Intro
Explore US Coast Guard enlisted ranks, from Seaman to Master Chief, and discover promotion requirements, insignia, and responsibilities, understanding the hierarchy and career progression within the Coast Guards enlisted personnel structure.
The United States Coast Guard is a unique branch of the military, operating under the Department of Homeland Security during peacetime and the Department of the Navy during wartime. As such, its rank structure is similar to that of the Navy, but with some distinct differences. For those interested in joining the Coast Guard, understanding the enlisted ranks is essential. The Coast Guard's enlisted ranks are divided into three main categories: Junior Enlisted, Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs), and Senior Enlisted.
The Coast Guard's mission is multifaceted, including maritime law enforcement, search and rescue, marine safety, and environmental protection, among others. The diversity of these tasks requires a well-structured and trained force, with each rank playing a vital role in the accomplishment of the Coast Guard's objectives. The enlisted ranks are the backbone of the Coast Guard, making up the majority of its personnel and executing the day-to-day operations that keep the service running.
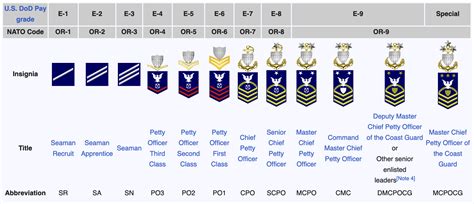
The Junior Enlisted ranks, from lowest to highest, are Seaman Recruit (E-1), Seaman Apprentice (E-2), and Seaman (E-3). These ranks are typically the entry points for new recruits. As Junior Enlisted members gain experience and complete advanced training, they can move up the ranks. The Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) ranks start at Petty Officer Third Class (E-4) and go up to Petty Officer First Class (E-6). These individuals have completed specialized training in a specific rating (or job specialty) and are considered technical experts in their field.
The Senior Enlisted ranks, from Chief Petty Officer (E-7) to Master Chief Petty Officer of the Coast Guard (E-9), represent the highest levels of enlisted leadership. These individuals have extensive experience, advanced training, and a deep understanding of the Coast Guard's operations and policies. They serve as mentors, leaders, and advisors, playing a crucial role in the development of junior personnel and the strategic planning of the service.
Junior Enlisted Ranks
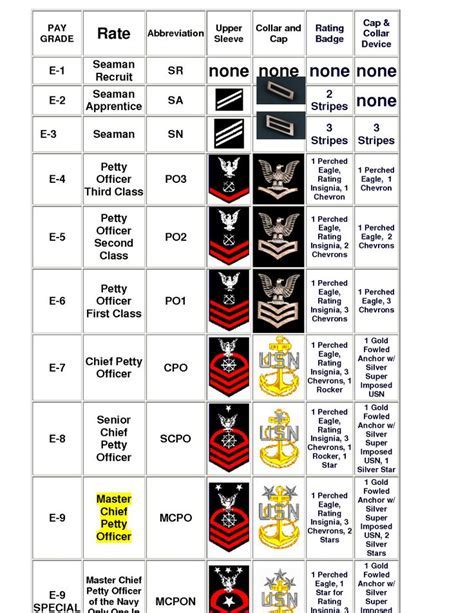
The Junior Enlisted ranks are the foundation of the Coast Guard's personnel structure. They are the newest members of the service and are in the process of learning their roles and responsibilities. The ranks include Seaman Recruit (E-1), Seaman Apprentice (E-2), and Seaman (E-3). These ranks are typically associated with entry-level training and the initial phases of a Coast Guardsman's career.
- Seaman Recruit (E-1): This is the most junior rank in the Coast Guard. Individuals at this rank are typically in the process of completing basic training.
- Seaman Apprentice (E-2): After completing basic training, members are advanced to Seaman Apprentice. They begin to receive training in their specific rating.
- Seaman (E-3): Seamen have completed their initial training and are considered to be fully integrated into the Coast Guard. They are expected to perform their duties with a higher level of proficiency.
Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) Ranks
NCOs are the technical experts in the Coast Guard. They have completed advanced training in their rating and are responsible for leading and mentoring junior personnel. The NCO ranks include Petty Officer Third Class (E-4), Petty Officer Second Class (E-5), and Petty Officer First Class (E-6).
- Petty Officer Third Class (E-4): This rank is the first level of NCO. Petty Officers Third Class are expected to take on more responsibilities and to lead by example.
- Petty Officer Second Class (E-5): At this rank, individuals are considered to be fully competent in their rating. They are involved in more complex tasks and may lead small teams.
- Petty Officer First Class (E-6): Petty Officers First Class are senior technical experts. They are responsible for leading teams, mentoring junior personnel, and contributing to the development of policies and procedures.
Senior Enlisted Ranks
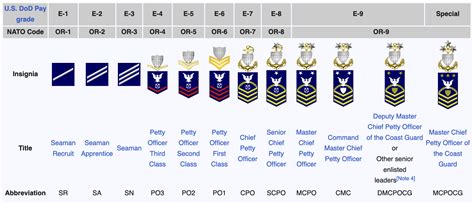
The Senior Enlisted ranks are the highest levels of enlisted leadership in the Coast Guard. Individuals at these ranks have achieved a high level of expertise and are recognized for their leadership abilities. The Senior Enlisted ranks include Chief Petty Officer (E-7), Senior Chief Petty Officer (E-8), Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9), and Master Chief Petty Officer of the Coast Guard (E-9).
- Chief Petty Officer (E-7): Chiefs are senior leaders who have demonstrated a high level of technical competence and leadership ability. They are involved in strategic planning and serve as advisors to officers.
- Senior Chief Petty Officer (E-8): Senior Chiefs are highly experienced leaders who play a critical role in the development of Coast Guard policies and procedures.
- Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9): Master Chiefs are the most senior enlisted leaders in the Coast Guard, with the exception of the Master Chief Petty Officer of the Coast Guard. They are involved in the highest levels of strategic planning and leadership.
- Master Chief Petty Officer of the Coast Guard (E-9): This is the highest enlisted rank in the Coast Guard. The Master Chief Petty Officer of the Coast Guard serves as the senior enlisted advisor to the Commandant of the Coast Guard and is a symbol of excellence for all enlisted personnel.
Gallery of US Coast Guard Enlisted Ranks
US Coast Guard Enlisted Ranks Image Gallery








Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of joining the Coast Guard?
+Joining the Coast Guard offers a wide range of benefits, including competitive pay, comprehensive health insurance, educational assistance, and the opportunity to serve in a unique and rewarding career.
How do I advance in rank in the Coast Guard?
+Advancement in the Coast Guard is based on a combination of factors, including performance evaluations, time in service, and completion of advanced training. Members must also meet specific eligibility requirements for each rank.
What kind of training does the Coast Guard offer?
+The Coast Guard offers a wide range of training opportunities, including basic training, advanced technical training, and leadership development courses. Members can also pursue higher education through the Coast Guard's tuition assistance program.
Can I choose my job specialty in the Coast Guard?
+While the Coast Guard considers members' preferences when assigning job specialties, the ultimate decision is based on the needs of the service. Members can, however, work towards qualifying for a specific rating through advanced training and experience.
How long do I have to serve in the Coast Guard?
+The length of service in the Coast Guard varies depending on the type of enlistment contract. Typically, enlistment contracts range from 4 to 6 years, although some specialized programs may require longer or shorter commitments.
In conclusion, the enlisted ranks of the US Coast Guard are a vital component of the service, providing the technical expertise, leadership, and manpower necessary to carry out its diverse missions. From the Junior Enlisted ranks, where new recruits begin their journey, to the Senior Enlisted ranks, which represent the pinnacle of enlisted leadership, each level plays a critical role in the functioning of the Coast Guard. Whether you're considering a career in the Coast Guard or are simply interested in learning more about this unique branch of the military, understanding the enlisted ranks is essential. We invite you to share your thoughts, ask questions, or explore further the opportunities and challenges that come with serving in the US Coast Guard.
