each stage presents its own set of challenges and opportunities, requiring careful planning, precise execution, and a commitment to delivering high-quality products or services. For companies new to military contracting, understanding these stages and how to navigate them effectively is essential. This includes being aware of the legal and regulatory framework that governs military contracting, as well as the specific requirements and expectations of the military and other government agencies involved.
Military Contract Basics

Types of Military Contracts
The military uses various types of contracts to acquire goods and services, each designed to meet specific needs and circumstances. Fixed-price contracts, for example, are used when the scope of work is well-defined and the risks are relatively low. In contrast, cost-plus contracts are used for more complex projects where the costs are uncertain and the military is willing to reimburse the contractor for actual costs plus a fee. Understanding the different types of contracts and when they are used is crucial for companies looking to bid on military contracts.Preparing for Military Contracting

Registration and Certification
Registration with the System for Award Management (SAM) and obtaining any necessary certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management, are critical steps in preparing for military contracting. These certifications demonstrate a company's commitment to quality and its ability to meet the military's stringent standards. Additionally, companies may need to obtain security clearances for their personnel, especially if they will be working with classified information.Negotiating Military Contracts

Key Negotiation Strategies
Several strategies can enhance a company's negotiation position, including building strong relationships with military procurement officials, understanding the military's budget cycle and procurement timelines, and being flexible and willing to negotiate contract terms. Companies should also be prepared to provide detailed pricing information and to discuss potential risks and mitigation strategies. Effective negotiation can make the difference between winning and losing a contract, making it a critical skill for companies in the military contracting sector.Executing Military Contracts

Quality Control and Assurance
Implementing robust quality control and assurance processes is essential for ensuring that products or services meet the military's quality standards. This includes establishing clear quality objectives, implementing quality control procedures, and conducting regular audits and inspections to ensure compliance. Companies must also be prepared to address any quality issues that arise, taking corrective action promptly to prevent recurrence.Maintaining Compliance

Regulatory Updates and Changes
The regulatory environment for military contracting is constantly evolving, with changes in laws, regulations, and contract terms. Companies must stay informed about these changes, updating their policies and procedures as necessary to ensure compliance. This includes participating in industry forums and conferences, monitoring government websites and publications, and consulting with legal and regulatory experts.Military Contracting Image Gallery

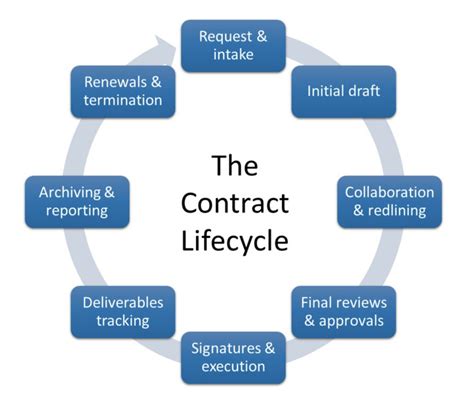



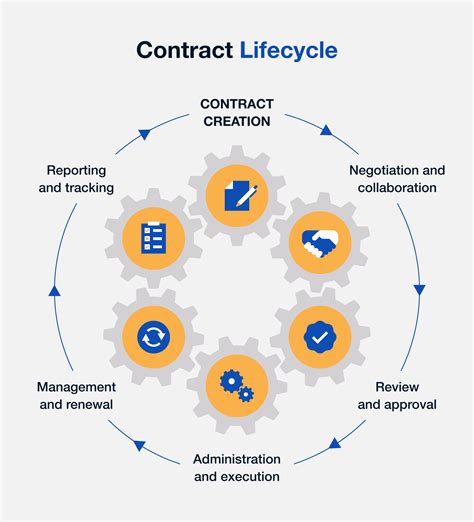



What are the key types of military contracts?
+The key types of military contracts include fixed-price contracts, cost-plus contracts, and time-and-materials contracts, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
How do companies prepare for military contracting?
+Companies prepare for military contracting by registering with the necessary government agencies, obtaining any required certifications or clearances, and developing a comprehensive business plan.
What is the importance of negotiation in military contracting?
+Negotiation is crucial in military contracting as it allows companies to articulate their value proposition, discuss contract terms, and reach a mutually beneficial agreement with the military.
How do companies maintain compliance with military contract regulations?
+Companies maintain compliance by staying up-to-date with changes in regulations, ensuring all contract requirements are met, and maintaining accurate records of contract performance.
What is the role of quality control in military contracting?
+Quality control is essential in military contracting to ensure that products or services meet the military's quality standards, involving the implementation of quality control procedures and regular audits.
In conclusion, succeeding in military contracting requires a deep understanding of the complex and highly regulated environment, a commitment to quality and compliance, and the ability to navigate the bureaucratic process effectively. By following the tips and strategies outlined above, companies can position themselves for success, build strong relationships with the military, and contribute to the defense and security of their country. Whether you're a seasoned contractor or just starting out, the world of military contracting offers significant opportunities for growth and expansion, making it an attractive and rewarding field for companies willing to invest the time and effort required to succeed. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with military contracting, and to explore the many resources available for companies looking to enter or expand their presence in this sector.
