Intro
Discover the weight to thrust ratio, a crucial metric in aerospace engineering, affecting propulsion systems, rocket performance, and overall efficiency, impacting flight dynamics and payload capacity.
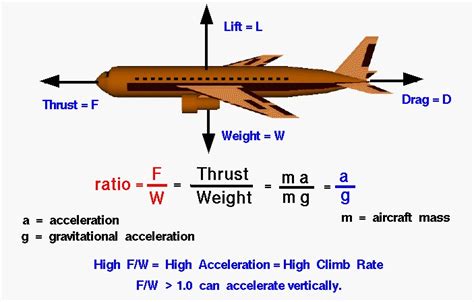
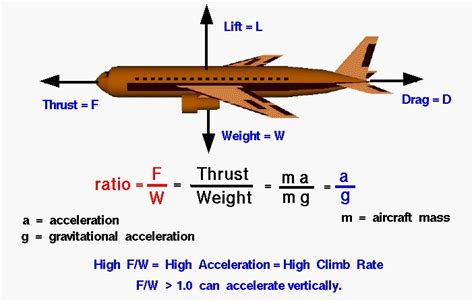
The weight to thrust ratio is a critical factor in the design and performance of aircraft, rockets, and other vehicles that generate thrust. It is a measure of the weight of a vehicle compared to the thrust it produces, and it plays a significant role in determining the vehicle's acceleration, climb rate, and overall efficiency. In this article, we will delve into the concept of weight to thrust ratio, its importance, and how it affects the performance of different types of vehicles.
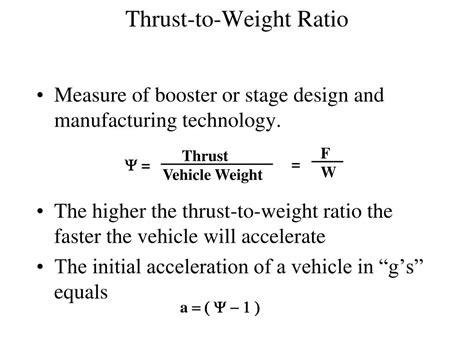
The weight to thrust ratio is calculated by dividing the weight of a vehicle by its thrust. For example, if a rocket has a weight of 100,000 pounds and produces 200,000 pounds of thrust, its weight to thrust ratio would be 0.5:1. This means that for every pound of weight, the rocket produces two pounds of thrust. A lower weight to thrust ratio indicates that a vehicle is more efficient and can accelerate faster, while a higher ratio indicates that a vehicle is less efficient and may struggle to gain speed.
The weight to thrust ratio is crucial in the design of aircraft, as it directly affects their performance and efficiency. For instance, a fighter jet with a low weight to thrust ratio can accelerate quickly and climb steeply, making it more effective in combat situations. On the other hand, a commercial airliner with a higher weight to thrust ratio may be less efficient but can still provide a comfortable and safe ride for passengers.
Understanding Weight to Thrust Ratio
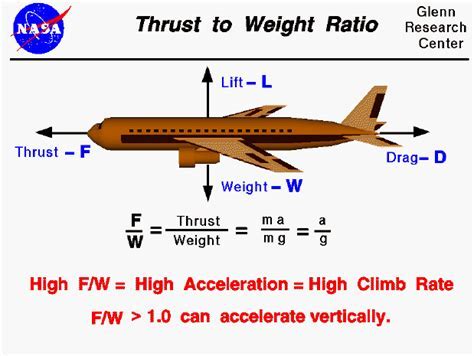
In addition to its importance in aerospace engineering, the weight to thrust ratio is also relevant in other fields, such as automotive engineering. For example, a car with a high power-to-weight ratio can accelerate quickly and efficiently, making it more desirable for racing and other high-performance applications.
Factors Affecting Weight to Thrust Ratio
The weight to thrust ratio can also be affected by the vehicle's operating conditions, such as altitude, temperature, and air density. For instance, an aircraft flying at high altitudes may experience a decrease in thrust due to the lower air density, which can affect its weight to thrust ratio. Similarly, a rocket launching in extreme temperatures may experience a decrease in thrust due to the thermal effects on its propulsion system.
Calculating Weight to Thrust Ratio
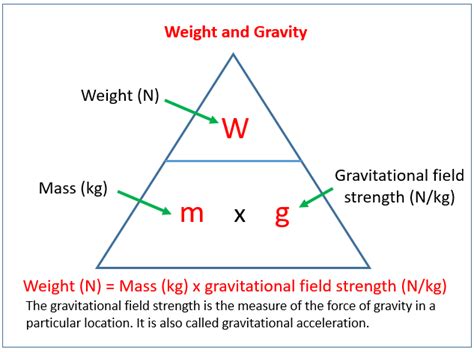
To calculate the weight to thrust ratio, the following formula can be used:
Weight to Thrust Ratio = Weight / Thrust
For example, if a rocket has a weight of 100,000 pounds and produces 200,000 pounds of thrust, its weight to thrust ratio would be:
Weight to Thrust Ratio = 100,000 pounds / 200,000 pounds-force = 0.5:1
This means that for every pound of weight, the rocket produces two pounds of thrust.
Importance of Weight to Thrust Ratio

In addition to its importance in aerospace engineering, the weight to thrust ratio is also relevant in other fields, such as automotive engineering. For example, a car with a high power-to-weight ratio can accelerate quickly and efficiently, making it more desirable for racing and other high-performance applications.
Applications of Weight to Thrust Ratio

In automotive engineering, the weight to thrust ratio is used to design and optimize cars for maximum acceleration and efficiency. For example, a car with a high power-to-weight ratio can accelerate quickly and efficiently, making it more desirable for racing and other high-performance applications.
In materials science, the weight to thrust ratio is used to develop new materials and technologies that can improve the efficiency and performance of vehicles. For example, the development of lightweight materials such as carbon fiber and aluminum has enabled the creation of more efficient and high-performance vehicles.
Gallery of Weight to Thrust Ratio
Weight to Thrust Ratio Image Gallery
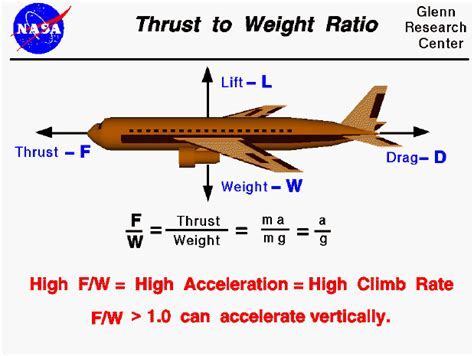


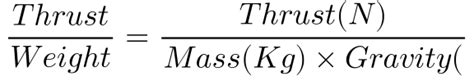

What is the weight to thrust ratio?
+The weight to thrust ratio is a measure of the weight of a vehicle compared to the thrust it produces.
Why is the weight to thrust ratio important?
+The weight to thrust ratio is important because it directly affects the acceleration, climb rate, and overall efficiency of a vehicle.
How is the weight to thrust ratio calculated?
+The weight to thrust ratio is calculated by dividing the weight of a vehicle by its thrust.
What are the applications of the weight to thrust ratio?
+The weight to thrust ratio has numerous applications in various fields, including aerospace engineering, automotive engineering, and materials science.
How does the weight to thrust ratio affect the performance of a vehicle?
+The weight to thrust ratio directly affects the acceleration, climb rate, and overall efficiency of a vehicle. A lower weight to thrust ratio indicates that a vehicle is more efficient and can accelerate faster, while a higher ratio indicates that a vehicle is less efficient and may struggle to gain speed.
In summary, the weight to thrust ratio is a critical factor in the design and performance of vehicles that generate thrust. It directly affects their acceleration, climb rate, and overall efficiency, and has numerous applications in various fields, including aerospace engineering, automotive engineering, and materials science. By understanding the weight to thrust ratio and its importance, engineers and designers can create more efficient and high-performance vehicles that meet the demands of various industries and applications. We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about the weight to thrust ratio in the comments section below, and to explore more topics related to aerospace engineering and vehicle design.
