Intro
Discover Geneticist job description, duties, and requirements. Learn about genetics careers, molecular biology, and genomics research, to pursue a career in genetic engineering and biotechnology.
The field of genetics has become increasingly important in recent years, with advancements in technology and research leading to a greater understanding of the role that genetics plays in our lives. As a result, the demand for skilled geneticists has never been higher. Geneticists are scientists who study the structure, function, and evolution of genes, as well as the ways in which they interact with each other and the environment. They use this knowledge to develop new treatments and therapies for genetic disorders, as well as to improve our understanding of the complex relationships between genes, environment, and disease.
Geneticists work in a variety of settings, including universities, research institutions, hospitals, and private industry. They may specialize in specific areas, such as molecular genetics, population genetics, or genetic counseling. Regardless of their specialty, geneticists are dedicated to advancing our understanding of the genetic basis of life and using this knowledge to improve human health and well-being. With the rapid advancement of genetic technology, the role of geneticists is becoming increasingly important, and their work has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach healthcare and disease prevention.
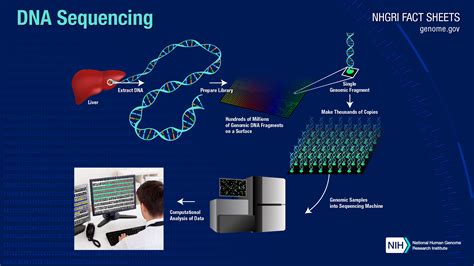
The work of geneticists is complex and multifaceted, involving a range of skills and techniques. They use advanced technologies, such as DNA sequencing and gene editing, to analyze and manipulate genes. They also use statistical and computational methods to analyze large datasets and identify patterns and trends. In addition, geneticists must be able to communicate complex scientific information to a variety of audiences, including patients, policymakers, and other scientists. With the increasing importance of genetics in our understanding of disease and health, the role of geneticists is becoming more critical, and their work has the potential to have a significant impact on public health and policy.
Introduction to Geneticist Job Description

Geneticists are highly trained scientists who have a deep understanding of the principles of genetics and the techniques used to analyze and manipulate genes. They use this knowledge to develop new treatments and therapies for genetic disorders, as well as to improve our understanding of the complex relationships between genes, environment, and disease. Geneticists may work in a variety of settings, including universities, research institutions, hospitals, and private industry. They may specialize in specific areas, such as molecular genetics, population genetics, or genetic counseling.
Key Responsibilities of Geneticists
Geneticists have a range of key responsibilities, including: * Conducting research to identify the genetic basis of diseases and disorders * Developing and implementing new treatments and therapies for genetic disorders * Analyzing and interpreting genetic data to identify patterns and trends * Communicating complex scientific information to a variety of audiences, including patients, policymakers, and other scientists * Collaborating with other scientists and healthcare professionals to develop new treatments and therapies * Staying up-to-date with the latest advancements in genetic technology and researchGeneticist Job Requirements

To become a geneticist, one typically needs to have a strong foundation in science and mathematics, as well as advanced training in genetics and related fields. The specific requirements may vary depending on the employer and the specific job, but some common requirements include:
- A bachelor's degree in a field such as biology, chemistry, or genetics
- A graduate degree, such as a master's or Ph.D., in genetics or a related field
- Advanced training in genetic techniques, such as DNA sequencing and gene editing
- Experience working in a laboratory or research setting
- Strong analytical and problem-solving skills
- Excellent communication and interpersonal skills
Types of Geneticists
There are several types of geneticists, including: * Molecular geneticists, who study the structure and function of genes at the molecular level * Population geneticists, who study the genetic variation within and among populations * Genetic counselors, who work with patients and families to provide information and guidance about genetic disorders * Clinical geneticists, who work in hospitals and clinics to diagnose and treat genetic disorders * Research geneticists, who conduct basic and applied research in genetics and related fieldsGeneticist Career Path

The career path for geneticists can vary depending on their specific interests and goals. Some common career paths include:
- Research scientist: conducting basic and applied research in genetics and related fields
- Clinical geneticist: working in hospitals and clinics to diagnose and treat genetic disorders
- Genetic counselor: working with patients and families to provide information and guidance about genetic disorders
- Professor/educator: teaching and mentoring students in genetics and related fields
- Industry professional: working in private industry to develop new products and technologies related to genetics
Geneticist Salary and Benefits
The salary and benefits for geneticists can vary depending on their specific job, employer, and location. However, some common benefits include: * Competitive salary: geneticists are typically well-compensated, with salaries ranging from $50,000 to over $100,000 per year * Comprehensive benefits: geneticists may receive benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off * Opportunities for advancement: geneticists may have opportunities to advance to leadership positions or to pursue specialized training and certification * Personal satisfaction: geneticists have the opportunity to make a meaningful contribution to our understanding of genetics and to improve human health and well-beingGeneticist Education and Training

Geneticists typically require advanced education and training in genetics and related fields. Some common educational pathways include:
- Bachelor's degree: a bachelor's degree in a field such as biology, chemistry, or genetics can provide a strong foundation for a career in genetics
- Master's degree: a master's degree in genetics or a related field can provide advanced training and qualify individuals for research and clinical positions
- Ph.D.: a Ph.D. in genetics or a related field can provide specialized training and qualify individuals for leadership positions and advanced research roles
- Postdoctoral training: postdoctoral training can provide additional specialized training and experience in genetics and related fields
Geneticist Certification and Licensure
Certification and licensure requirements for geneticists can vary depending on their specific job and employer. Some common certifications and licenses include: * Board certification: geneticists may become board certified through professional organizations such as the American Board of Medical Genetics and Genomics * Licensure: geneticists may require licensure to practice in certain states or countries * Specialty certification: geneticists may pursue specialty certification in areas such as genetic counseling or clinical geneticsGeneticist Job Outlook

The job outlook for geneticists is strong, with the Bureau of Labor Statistics predicting rapid growth in employment opportunities for geneticists and related professionals. Some common factors driving this growth include:
- Advances in genetic technology: advances in genetic technology, such as DNA sequencing and gene editing, are creating new opportunities for geneticists to contribute to research and clinical practice
- Increasing demand for genetic services: the increasing demand for genetic services, such as genetic counseling and genetic testing, is creating new job opportunities for geneticists
- Expanding applications of genetics: the expanding applications of genetics, such as in agriculture and biotechnology, are creating new job opportunities for geneticists
Geneticist Professional Organizations
Geneticists may join professional organizations to stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in genetics and to network with other professionals in the field. Some common professional organizations include: * American Society of Human Genetics * Genetics Society of America * American Board of Medical Genetics and Genomics * National Society of Genetic CounselorsGeneticist Image Gallery








What is the role of a geneticist?
+A geneticist is a scientist who studies the structure, function, and evolution of genes, as well as the ways in which they interact with each other and the environment.
What are the educational requirements for a geneticist?
+Geneticists typically require a bachelor's degree in a field such as biology, chemistry, or genetics, as well as advanced training in genetics and related fields.
What are the career paths available to geneticists?
+Geneticists may pursue careers in research, clinical practice, education, and industry, among other areas.
What are the benefits of a career in genetics?
+A career in genetics can provide personal satisfaction, opportunities for advancement, and a competitive salary, among other benefits.
How can I stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in genetics?
+Geneticists can stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in genetics by attending conferences, reading scientific journals, and participating in professional organizations.
In conclusion, a career as a geneticist can be a rewarding and challenging profession that offers the opportunity to contribute to our understanding of genetics and to improve human health and well-being. With the rapid advancement of genetic technology, the role of geneticists is becoming increasingly important, and their work has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach healthcare and disease prevention. If you are interested in pursuing a career in genetics, we encourage you to learn more about the educational requirements, career paths, and benefits of this exciting and rapidly evolving field. Share your thoughts and questions about geneticists in the comments below, and don't forget to share this article with others who may be interested in this topic.
