Intro
Learn effective warthog defense tips, including habitat protection, predator avoidance, and threat response strategies, to safeguard these African mammals from dangers like lions, leopards, and hyenas.
Warthogs are fascinating creatures known for their distinctive physical appearance and unique behaviors. Despite their seemingly tough exterior, warthogs can be vulnerable to various threats in the wild, including predators, harsh environmental conditions, and human activities. Understanding warthog defense mechanisms is crucial for appreciating these animals' adaptability and resilience. In this article, we will delve into five key warthog defense tips, exploring how these remarkable creatures protect themselves and their habitats.
Warthogs are found in a variety of habitats across sub-Saharan Africa, from grasslands to woodlands. Their ability to adapt to different environments is a testament to their robust defense strategies. One of the primary reasons warthogs are able to thrive in diverse habitats is their keen sense of awareness. They are constantly on the lookout for potential threats, using their keen senses of smell and hearing to detect danger. This heightened state of alertness is the first line of defense for warthogs, allowing them to respond quickly to potential threats.
The social structure of warthogs also plays a significant role in their defense mechanisms. Warthogs often live in groups, known as sounders, which typically consist of females and their young. These groups provide additional protection for individual warthogs, as there is safety in numbers. When a warthog detects a predator, it will sound an alarm call to alert other members of the sounder, allowing them to take necessary precautions. This social defense strategy is effective against a variety of predators, including lions, leopards, and hyenas.
Warthog Physical Defenses
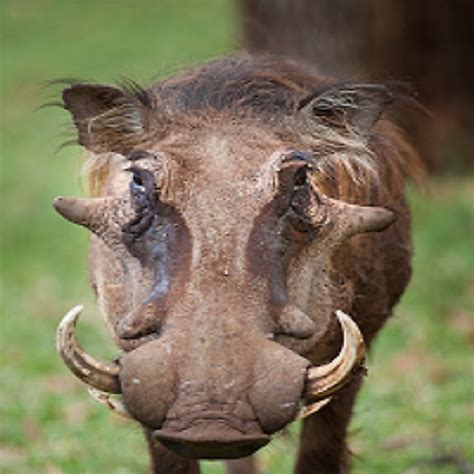

Warthogs are equipped with several physical defense mechanisms that help protect them from predators. One of their most distinctive features is their pair of tusks, which are actually elongated canine teeth. These tusks are used for defense, fighting, and even digging. Warthogs will often use their tusks to defend themselves when cornered or threatened, and they are capable of inflicting serious injury on predators. In addition to their tusks, warthogs have thick, tough skin that provides protection against bites and claws.
Warthog Behavioral Defenses

Warthogs also exhibit a range of behavioral defenses that help them avoid predators and protect their young. One of the most interesting warthog behaviors is their use of burrows. Warthogs will often dig complex networks of burrows, which provide them with a safe haven from predators. These burrows can be extensive, with multiple entrances and exits, and are often shared among members of the same sounder. Warthogs will also use their burrows to protect themselves from extreme weather conditions, such as heat and cold.
Warthog Speed and Agility
Despite their size, warthogs are surprisingly fast and agile. They are capable of running at speeds of up to 30 miles per hour, making them difficult to catch for many predators. Warthogs will often use their speed to outrun predators, particularly when they are in open areas with minimal cover. In addition to their speed, warthogs are also highly agile, able to make sharp turns and quick changes in direction. This agility allows them to evade predators in dense vegetation, where their speed would be less effective.
Warthog Group Defense

Warthogs are highly social animals that often live in large groups. These groups, known as sounders, typically consist of females and their young, while males will often wander on their own or form bachelor groups. The social structure of warthog groups plays a significant role in their defense mechanisms. When a warthog detects a predator, it will sound an alarm call to alert other members of the sounder. This alarm call will often trigger a response from other warthogs in the group, which will then work together to defend themselves and their young.
Warthog Adaptation to Human Activities

Unfortunately, warthogs are often threatened by human activities, such as habitat destruction, hunting, and agriculture. However, warthogs have shown a remarkable ability to adapt to these threats. In areas where warthogs are hunted for their meat, they have learned to be more cautious and alert, often becoming nocturnal to avoid human contact. Warthogs have also adapted to living in areas with high levels of human activity, such as farmland and urban fringes. In these areas, they will often feed on crops and other human-provided food sources, allowing them to thrive in environments that would otherwise be hostile.
Benefits of Warthog Defense Mechanisms
The defense mechanisms employed by warthogs have several benefits, including: * Protection from predators: Warthog defense mechanisms, such as their tusks and burrows, provide them with protection from predators like lions, leopards, and hyenas. * Adaptation to human activities: Warthogs have adapted to living in areas with high levels of human activity, allowing them to thrive in environments that would otherwise be hostile. * Social bonding: The social structure of warthog groups plays a significant role in their defense mechanisms, promoting social bonding and cooperation among members of the sounder. * Improved survival rates: The defense mechanisms employed by warthogs have improved their survival rates, allowing them to thrive in a variety of habitats across sub-Saharan Africa.Warthog Defense Mechanisms Image Gallery









What are the primary defense mechanisms employed by warthogs?
+The primary defense mechanisms employed by warthogs include their tusks, burrows, speed, agility, and social structure. These mechanisms provide warthogs with protection from predators and allow them to adapt to human activities.
How do warthogs adapt to living in areas with high levels of human activity?
+Warthogs have adapted to living in areas with high levels of human activity by becoming more cautious and alert, often becoming nocturnal to avoid human contact. They will also feed on crops and other human-provided food sources, allowing them to thrive in environments that would otherwise be hostile.
What are the benefits of warthog defense mechanisms?
+The benefits of warthog defense mechanisms include protection from predators, adaptation to human activities, social bonding, and improved survival rates. These mechanisms have allowed warthogs to thrive in a variety of habitats across sub-Saharan Africa.
In conclusion, the defense mechanisms employed by warthogs are fascinating and highly effective. By understanding these mechanisms, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the adaptability and resilience of these remarkable creatures. Whether you're a wildlife enthusiast, a conservationist, or simply someone who appreciates the natural world, learning about warthog defense mechanisms is sure to be an enriching experience. We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about warthog defense mechanisms in the comments below, and to explore more articles about wildlife and conservation.
