Intro
Discover military welding salary ranges and career opportunities. Learn about welder certifications, benefits, and job requirements in naval, army, and defense industries.
The field of military welding is a specialized and highly skilled profession that requires a unique combination of technical expertise, physical stamina, and attention to detail. Military welders play a critical role in maintaining and repairing the equipment and infrastructure used by the armed forces, from tanks and aircraft to ships and submarines. As a result, military welding salary can vary depending on factors such as location, level of experience, and specific job requirements.
Military welding is a challenging and demanding career that requires a strong foundation in welding techniques, metallurgy, and safety protocols. Military welders must be able to work with a variety of metals and alloys, including steel, aluminum, and titanium, and must be proficient in multiple welding processes, such as shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), gas metal arc welding (GMAW), and gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW). They must also be able to work in a fast-paced, dynamic environment, often in extreme temperatures and under tight deadlines.
Despite the challenges, military welding can be a highly rewarding career, both financially and personally. Military welders have the opportunity to work on complex and high-tech equipment, and to contribute to the safety and effectiveness of the armed forces. They also have access to a range of benefits, including competitive pay, comprehensive health insurance, and opportunities for advancement and professional development.
Military Welding Salary Ranges

The salary range for military welders can vary depending on factors such as location, level of experience, and specific job requirements. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual salary for welders, cutters, solderers, and brazers was $41,400 in May 2020. However, military welders can earn significantly more, with salaries ranging from $50,000 to over $100,000 per year.
Factors Affecting Military Welding Salary
Several factors can affect the salary of a military welder, including: * Level of experience: More experienced welders can earn higher salaries, with senior welders earning up to $90,000 per year. * Location: Military welders working in certain locations, such as shipyards or aircraft manufacturers, may earn higher salaries than those working in other locations. * Specific job requirements: Military welders working on complex or high-tech equipment, such as submarines or aircraft carriers, may earn higher salaries than those working on simpler equipment. * Level of certification: Military welders who hold specialized certifications, such as the Certified Welding Inspector (CWI) or the Certified Welding Educator (CWE), may earn higher salaries than those without certification.Military Welding Career Paths
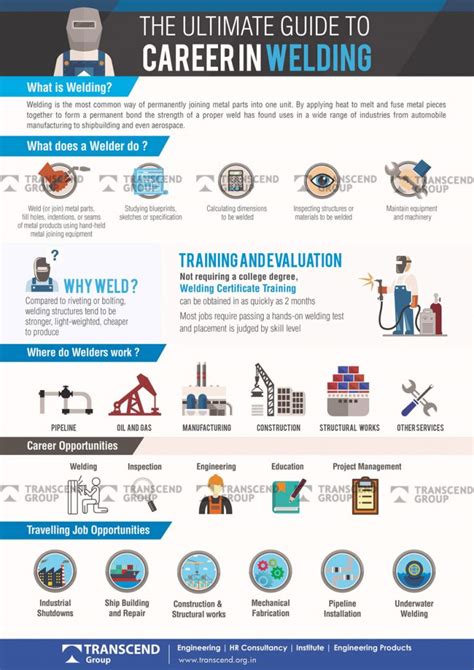
There are several career paths available to military welders, including:
- Welding technician: Welding technicians assist senior welders and perform routine maintenance and repair tasks.
- Welding inspector: Welding inspectors examine welds and welding equipment to ensure that they meet safety and quality standards.
- Welding engineer: Welding engineers design and develop welding equipment and processes, and oversee the production of welded components.
- Welding supervisor: Welding supervisors oversee teams of welders and coordinate welding operations.
Military Welding Education and Training
Military welders typically require a combination of formal education and on-the-job training to perform their duties. Many military welders complete an apprenticeship program or a postsecondary training program in welding, and may also complete specialized training in areas such as metallurgy or welding inspection.Some of the key skills and knowledge required by military welders include:
- Welding techniques: Military welders must be proficient in multiple welding processes, including SMAW, GMAW, and GTAW.
- Metallurgy: Military welders must have a strong understanding of metallurgy, including the properties and characteristics of different metals and alloys.
- Safety protocols: Military welders must be familiar with safety protocols, including personal protective equipment (PPE) and hazard communication.
- Quality control: Military welders must be able to inspect and test welds to ensure that they meet safety and quality standards.
Military Welding Job Outlook
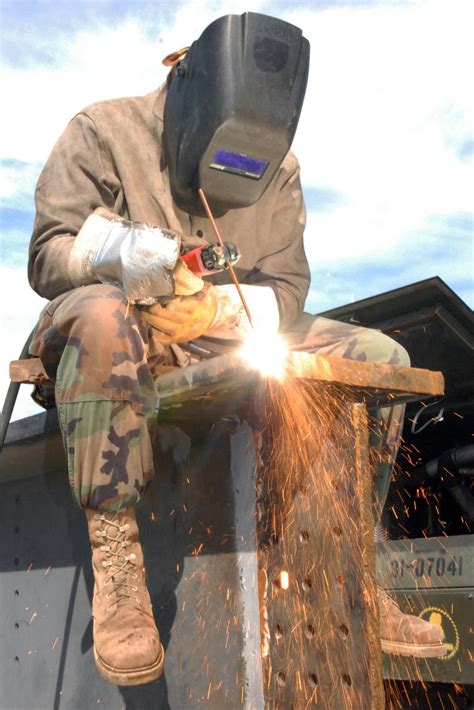

The job outlook for military welders is positive, with the BLS predicting that employment of welders, cutters, solderers, and brazers will grow 6% from 2020 to 2030, faster than the average for all occupations. This growth will be driven by the increasing demand for skilled welders in industries such as shipbuilding, aircraft manufacturing, and construction.
Military Welding Industry Trends
Several trends are shaping the military welding industry, including: * Increased use of automation: The use of automation and robotics is becoming more widespread in the welding industry, and military welders must be able to work with these technologies. * Growing demand for skilled welders: The demand for skilled welders is increasing, driven by the need for complex and high-tech equipment. * Emphasis on safety and quality: The military welding industry is placing a growing emphasis on safety and quality, and military welders must be able to meet these standards.Military Welding Certifications and Credentials

There are several certifications and credentials available to military welders, including:
- Certified Welding Inspector (CWI): The CWI certification is offered by the American Welding Society (AWS) and demonstrates expertise in welding inspection.
- Certified Welding Educator (CWE): The CWE certification is offered by the AWS and demonstrates expertise in welding education.
- Certified Welding Supervisor (CWS): The CWS certification is offered by the AWS and demonstrates expertise in welding supervision.
Benefits of Military Welding Certifications
Obtaining a certification or credential can have several benefits for military welders, including: * Increased earning potential: Certified welders can earn higher salaries than non-certified welders. * Improved job prospects: Certification can improve job prospects and make it easier to advance in the industry. * Enhanced skills and knowledge: Certification requires a strong foundation in welding techniques, metallurgy, and safety protocols, and can help military welders develop their skills and knowledge.Military Welding Equipment and Tools
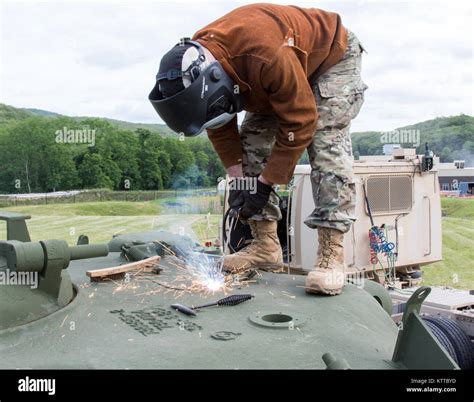

Military welders use a variety of equipment and tools to perform their duties, including:
- Welding machines: Welding machines are used to generate the heat and energy needed for welding.
- Welding torches: Welding torches are used to apply the heat and energy to the metal.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE): PPE, such as helmets, gloves, and safety glasses, is used to protect military welders from injury.
Military Welding Safety Protocols
Safety is a critical concern in the military welding industry, and military welders must follow strict safety protocols to protect themselves and others from injury. Some of the key safety protocols include: * Use of PPE: Military welders must wear PPE, such as helmets, gloves, and safety glasses, to protect themselves from injury. * Hazard communication: Military welders must be familiar with hazard communication protocols, including the use of warning signs and labels. * Fire prevention: Military welders must take steps to prevent fires, including the use of fire-resistant materials and the maintenance of fire extinguishers.Military Welding Image Gallery






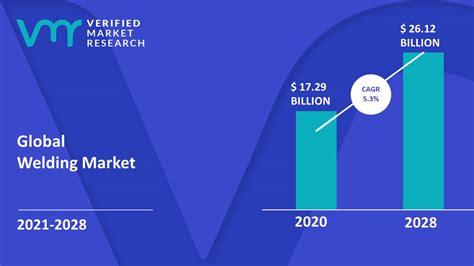



What is the average salary for a military welder?
+The average salary for a military welder can range from $50,000 to over $100,000 per year, depending on factors such as location, level of experience, and specific job requirements.
What are the benefits of becoming a military welder?
+The benefits of becoming a military welder include competitive pay, comprehensive health insurance, and opportunities for advancement and professional development. Military welders also have the opportunity to work on complex and high-tech equipment, and to contribute to the safety and effectiveness of the armed forces.
What are the requirements for becoming a military welder?
+The requirements for becoming a military welder typically include a combination of formal education and on-the-job training, as well as specialized certifications and credentials. Military welders must also be physically fit and able to work in a fast-paced, dynamic environment.
What are the different types of military welding careers?
+There are several different types of military welding careers, including welding technician, welding inspector, welding engineer, and welding supervisor. Each of these careers requires a unique combination of skills and knowledge, and offers different opportunities for advancement and professional development.
How do I get started in a military welding career?
+To get started in a military welding career, you should research the different types of military welding careers and the requirements for each. You should also consider completing an apprenticeship program or a postsecondary training program in welding, and obtaining specialized certifications and credentials. Finally, you should be prepared to work hard and dedication to advancing in your career.
In conclusion, military welding is a challenging and rewarding career that requires a unique combination of technical expertise, physical stamina, and attention to detail. Military welders play a critical role in maintaining and repairing the equipment and infrastructure used by the armed forces, and have access to a range of benefits, including competitive pay, comprehensive health insurance, and opportunities for advancement and professional development. If you are interested in pursuing a career in military welding, you should research the different types of military welding careers and the requirements for each, and be prepared to work hard and dedication to advancing in your career. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with military welding in the comments section below, and to explore the many resources and opportunities available to those interested in this exciting and rewarding field.
