Intro
Discover key facts about bases, including acid-base chemistry, alkaline properties, and chemical reactions, to understand their role in chemistry and everyday applications.
Bases are a fundamental concept in chemistry, and understanding their properties and behaviors is crucial for various applications in science and industry. The importance of bases cannot be overstated, as they play a vital role in many chemical reactions and are used in a wide range of products, from household cleaning agents to pharmaceuticals. In this article, we will delve into the world of bases, exploring their definition, types, and characteristics, as well as their uses and applications.
The study of bases is a fascinating field that has led to numerous breakthroughs and discoveries in chemistry. From the discovery of new elements to the development of innovative materials and technologies, the understanding of bases has been instrumental in advancing our knowledge of the chemical world. Moreover, the applications of bases are diverse and widespread, ranging from industrial processes to medical treatments. As we continue to explore and learn more about bases, we are likely to uncover new and exciting uses for these essential chemical compounds.
The significance of bases in our daily lives is often overlooked, yet they are an integral part of many products and processes that we rely on. For instance, bases are used in the production of soap, paper, and textiles, as well as in the manufacture of fertilizers and pesticides. Additionally, bases are used in various medical applications, such as in the treatment of diseases and the development of new medicines. As we explore the world of bases, we will discover the many ways in which they impact our lives and the importance of continued research and development in this field.
Introduction to Bases

Types of Bases
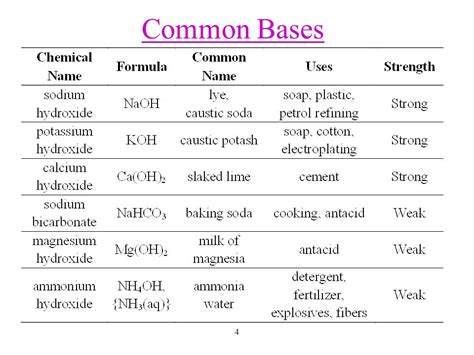
Strong Bases
Strong bases are highly reactive and completely dissociate in water to produce hydroxide ions. Examples of strong bases include: * Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) * Potassium hydroxide (KOH) * Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) * Barium hydroxide (Ba(OH)2)Weak Bases
Weak bases are less reactive and only partially dissociate in water. Examples of weak bases include: * Ammonia (NH3) * Methylamine (CH3NH2) * Ethylamine (C2H5NH2) * Aniline (C6H5NH2)Characteristics of Bases
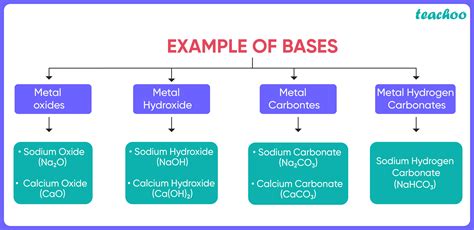
Chemical Properties of Bases
Bases have several chemical properties that are important in understanding their behavior and applications. Some of the key chemical properties of bases include: * Basicity: The ability of a base to produce hydroxide ions in solution. * Strength: The ability of a base to completely or partially dissociate in water. * Reactivity: The ability of a base to react with acids and other substances.Uses and Applications of Bases

Industrial Applications of Bases
Bases have several industrial applications, including: * Petroleum refining: Bases are used to refine petroleum products, such as gasoline and diesel fuel. * Chemical synthesis: Bases are used to synthesize a wide range of chemicals, including pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. * Water treatment: Bases are used to treat wastewater and drinking water, as they can help to remove impurities and contaminants.Medical Applications of Bases
Bases have several medical applications, including: * Antacids: Bases are used to produce antacids, which can help to neutralize stomach acid and relieve heartburn and indigestion. * Wound care: Bases are used to produce wound care products, such as bandages and dressings, which can help to promote healing and prevent infection. * Pharmaceutical production: Bases are used to produce pharmaceuticals, such as tablets and capsules, which can help to treat a wide range of diseases and conditions.Bases Image Gallery
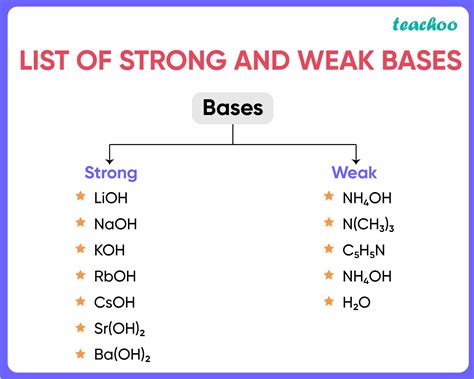

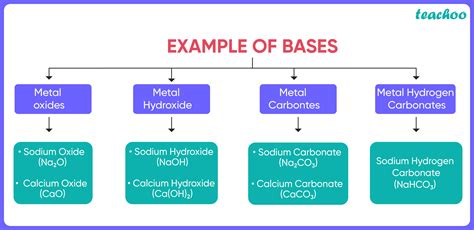


What is the difference between a strong base and a weak base?
+A strong base is a base that completely dissociates in water to produce hydroxide ions, while a weak base only partially dissociates in water.
What are some common uses of bases in industry?
+Bases are used in a wide range of industrial applications, including soap and detergent production, paper production, textile production, and fertilizer production.
What are some medical applications of bases?
+Bases are used in a variety of medical applications, including antacids, wound care products, and pharmaceuticals.
How do bases affect the environment?
+Bases can have both positive and negative effects on the environment, depending on their concentration and application. For example, bases can help to neutralize acidic pollutants in water, but they can also harm aquatic life if present in high concentrations.
What are some safety precautions to take when handling bases?
+When handling bases, it is essential to wear protective clothing, including gloves and goggles, and to work in a well-ventilated area. Bases can cause skin and eye irritation, and can also release toxic fumes if not handled properly.
In conclusion, bases are a vital component of chemistry, and their properties and applications are diverse and widespread. From their use in industrial processes to their role in medical treatments, bases play a crucial role in many aspects of our lives. As we continue to learn more about bases and their behavior, we are likely to uncover new and exciting uses for these essential chemical compounds. We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of bases and their importance in chemistry and industry. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about this topic, please do not hesitate to comment or share this article with others.
