Intro
Discover the Rot Meaning Explained, exploring decay, deterioration, and corruption, with related concepts like rotting, spoilage, and decomposition, to understand its significance.
The term "rot" has multiple meanings and interpretations, depending on the context in which it is used. In general, rot refers to the process of decay, decomposition, or deterioration of something, whether it be a physical object, a concept, or an idea. This can occur due to various factors such as exposure to moisture, lack of maintenance, or the passage of time. Understanding the different aspects of rot can provide insights into its causes, effects, and ways to prevent or mitigate it.
Rot can be observed in various forms, including the decay of organic matter, the deterioration of building materials, and the erosion of moral or social values. In the context of biology, rot is a natural process that occurs when microorganisms such as bacteria or fungi break down dead or dying tissue. This process is essential for the recycling of nutrients and the maintenance of ecosystem balance. However, when rot occurs in living tissues or structures, it can have detrimental effects, leading to illness, damage, or even collapse.
The concept of rot can also be applied to abstract ideas, such as the decay of social norms, the erosion of trust, or the deterioration of relationships. In these cases, rot can refer to the gradual decline or corruption of something that was once strong or vibrant. This can occur due to various factors, including neglect, abuse, or the influence of negative forces. Recognizing the signs of rot in these contexts can help individuals or communities take corrective action to prevent further decline and promote renewal.
Types of Rot
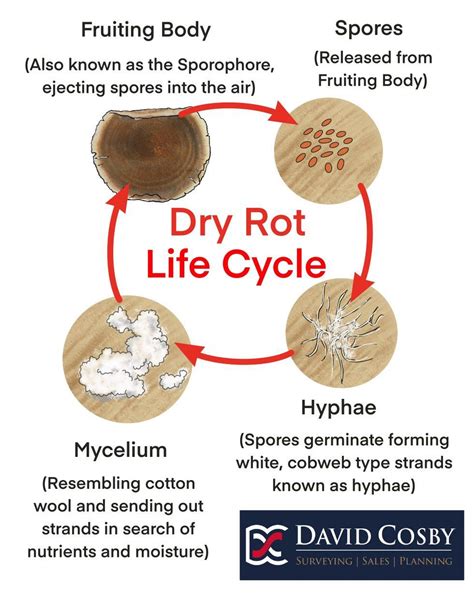
There are several types of rot, each with its own characteristics and causes. Dry rot, for example, is a type of fungal decay that occurs in dry environments, often affecting wood or other cellulose-based materials. Wet rot, on the other hand, occurs in moist environments and is typically caused by bacterial or fungal activity. Brown rot and white rot are other types of fungal decay that can affect various materials, including wood, fabric, and paper.
In addition to these physical forms of rot, there are also abstract types of rot, such as moral rot, social rot, or cultural rot. These refer to the decline or corruption of values, norms, or institutions that are essential to the well-being of individuals or communities. Recognizing the signs of rot in these contexts can help individuals or communities take corrective action to promote renewal and prevent further decline.
Causes of Rot
The causes of rot can vary depending on the context and the type of rot. In general, however, rot is often the result of a combination of factors, including exposure to moisture, lack of maintenance, or the presence of microorganisms. In the case of physical rot, such as dry rot or wet rot, the causes can include poor ventilation, water damage, or the use of materials that are prone to decay.
In the case of abstract types of rot, such as moral rot or social rot, the causes can be more complex and nuanced. These can include factors such as neglect, abuse, or the influence of negative forces, as well as broader societal or cultural trends. Recognizing the causes of rot in these contexts can help individuals or communities develop strategies to prevent or mitigate its effects.
Effects of Rot

The effects of rot can be significant, whether it occurs in physical materials or abstract concepts. In the case of physical rot, the effects can include damage to structures, illness, or even collapse. In the case of abstract types of rot, the effects can include the decline of social norms, the erosion of trust, or the deterioration of relationships.
In addition to these direct effects, rot can also have broader consequences, such as economic losses, environmental damage, or social unrest. Recognizing the effects of rot can help individuals or communities take corrective action to prevent further decline and promote renewal.
Prevention and Mitigation

Preventing or mitigating rot requires a combination of strategies, depending on the context and the type of rot. In the case of physical rot, this can include measures such as proper ventilation, regular maintenance, and the use of materials that are resistant to decay.
In the case of abstract types of rot, prevention and mitigation can involve strategies such as promoting social norms, building trust, and fostering positive relationships. This can also involve addressing broader societal or cultural trends that may be contributing to rot.
Real-World Examples

There are many real-world examples of rot, ranging from the decay of physical materials to the decline of social norms. For instance, the rot of wooden buildings can be prevented by using materials that are resistant to decay, such as treated wood or composite materials.
In the case of abstract types of rot, real-world examples can include the decline of social norms, such as the erosion of trust in institutions or the deterioration of relationships. These can be addressed through strategies such as promoting transparency, building trust, and fostering positive relationships.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, rot is a complex and multifaceted concept that can have significant effects on physical materials and abstract concepts. Understanding the causes, effects, and prevention strategies for rot can help individuals or communities take corrective action to prevent further decline and promote renewal.
As we look to the future, it is essential to recognize the importance of addressing rot in all its forms. This can involve developing new materials or technologies that are resistant to decay, as well as promoting social norms and values that foster positive relationships and trust.
Rot Image Gallery








What is rot and how does it occur?
+Rot is the process of decay or decomposition of something, whether it be a physical object or an abstract concept. It can occur due to various factors, including exposure to moisture, lack of maintenance, or the presence of microorganisms.
What are the different types of rot?
+There are several types of rot, including dry rot, wet rot, brown rot, and white rot. Each type has its own characteristics and causes, and can affect various materials, including wood, fabric, and paper.
How can rot be prevented or mitigated?
+Preventing or mitigating rot requires a combination of strategies, depending on the context and the type of rot. This can include measures such as proper ventilation, regular maintenance, and the use of materials that are resistant to decay.
What are the effects of rot on physical materials and abstract concepts?
+The effects of rot can be significant, whether it occurs in physical materials or abstract concepts. In physical materials, rot can cause damage, illness, or even collapse. In abstract concepts, rot can lead to the decline of social norms, the erosion of trust, or the deterioration of relationships.
How can individuals or communities address rot and promote renewal?
+Individuals or communities can address rot and promote renewal by recognizing the signs of rot, understanding its causes and effects, and developing strategies to prevent or mitigate it. This can involve promoting social norms, building trust, and fostering positive relationships, as well as addressing broader societal or cultural trends that may be contributing to rot.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of rot and its various forms. Whether you are looking to prevent or mitigate physical rot or address abstract types of rot, we encourage you to take action and promote renewal in your community. Share this article with others, and let's work together to prevent the negative effects of rot and foster a more positive and sustainable future.
