Intro
Discover the 5 ways Army MOS works, including Military Occupational Specialties, job training, and career advancement, to unlock your potential in the US Army with specialized skills and roles.
The Army Military Occupational Specialty (MOS) system is a crucial aspect of the United States Army, as it determines the role and responsibilities of each soldier. Understanding how the Army MOS works is essential for individuals who are considering a career in the Army, as well as for those who are already serving. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the Army MOS system, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and the various steps involved in selecting an MOS.
The Army MOS system is designed to ensure that each soldier is assigned to a role that aligns with their skills, abilities, and interests. This not only enhances job satisfaction but also contributes to the overall effectiveness of the Army. With over 150 different MOSs to choose from, soldiers can select a career path that suits their strengths and career goals. From combat roles such as infantry and artillery to support roles like logistics and administration, the Army MOS system offers a diverse range of career opportunities.
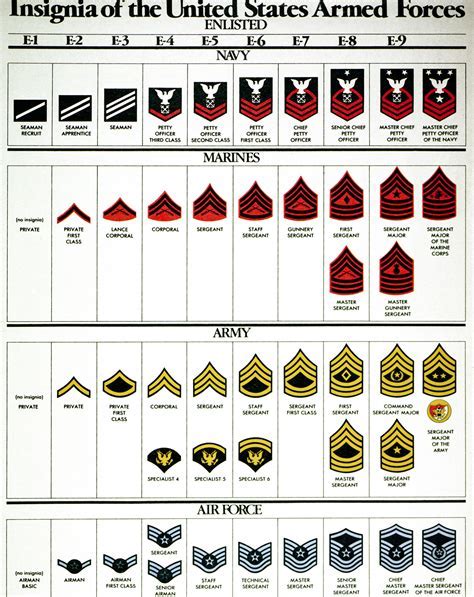
The Army MOS system is based on a classification system that categorizes soldiers into different occupational fields. Each MOS is identified by a unique code, which consists of a two-digit number and a letter. For example, the MOS code for an infantryman is 11B, while the code for a combat medic is 68W. This coding system enables the Army to efficiently manage its personnel and ensure that each soldier is assigned to a role that matches their skills and training.
How Army Mos Works

The Army MOS system works by assigning soldiers to a specific role based on their skills, abilities, and interests. The process of selecting an MOS typically begins during the recruitment phase, where potential soldiers are assessed to determine which MOSs they are eligible for. This assessment takes into account factors such as the individual's education, work experience, and aptitude test scores. Once a soldier has been assigned to an MOS, they will undergo training to develop the necessary skills and knowledge required for their role.
Benefits of Army Mos
The Army MOS system offers numerous benefits to soldiers, including career advancement opportunities, specialized training, and a sense of purpose and fulfillment. By assigning soldiers to roles that align with their strengths and interests, the Army MOS system helps to boost morale and job satisfaction. Additionally, the system provides soldiers with a clear career path, enabling them to plan and prepare for future roles and responsibilities.Army Mos Classification

The Army MOS classification system is based on a categorization of occupational fields, which are grouped into broader categories known as Army Branches. There are 16 Army Branches, each representing a specific area of specialization, such as infantry, artillery, and logistics. Within each Branch, there are multiple MOSs, each with its own unique code and job description. For example, the Infantry Branch includes MOSs such as 11B (Infantryman), 11C (Indirect Fire Infantryman), and 11X (Infantryman (Enlisted)).
Steps to Select an Army Mos
Selecting an Army MOS involves several steps, including taking the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test, researching different MOSs, and consulting with a recruiter or career counselor. The ASVAB test is used to determine an individual's eligibility for different MOSs, while researching MOSs enables soldiers to learn more about the roles and responsibilities associated with each job. Consulting with a recruiter or career counselor provides soldiers with personalized guidance and advice, helping them to make informed decisions about their career path.Army Mos Training

Army MOS training is an essential component of the Army MOS system, as it provides soldiers with the necessary skills and knowledge required for their role. The type and duration of training vary depending on the MOS, with some roles requiring several months of training, while others may require a year or more. For example, infantrymen typically undergo 14 weeks of Basic Combat Training (BCT) followed by 14 weeks of Advanced Individual Training (AIT), while combat medics may undergo 16 weeks of BCT followed by 16 weeks of AIT.
Army Mos Career Advancement
The Army MOS system offers numerous career advancement opportunities, enabling soldiers to progress through the ranks and take on more challenging roles and responsibilities. Career advancement is based on a combination of factors, including time in service, performance evaluations, and completion of specialized training. Soldiers can advance through the ranks by completing Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) training, attending specialized courses, and taking on leadership roles.Army Mos Specializations
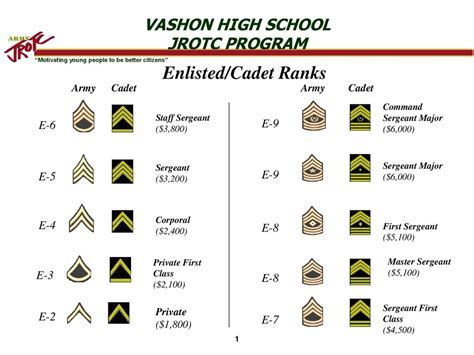
The Army MOS system includes a wide range of specializations, each with its own unique job description and requirements. Some examples of Army MOS specializations include:
- Combat roles: infantry, artillery, armor
- Support roles: logistics, administration, communications
- Technical roles: engineering, intelligence, signals
- Medical roles: combat medic, nurse, physician
Each specialization requires unique skills and training, and soldiers can choose to specialize in a particular area based on their interests and abilities.
Army Mos and Civilian Careers
The skills and training acquired through the Army MOS system can be highly transferable to civilian careers. Many Army MOSs have direct equivalents in the civilian workforce, while others may require additional training or education. For example, a soldier who has worked as a combat medic may be eligible to work as an emergency medical technician (EMT) or paramedic in the civilian sector.Army Mos and Education

The Army MOS system offers numerous education and training opportunities, enabling soldiers to acquire new skills and advance their careers. The Army provides financial assistance for education, including tuition reimbursement and the GI Bill, which can be used to pursue higher education or vocational training. Additionally, the Army offers specialized training programs, such as the Army's Credentialing Assistance Program, which helps soldiers to acquire industry-recognized certifications and credentials.
Army Mos and Leadership
The Army MOS system places a strong emphasis on leadership, with soldiers expected to take on leadership roles and responsibilities as they advance through the ranks. Leadership training is an essential component of the Army MOS system, with soldiers attending courses such as the Basic Leader Course (BLC) and the Advanced Leader Course (ALC). These courses provide soldiers with the skills and knowledge required to lead and manage teams, make decisions, and solve problems.Army Mos and Teamwork

The Army MOS system emphasizes the importance of teamwork, with soldiers expected to work collaboratively with others to achieve common goals. Teamwork is essential in the Army, where soldiers often work in high-stress environments and must rely on each other to complete tasks and missions. The Army provides training on teamwork and communication, enabling soldiers to develop the skills required to work effectively with others.
Army Mos and Adaptability
The Army MOS system requires soldiers to be adaptable and flexible, as they may be assigned to different roles and responsibilities throughout their careers. Adaptability is essential in the Army, where soldiers may be deployed to different parts of the world and must be able to adjust to new environments and situations. The Army provides training on adaptability and resilience, enabling soldiers to develop the skills required to thrive in challenging and unpredictable environments.Army Mos Image Gallery
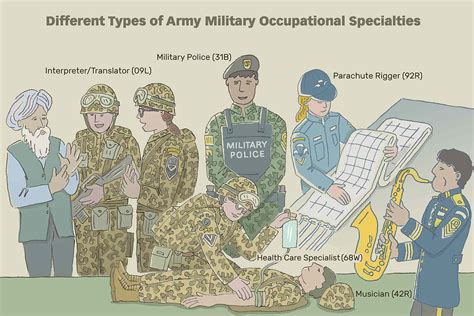





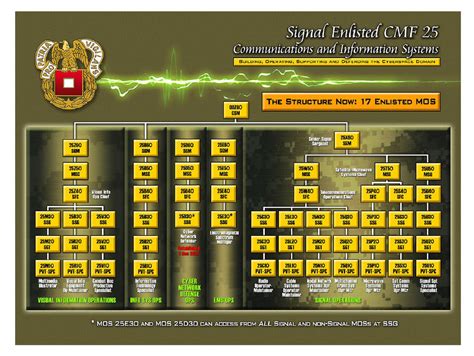


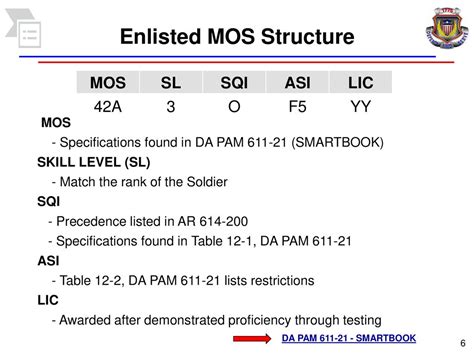
What is the Army MOS system?
+The Army MOS system is a classification system that categorizes soldiers into different occupational fields based on their skills, abilities, and interests.
How do I select an Army MOS?
+To select an Army MOS, you will need to take the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test, research different MOSs, and consult with a recruiter or career counselor.
What are the benefits of the Army MOS system?
+The Army MOS system offers numerous benefits, including career advancement opportunities, specialized training, and a sense of purpose and fulfillment.
Can I change my Army MOS?
+Yes, it is possible to change your Army MOS, but this may require additional training and education. You should consult with a career counselor to discuss your options.
How long does Army MOS training last?
+The length of Army MOS training varies depending on the MOS, but it can last from several weeks to several months or even years.
In conclusion, the Army MOS system is a complex and multifaceted system that plays a critical role in the United States Army. By understanding how the system works and the various steps involved in selecting an MOS, soldiers can make informed decisions about their career paths and take advantage of the numerous benefits and opportunities that the system offers. Whether you are considering a career in the Army or are already serving, the Army MOS system is an essential component of your military experience. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with the Army MOS system in the comments below, and to consider sharing this article with others who may be interested in learning more about this topic.
