Intro
Discover the National Guards role, benefits, and requirements, including military service, training, and deployment, to understand this reserve components importance in domestic and overseas operations.
The National Guard is a reserve component of the United States Armed Forces, comprising both the Army National Guard and the Air National Guard. It is a unique branch of the military that serves both state and federal governments, playing a crucial role in national defense, disaster response, and community service. The National Guard has a rich history, dating back to the colonial era, and has evolved over time to meet the changing needs of the country.
The National Guard is often referred to as the "citizen-soldier" force, as its members are part-time soldiers who balance their military service with civilian careers and family life. This dual role allows National Guard members to maintain their connection to their communities while also serving their country. The National Guard is organized into units that are typically based in specific states or territories, with each unit having its own unique history, traditions, and specialties.
In times of war or national emergency, the National Guard can be called upon to serve alongside active-duty military personnel, providing critical support and reinforcements. National Guard members have served in numerous conflicts, including World War I, World War II, the Korean War, the Vietnam War, and more recent operations in Iraq and Afghanistan. The National Guard has also played a vital role in responding to natural disasters, such as hurricanes, floods, and wildfires, providing aid and assistance to affected communities.
The National Guard's dual mission is to provide military support to the federal government and to serve as a state militia, responding to emergencies and disasters within their respective states. This dual role requires National Guard members to be highly adaptable, flexible, and responsive to changing circumstances. The National Guard is also involved in a range of community-based activities, such as youth programs, disaster preparedness, and environmental conservation.
History of the National Guard

The history of the National Guard dates back to the colonial era, when militia units were formed to defend against British and Native American attacks. The first militia units were established in the 1630s, and they played a significant role in the American Revolution. The National Guard as we know it today was formally established in 1903, with the passage of the Dick Act, which created the modern National Guard system. Since then, the National Guard has evolved to meet the changing needs of the country, with significant expansions during World War I and World War II.
Key Milestones in National Guard History
The National Guard has a rich and storied history, with numerous key milestones and events that have shaped its development. Some of the most significant events include: * The American Revolution: The National Guard's predecessor, the militia, played a crucial role in the fight for independence. * The Civil War: The National Guard was instrumental in preserving the Union and ending the institution of slavery. * World War I: The National Guard was deployed overseas for the first time, serving in France and other parts of Europe. * World War II: The National Guard played a significant role in the war effort, with units serving in Europe, Africa, and the Pacific.Structure and Organization
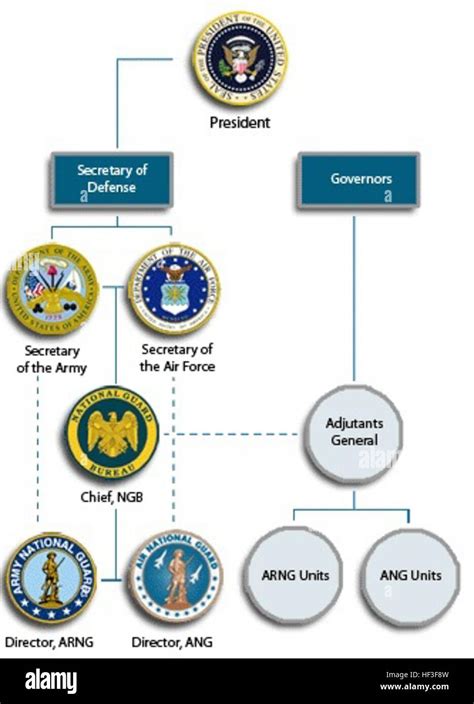
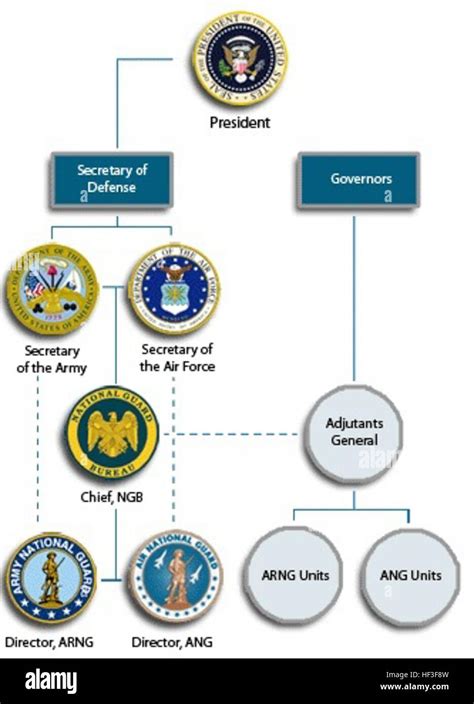
The National Guard is organized into two main components: the Army National Guard and the Air National Guard. The Army National Guard is the larger of the two components, with approximately 450,000 soldiers. The Air National Guard has around 105,000 airmen. Each component has its own unique structure and organization, with units and formations that reflect their specific missions and specialties.
The National Guard is also organized into different types of units, including infantry, artillery, engineering, and logistics units. These units are typically based in specific states or territories and are trained to respond to a range of scenarios, from natural disasters to military operations. The National Guard also has a number of specialized units, such as aviation and medical units, which provide critical support to military operations and disaster response efforts.
Key Components of the National Guard
The National Guard has several key components that work together to achieve its mission. These include: * The Army National Guard: The largest component of the National Guard, with approximately 450,000 soldiers. * The Air National Guard: The second-largest component, with around 105,000 airmen. * The National Guard Bureau: The headquarters element of the National Guard, responsible for overseeing the overall strategy and direction of the organization.Mission and Responsibilities

The National Guard has a dual mission, serving both state and federal governments. The National Guard's federal mission is to provide military support to the active-duty military, while its state mission is to serve as a militia, responding to emergencies and disasters within their respective states. The National Guard is also involved in a range of community-based activities, such as youth programs, disaster preparedness, and environmental conservation.
The National Guard's responsibilities include:
- Providing military support to the federal government
- Serving as a state militia, responding to emergencies and disasters
- Participating in community-based activities, such as youth programs and disaster preparedness
- Maintaining a high level of readiness and training, to ensure that units are prepared to respond to a range of scenarios.
Key Responsibilities of the National Guard
The National Guard has a number of key responsibilities that reflect its dual mission. These include: * Providing military support to the federal government, including deploying units overseas and providing support to active-duty military operations. * Serving as a state militia, responding to emergencies and disasters within their respective states. * Participating in community-based activities, such as youth programs and disaster preparedness.Training and Equipment

The National Guard places a strong emphasis on training and equipment, to ensure that units are prepared to respond to a range of scenarios. National Guard members typically train one weekend per month and two weeks per year, with additional training opportunities available. The National Guard also has access to a range of equipment, including infantry fighting vehicles, artillery systems, and aircraft.
The National Guard's training program is designed to prepare units for a range of scenarios, from natural disasters to military operations. The training program includes:
- Basic training: New recruits undergo basic training, which teaches them the fundamental skills and knowledge needed to succeed in the National Guard.
- Advanced training: More experienced soldiers undergo advanced training, which focuses on specialized skills and knowledge.
- Unit training: Units train together to develop teamwork and cohesion, and to practice responding to a range of scenarios.
Key Equipment Used by the National Guard
The National Guard has access to a range of equipment, including: * Infantry fighting vehicles, such as the M2 Bradley * Artillery systems, such as the M109 Paladin * Aircraft, such as the UH-60 Black Hawk helicopter * Communications equipment, such as radios and satellite systems.Gallery of National Guard Images
National Guard Image Gallery








Frequently Asked Questions
What is the National Guard?
+The National Guard is a reserve component of the United States Armed Forces, comprising both the Army National Guard and the Air National Guard.
What is the mission of the National Guard?
+The National Guard has a dual mission, serving both state and federal governments. The National Guard's federal mission is to provide military support to the active-duty military, while its state mission is to serve as a militia, responding to emergencies and disasters within their respective states.
How do I join the National Guard?
+To join the National Guard, you must meet certain eligibility requirements, such as being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 35, and meeting certain physical and educational standards. You can contact a National Guard recruiter for more information.
What kind of training does the National Guard provide?
+The National Guard provides a range of training opportunities, including basic training, advanced training, and unit training. National Guard members typically train one weekend per month and two weeks per year, with additional training opportunities available.
Can I serve in the National Guard and go to college?
+Yes, you can serve in the National Guard and go to college. The National Guard offers a range of education benefits, including tuition assistance and the GI Bill, to help members pay for college.
In conclusion, the National Guard is a vital component of the United States Armed Forces, playing a crucial role in national defense, disaster response, and community service. With its rich history, diverse structure, and wide range of responsibilities, the National Guard is an organization that is dedicated to serving both state and federal governments. Whether you are interested in serving your country, pursuing a career in the military, or simply learning more about this important organization, the National Guard is definitely worth exploring. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with the National Guard in the comments section below, and to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about this important topic.
