Intro
US carriers played a crucial role in WW2 battles, utilizing naval aviation and aircraft carriers to gain strategic advantages in Pacific Theater operations, including Midway and Leyte Gulf, showcasing their importance in wartime tactics and military history.
The United States Navy played a crucial role in World War II, with its aircraft carriers being a key component of the naval fleet. These carriers, which served as floating airbases, enabled the U.S. to project air power across the vast distances of the Pacific and Atlantic oceans. The U.S. carriers were involved in many significant battles throughout the war, and their contributions were instrumental in the ultimate Allied victory.
In the early years of the war, the U.S. Pacific Fleet was still reeling from the surprise attack on Pearl Harbor, which had damaged or destroyed many of its battleships. However, the U.S. carriers, which had been out to sea at the time of the attack, were able to escape the carnage and would go on to play a major role in the war. The first major naval battle of the war, the Battle of the Coral Sea, was fought in May 1942, and it was the first naval battle in history in which the opposing ships did not come within sight of each other. Instead, the battle was fought entirely by aircraft, with the U.S. carriers USS Lexington and USS Yorktown engaging the Japanese carriers Shōhō, Shōkaku, and Zuikaku.

The U.S. carriers suffered significant losses during the battle, with the USS Lexington being sunk and the USS Yorktown being damaged. However, the Japanese also suffered losses, and the battle was considered a strategic victory for the U.S. because it prevented the Japanese from capturing Port Moresby in New Guinea, which would have given them a foothold in the region. The Battle of Midway, which was fought in June 1942, is widely considered to be one of the most important naval battles in history. The Japanese, who were seeking to capture the Midway Atoll, launched a massive naval and air campaign against the U.S. forces stationed there.
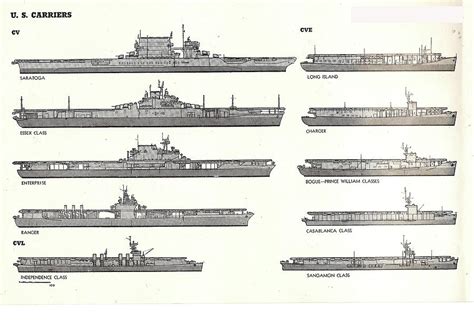
Major Us Carriers In Ww2
The U.S. had three carriers available to defend Midway: the USS Enterprise, the USS Yorktown, and the USS Hornet. The Japanese, on the other hand, had four carriers: the Akagi, the Kaga, the Sōryū, and the Hiryū. The battle was fierce and intense, with both sides suffering significant losses. However, in the end, the U.S. emerged victorious, having sunk all four Japanese carriers and one heavy cruiser, while losing only one carrier, the USS Yorktown, and one destroyer. The Battle of Midway was a turning point in the war, as it prevented the Japanese from continuing their expansion in the Pacific and gave the U.S. the initiative.

The U.S. carriers continued to play a major role in the war, participating in many significant battles, including the Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands, the Battle of the Philippine Sea, and the Battle of Leyte Gulf. The latter battle, which was fought in October 1944, was the largest naval battle in history, involving over 280 ships and 200,000 sailors. The U.S. had 17 carriers available for the battle, while the Japanese had only 9. The battle was a decisive victory for the U.S., with the Japanese suffering significant losses, including the sinking of four carriers, three battleships, and numerous smaller ships.
Us Carrier Based Aircraft
The U.S. carriers were able to achieve these victories due to the superior training and equipment of their aircrews, as well as the development of new tactics and strategies. The U.S. had several types of carrier-based aircraft, including the F4F Wildcat, the F6F Hellcat, and the TBF Avenger. These aircraft were highly effective in combat, with the F6F Hellcat being particularly successful, accounting for over 5,000 enemy aircraft shot down during the war. The U.S. also developed new tactics, such as the "Thach Weave," which allowed its pilots to effectively engage enemy aircraft.

In addition to their role in naval battles, the U.S. carriers also played a significant role in supporting amphibious landings and providing air support for ground troops. The carriers were able to provide close air support, bombing and strafing enemy positions, as well as conducting reconnaissance and surveillance missions. The U.S. carriers were also used to transport aircraft and supplies to remote locations, helping to maintain the flow of logistics and equipment to front-line troops.
Us Carriers In The Atlantic
While the U.S. carriers are perhaps most famous for their role in the Pacific, they also played a significant role in the Atlantic. The U.S. had several carriers operating in the Atlantic, including the USS Ranger, the USS Wasp, and the USS Independence. These carriers were used to support convoys and escort ships, as well as to conduct anti-submarine warfare against German U-boats. The U.S. carriers were also used to support the Allied invasion of North Africa, providing air support for the landings and helping to secure the beachhead.

The U.S. carriers in the Atlantic also played a significant role in the Battle of the Atlantic, which was a prolonged and brutal campaign fought between the Allies and the Germans. The U.S. carriers were used to hunt down and sink German U-boats, which were attempting to cut off the flow of supplies and equipment to the UK. The U.S. carriers were highly effective in this role, with the USS Core and the USS Bogue being particularly successful, sinking several U-boats and helping to turn the tide of the battle.
Us Carrier Losses In Ww2
Despite their many successes, the U.S. carriers did suffer significant losses during the war. A total of 12 U.S. carriers were sunk or damaged during the war, including the USS Lexington, the USS Yorktown, and the USS Wasp. The U.S. also lost many aircraft and aircrew, with over 14,000 airmen killed or missing in action. However, the U.S. was able to replace its losses and continue to produce new carriers and aircraft, ultimately emerging victorious from the war.

In conclusion, the U.S. carriers played a crucial role in World War II, participating in many significant battles and helping to secure the ultimate Allied victory. The U.S. carriers were able to achieve these victories due to the superior training and equipment of their aircrews, as well as the development of new tactics and strategies. The U.S. carriers continued to play a major role in the war, supporting amphibious landings and providing air support for ground troops, and their contributions will always be remembered as a key factor in the Allied victory.
Gallery of Us Carriers In Ww2
Us Carriers In Ww2 Image Gallery









What was the role of US carriers in WW2?
+The US carriers played a crucial role in WW2, participating in many significant battles and helping to secure the ultimate Allied victory. They provided air support for ground troops, supported amphibious landings, and conducted anti-submarine warfare against German U-boats.
How many US carriers were sunk or damaged during WW2?
+A total of 12 US carriers were sunk or damaged during WW2, including the USS Lexington, the USS Yorktown, and the USS Wasp.
What were some of the most significant battles fought by US carriers in WW2?
+Some of the most significant battles fought by US carriers in WW2 included the Battle of the Coral Sea, the Battle of Midway, the Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands, the Battle of the Philippine Sea, and the Battle of Leyte Gulf.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the role of US carriers in WW2. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about this topic, please don't hesitate to comment below or share this article with others. Additionally, if you have any specific questions or topics you would like us to cover in future articles, please let us know and we will do our best to accommodate your requests. Thank you for reading!
