Intro
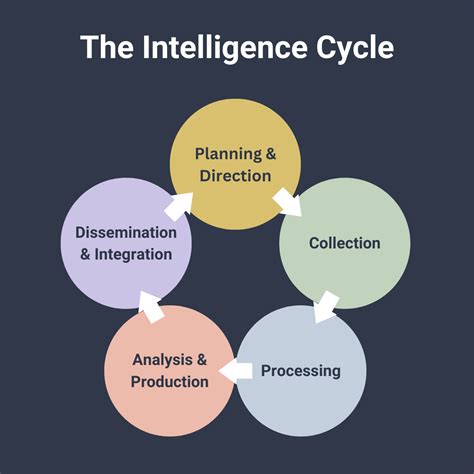
Discover the 5 crucial roles of an Intelligence Officer, including surveillance, analysis, and strategy, utilizing intelligence gathering, counterintelligence, and geopolitical expertise.
Intelligence officers play a crucial role in gathering and analyzing information to support national security, law enforcement, and military operations. Their work is often secretive and demanding, requiring a unique blend of skills, knowledge, and personal qualities. In this article, we will delve into the 5 key roles of intelligence officers, exploring their responsibilities, challenges, and contributions to their respective organizations.
The importance of intelligence officers cannot be overstated. They are the eyes and ears of their organizations, providing critical information that informs decision-making, prevents threats, and protects people. From counter-terrorism to cyber security, intelligence officers work tirelessly behind the scenes to keep us safe. As we explore the 5 roles of intelligence officers, we will gain a deeper understanding of their work and the impact it has on our daily lives.
Intelligence officers are highly trained professionals who undergo rigorous education and training to develop their skills and expertise. They must be able to collect, analyze, and disseminate information quickly and accurately, often in high-pressure situations. Their work requires a strong foundation in research, analysis, and communication, as well as the ability to think critically and make sound judgments. As we examine the 5 roles of intelligence officers, we will see how these skills are applied in different contexts and how they contribute to the success of their organizations.
Role 1: Intelligence Gathering

For example, an intelligence officer working in counter-terrorism might gather information on a suspected terrorist organization, including its leadership, financing, and operational plans. This information would be used to support law enforcement and military operations, as well as to inform policy decisions. Intelligence gathering is a critical role that requires strong research and analytical skills, as well as the ability to think critically and make sound judgments.
Role 2: Analysis and Assessment

For instance, an intelligence officer working in cyber security might analyze data on cyber attacks to identify the source, motivations, and tactics of the attackers. This analysis would be used to inform the development of counter-measures and to support incident response efforts. Analysis and assessment are critical roles that require strong analytical and problem-solving skills, as well as the ability to think critically and make sound judgments.
Role 3: Dissemination and Communication

For example, an intelligence officer working in law enforcement might brief a team of officers on the intelligence gathered on a suspected criminal organization. This briefing would provide the officers with the information they need to conduct a successful operation, including the location, movements, and associates of the suspects. Dissemination and communication are critical roles that require strong communication and interpersonal skills, as well as the ability to think critically and make sound judgments.
Role 4: Operational Support

For instance, an intelligence officer working in counter-narcotics might provide operational support to a team of agents conducting a raid on a suspected drug trafficking organization. This support would include providing intelligence on the location, movements, and associates of the suspects, as well as conducting surveillance and gathering evidence. Operational support is a critical role that requires strong analytical and problem-solving skills, as well as the ability to think critically and make sound judgments.
Role 5: Strategic Planning
For example, an intelligence officer working in national security might provide strategic planning support to a team of policymakers developing a new national security strategy. This support would include providing intelligence on potential threats, trends, and opportunities, as well as conducting analysis and assessment to inform decision-making. Strategic planning is a critical role that requires strong analytical and problem-solving skills, as well as the ability to think critically and make sound judgments.
Gallery of Intelligence Officers
Intelligence Officers Image Gallery







What is the primary role of intelligence officers?
+The primary role of intelligence officers is to gather and analyze information to support national security, law enforcement, and military operations.
What skills do intelligence officers need to be successful?
+Intelligence officers need strong research, analytical, and communication skills, as well as the ability to think critically and make sound judgments.
What are the 5 key roles of intelligence officers?
+The 5 key roles of intelligence officers are intelligence gathering, analysis and assessment, dissemination and communication, operational support, and strategic planning.
How do intelligence officers support law enforcement and military operations?
+Intelligence officers support law enforcement and military operations by providing intelligence, conducting surveillance, and gathering evidence.
What is the importance of strategic planning in intelligence work?
+Strategic planning is critical in intelligence work as it informs long-term planning and decision-making, and helps to identify potential threats and opportunities.
In conclusion, the 5 roles of intelligence officers are critical to supporting national security, law enforcement, and military operations. Intelligence officers play a vital role in gathering and analyzing information, disseminating and communicating their findings, providing operational support, and informing strategic planning. Their work requires strong research, analytical, and communication skills, as well as the ability to think critically and make sound judgments. As we have seen, the roles of intelligence officers are diverse and demanding, but also highly rewarding. If you are interested in pursuing a career in intelligence, we encourage you to learn more about the opportunities and challenges involved. Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below, and don't forget to share this article with others who may be interested in the important work of intelligence officers.
